J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 Sep;59(5):430-436. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.5.430.
Chronic Paraspinal Muscle Injury Model in Rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nspsw@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2351709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.5.430
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this study is to establish an animal model of chronic paraspinal muscle injury in rat.
METHODS
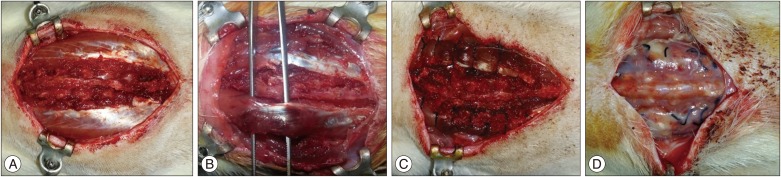
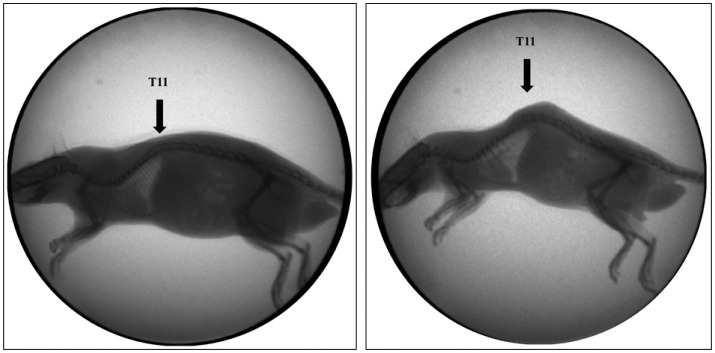
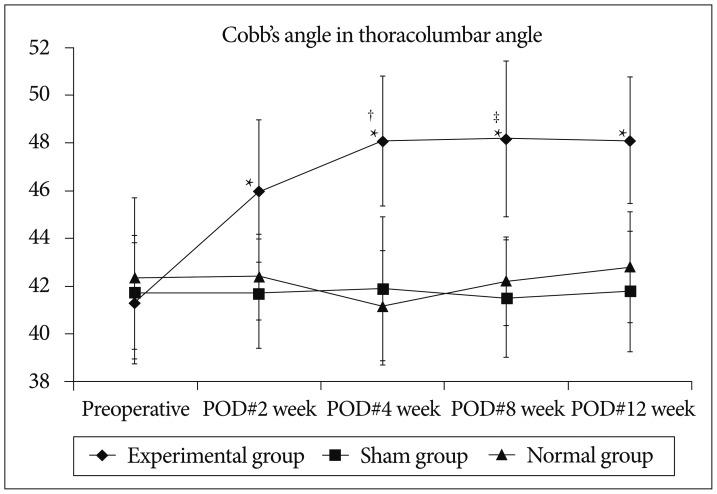
Fifty four Sprague-Dawley male rats were divided into experimental group (n=30), sham (n=15), and normal group (n=9). Incision was done from T7 to L2 and paraspinal muscles were detached from spine and tied at each level. The paraspinal muscles were exposed and untied at 2 weeks after surgery. Sham operation was done by paraspinal muscles dissection at the same levels and wound closure was done without tying. Kyphotic index and thoracolumbar Cobb's angle were measured at preoperative, 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after the first surgery for all groups. The rats were sacrificed at 4, 8, and 12 weeks after the first surgery, and performed histological examinations.
RESULTS
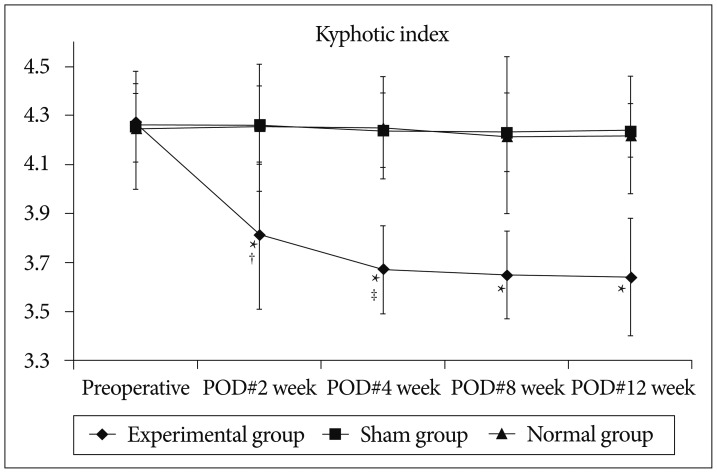
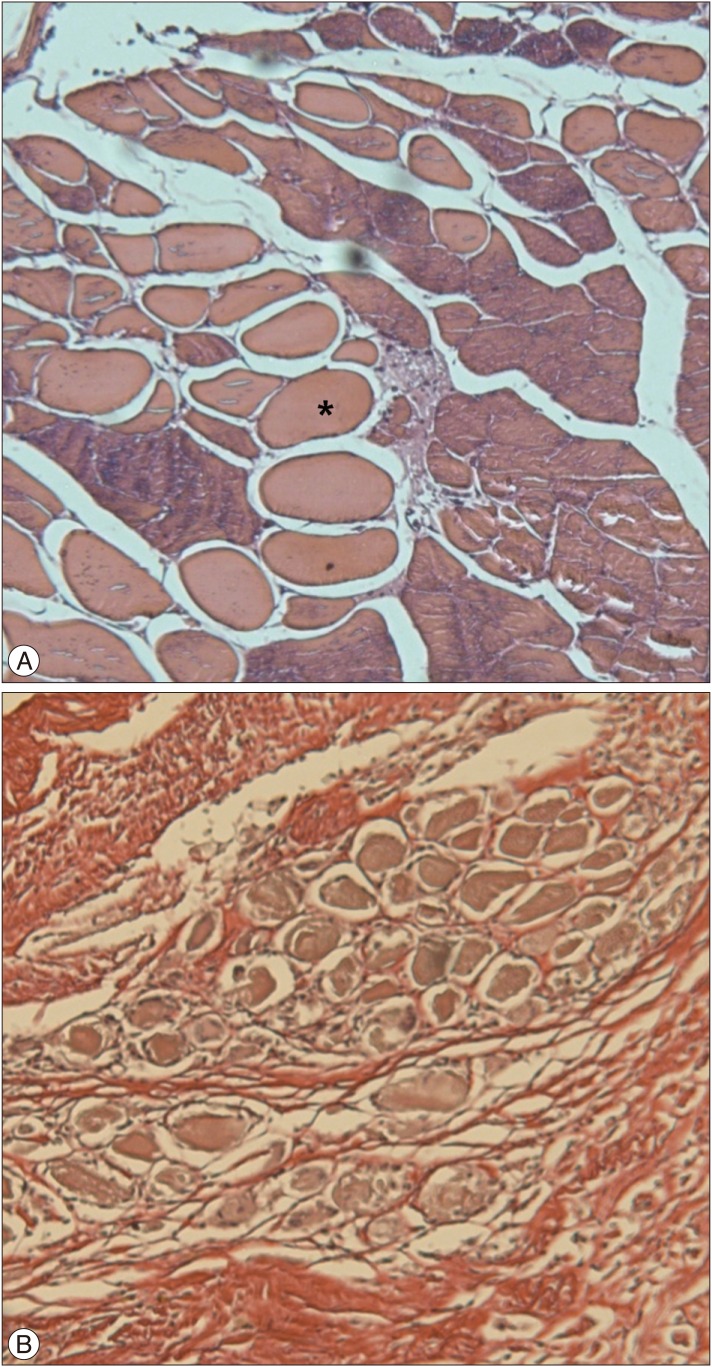
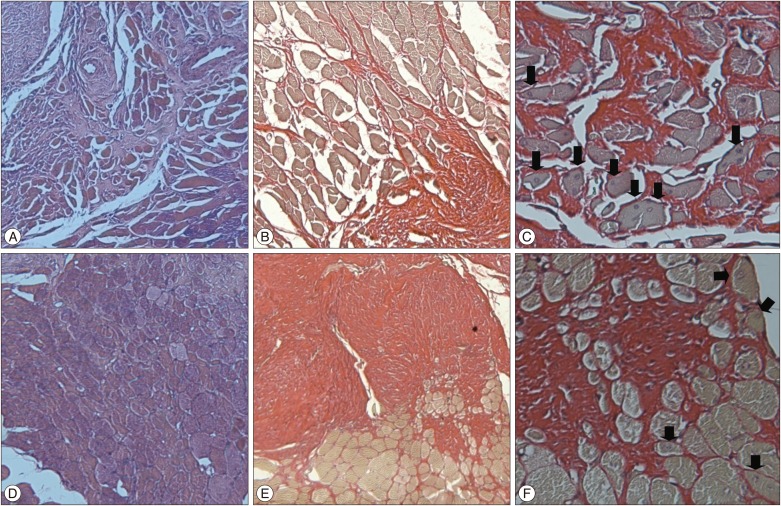
At 4 weeks after surgery, the kyphotic index decreased, but, Cobb's angle increased significantly in the experimental group (p<0.05), and then that were maintained until the end of the experiment. However, there were no significant differences of the kyphotic index and Cobb's angle between sham and normal groups. In histological examinations, necrosis and fibrosis were observed definitely and persisted until 12 weeks after surgery. There were also presences of regenerated muscle cells which nucleus is at the center of cytoplasm, centronucleated myofibers.
CONCLUSION
Our chronic injury model of paraspinal muscles in rats shows necrosis and fibrosis in the muscles for 12 weeks after surgery, which might be useful to study the pathophysiology of the degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis or degeneration of paraspinal muscles.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ball JM, Cagle P, Johnson BE, Lucasey C, Lukert BP. Spinal extension exercises prevent natural progression of kyphosis. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:481–489. PMID: 18661090.
Article2. Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus CR, Blanke KM. Complications and predictive factors for the successful treatment of flatback deformity (fixed sagittal imbalance). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1712–1720. PMID: 10472106.
Article3. Brereton D, Plochocki J, An D, Costas J, Simons E. The effects of glucocorticoid and voluntary exercise treatment on the development of thoracolumbar kyphosis in dystrophin-deficient mice. PLoS Curr. 2012; 4:e4ffdff160de8b.
Article4. Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Lewis SJ. Treatment of spinal stenosis and fixed sagittal imbalance. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (384):35–44. PMID: 11249178.
Article5. Cabukoglu C, Güven O, Yildirim Y, Kara H, Ramadan SS. Effect of sagittal plane deformity of the lumbar spine on epidural fibrosis formation after laminectomy : an experimental study in the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 2242–2247. PMID: 15480135.6. Cho KJ, Kim KT, Kim WJ, Lee SH, Jung JH, Kim YT, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in elderly patients with degenerative sagittal imbalance. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:E1561–E1566. PMID: 23921326.
Article7. Coleman R. Picrosirius red staining revisited. Acta Histochem. 2011; 113:231–233. PMID: 20188402.
Article8. Granito RN, Aveiro MC, Renno AC, Oishi J, Driusso P. Comparison of thoracic kyphosis degree, trunk muscle strength and joint position sense among healthy and osteoporotic elderly women : a cross-sectional preliminary study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012; 54:e199–e202. PMID: 21831460.9. Gutiérrez JM, Ownby CL. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2 : insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon. 2003; 42:915–931. PMID: 15019491.
Article10. Huynh AM, Aubin CE, Mathieu PA, Labelle H. Simulation of progressive spinal deformities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy using a biomechanical model integrating muscles and vertebral growth modulation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2007; 22:392–399.
Article11. Hyun SJ, Rhim SC. Clinical outcomes and complications after pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance patients : a long-term follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; 47:95–101. PMID: 20224706.
Article12. Kang CH, Shin MJ, Kim SM, Lee SH, Lee CS. MRI of paraspinal muscles in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients and control patients with chronic low back pain. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62:479–486. PMID: 17398274.
Article13. Kim WJ, Kang JW, Kang SI, Sung HI, Park KY, Park JG, et al. Factors affecting clinical results after corrective osteotomy for lumbar degenerative kyphosis. Asian Spine J. 2010; 4:7–14. PMID: 20622949.
Article14. Lattouf R, Younes R, Lutomski D, Naaman N, Godeau G, Senni K, et al. Picrosirius red staining : a useful tool to appraise collagen networks in normal and pathological tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014; 62:751–758. PMID: 25023614.15. Laws N, Cornford-Nairn RA, Irwin N, Johnsen R, Fletcher S, Wilton SD, et al. Long-term administration of antisense oligonucleotides into the paraspinal muscles of mdx mice reduces kyphosis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008; 105:662–668. PMID: 18499783.
Article16. Laws N, Hoey A. Progression of kyphosis in mdx mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004; 97:1970–1977. PMID: 15234960.17. McNeill Ingham SJ, de Castro Pochini A, Oliveira DA, Garcia Lisboa BC, Beutel A, Valero-Lapchik VB, et al. Bupivacaine injection leads to muscle force reduction and histologic changes in a murine model. PM R. 2011; 3:1106–1109. PMID: 21974904.
Article18. Modi HN, Suh SW, Hong JY, Yang JH. Posterior multilevel vertebral osteotomy for severe and rigid idiopathic and nonidiopathic kyphoscoliosis : a further experience with minimum two-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:1146–1153. PMID: 20948461.
Article19. Narita S, Yorifuji H. Centrally nucleated fibers (CNFs) compensate the fragility of myofibers in mdx mouse. Neuroreport. 1999; 10:3233–3235. PMID: 10574566.
Article20. Plant DR, Colarossi FE, Lynch GS. Notexin causes greater myotoxic damage and slower functional repair in mouse skeletal muscles than bupivacaine. Muscle Nerve. 2006; 34:577–585. PMID: 16881061.
Article21. Sanderson RA, Foley RK, McIvor GW, Kirkaldy-Willis WH. Histological response on skeletal muscle to ischemia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975; (113):27–35. PMID: 811419.
Article22. Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, Miyamoto M, Miyatake Y. Lumbar degenerative kyphosis. Clinical, radiological and epidemiological studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13:1317–1326. PMID: 2974629.23. Werneck LC, Cousseau VA, Graells XS, Werneck MC, Scola RH. Muscle study in experimental scoliosis in rabbits with costotransversectomy : evidence of ischemic process. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:726–733. PMID: 18210168.
Article24. Wiggins GC, Ondra SL, Shaffrey CI. Management of iatrogenic flatback syndrome. Neurosurg Focus. 2003; 15:E8. PMID: 15347226.
Article25. Zoabli G, Mathieu PA, Aubin CE. Magnetic resonance imaging of the erector spinae muscles in Duchenne muscular dystrophy : implication for scoliotic deformities. Scoliosis. 2008; 3:21. PMID: 19114022.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paraspinal Muscles Wasting in the Patients wih Chronic Low Back Pain
- Factors associated with paravertebral muscle cross-sectional area in patients with chronic low back pain
- The Important Role of Paraspinal Muscle Quality for Maintaining Sagittal Balance While Walking: Commentary on “Correlation of Paraspinal Muscle Mass With Decompensation of Sagittal Adult Spinal Deformity After Setting of Fatigue Post 10-Minute Walk”
- Optimal Sampling of Muscles to Detect Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Postoperative Changes in Paraspinal Muscle Volume: Comparison between Paramedian Interfascial and Midline Approaches for Lumbar Fusion