Yonsei Med J.
2015 Nov;56(6):1597-1603. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1597.
All-Trans Retinoic Acid Has a Potential Therapeutic Role for Diabetic Nephropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. ironeat@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. acw@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2345888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1597
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine the effects of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) on diabetic nephropathy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We measured amounts of urinary albumin excretion (UAE) after administrating ATRA to Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. In order to understand the mechanism of action for ATRA, we administrated ATRA to examine its inhibitory action on the production of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), protein kinase C (PKC), and reactive oxidative stress (ROS) in cultured rat mesangial cells (RMCs).
RESULTS
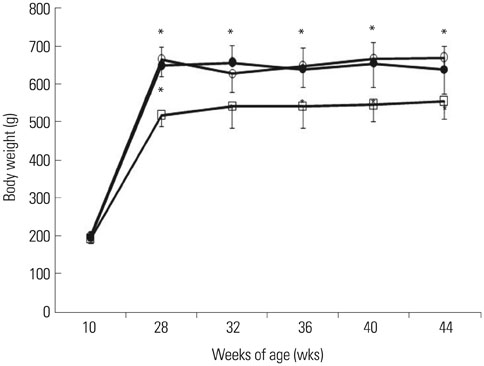
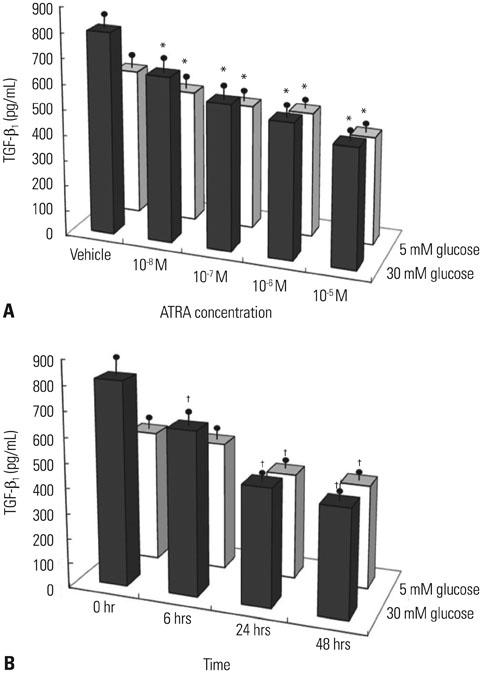
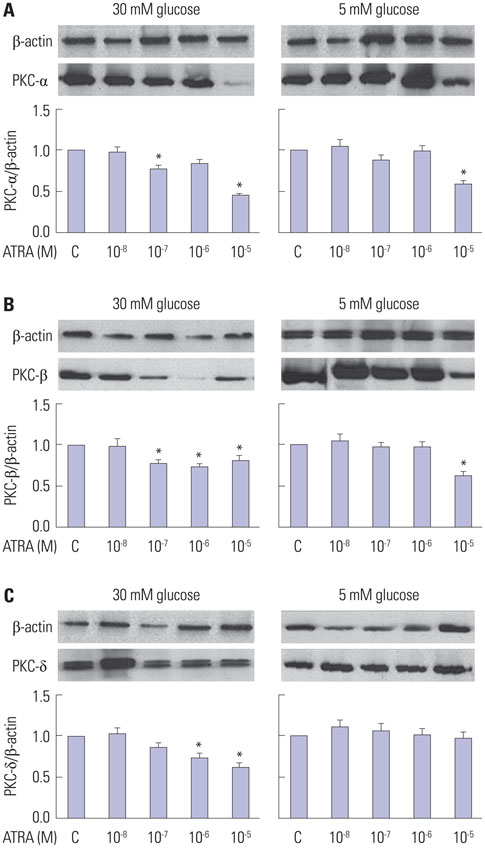
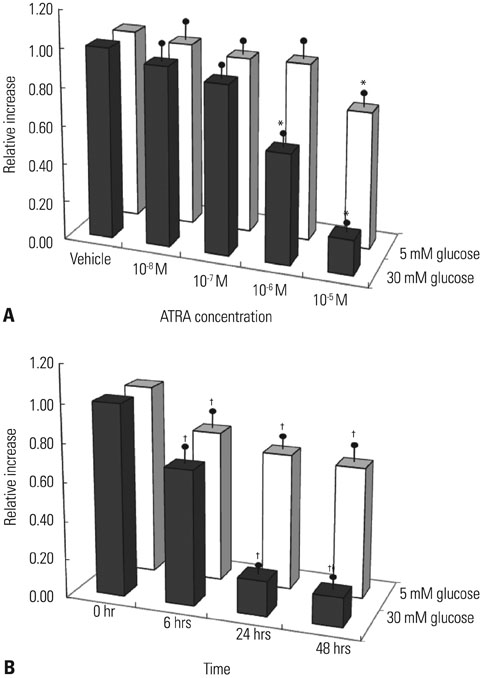
After 16 weeks of treatment, UAE was lower in the ATRA-treated OLETF rats than in the non-treated OLETF rats (0.07+/-0.03 mg/mgCr vs. 0.17+/-0.15 mg/mgCr, p<0.01). After incubation of RMCs in media containing 30 or 5 mM of glucose, treatment with ATRA showed time- and dose-dependent decreases in TGF-beta1 levels and ROS. Moreover, ATRA treatment showed a dose-dependent decrease in PKC expression.
CONCLUSION
ATRA treatment suppressed UAE and TGF-beta1 synthesis, which was mediated by significant reductions in PKC activity and ROS production. Our results suggest that ATRA has a potential therapeutic role for diabetic nephropathy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/*complications
Diabetic Nephropathies/*complications/*drug therapy/pathology
Mesangial Cells/*metabolism
Oxidative Stress/drug effects
Rats
Rats, Inbred OLETF
Reactive Oxygen Species/metabolism
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/analysis/pharmacology
Tretinoin/*pharmacology/therapeutic use
Reactive Oxygen Species
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Tretinoin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Phillips AO, Baboolal K, Riley S, Gröne H, Janssen U, Steadman R, et al. Association of prolonged hyperglycemia with glomerular hypertrophy and renal basement membrane thickening in the Goto Kakizaki model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 37:400–410.2. Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T. Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:164–176.3. Giguère V. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins: complex interplay in retinoid signaling. Endocr Rev. 1994; 15:61–79.
Article4. Morath C, Dechow C, Lehrke I, Haxsen V, Waldherr R, Floege J, et al. Effects of retinoids on the TGF-beta system and extracellular matrix in experimental glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:2300–2309.
Article5. Nishimura C, Kuriyama K. Alteration of lipid peroxide and endogenous antioxidant contents in retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: effect of vitamin A administration. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1985; 37:365–372.
Article6. Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Saitoh Y, Kurosumi M, Natori T. Spontaneous long-term hyperglycemic rat with diabetic complications. Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) strain. Diabetes. 1992; 41:1422–1428.
Article7. Dechow C, Morath C, Peters J, Lehrke I, Waldherr R, Haxsen V, et al. Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on renin-angiotensin system in rats with experimental nephritis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 281:F909–F919.8. Han SY, So GA, Jee YH, Han KH, Kang YS, Kim HK, et al. Effect of retinoic acid in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Immunol Cell Biol. 2004; 82:568–576.
Article9. Schaier M, Liebler S, Schade K, Shimizu F, Kawachi H, Grone HJ, et al. Retinoic acid receptor alpha and retinoid X receptor specific agonists reduce renal injury in established chronic glomerulonephritis of the rat. J Mol Med (Berl). 2004; 82:116–125.
Article10. Soprano DR, Qin P, Soprano KJ. Retinoic acid receptors and cancers. Annu Rev Nutr. 2004; 24:201–221.
Article11. Oseto S, Moriyama T, Kawada N, Nagatoya K, Takeji M, Ando A, et al. Therapeutic effect of all-trans retinoic acid on rats with anti-GBM antibody glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:1241–1252.12. Okauchi N, Mizuno A, Yoshimoto S, Zhu M, Sano T, Shima K. Is caloric restriction effective in preventing diabetes mellitus in the Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima fatty rat, a model of spontaneous non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995; 27:97–106.13. Ozpolat B, Lopez-Berestein G, Adamson P, Fu CJ, Williams AH. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered liposomal all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and orally administered ATRA in healthy volunteers. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2003; 6:292–301.14. Nakamura T, Miller D, Ruoslahti E, Border WA. Production of extracellular matrix by glomerular epithelial cells is regulated by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Kidney Int. 1992; 41:1213–1221.15. Kaneto H, Morrissey J, Klahr S. Increased expression of TGF-beta 1 mRNA in the obstructed kidney of rats with unilateral ureteral ligation. Kidney Int. 1993; 44:313–321.
Article16. Salbert G, Fanjul A, Piedrafita FJ, Lu XP, Kim SJ, Tran P, et al. Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptor-alpha down-regulate the transforming growth factor-beta 1 promoter by antagonizing AP-1 activity. Mol Endocrinol. 1993; 7:1347–1356.
Article17. Derubertis FR, Craven PA. Activation of protein kinase C in glomerular cells in diabetes. Mechanisms and potential links to the pathogenesis of diabetic glomerulopathy. Diabetes. 1994; 43:1–8.
Article18. Pugliese G, Pricci F, Pugliese F, Mene P, Lenti L, Andreani D, et al. Mechanisms of glucose-enhanced extracellular matrix accumulation in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Diabetes. 1994; 43:478–490.
Article19. Koya D, Jirousek MR, Lin YW, Ishii H, Kuboki K, King GL. Characterization of protein kinase C beta isoform activation on the gene expression of transforming growth factor-beta, extracellular matrix components, and prostanoids in the glomeruli of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100:115–126.
Article20. Babazono T, Kapor-Drezgic J, Dlugosz JA, Whiteside C. Altered expression and subcellular localization of diacylglycerol-sensitive protein kinase C isoforms in diabetic rat glomerular cells. Diabetes. 1998; 47:668–676.
Article21. Pfaff IL, Vallon V. Protein kinase C beta isoenzymes in diabetic kidneys and their relation to nephroprotective actions of the ACE inhibitor lisinopril. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2002; 25:329–340.
Article22. Koya D, Haneda M, Nakagawa H, Isshiki K, Sato H, Maeda S, et al. Amelioration of accelerated diabetic mesangial expansion by treatment with a PKC beta inhibitor in diabetic db/db mice, a rodent model for type 2 diabetes. FASEB J. 2000; 14:439–447.
Article23. Carter CA, Kane CJ. Therapeutic potential of natural compounds that regulate the activity of protein kinase C. Curr Med Chem. 2004; 11:2883–2902.
Article24. Kahl-Rainer P, Marian B. Retinoids inhibit protein kinase C-dependent transduction of 1,2-diglyceride signals in human colonic tumor cells. Nutr Cancer. 1994; 21:157–168.
Article25. Simonson MS. Anti-AP-1 activity of all-trans retinoic acid in glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1994; 267(5 Pt 2):F805–F815.
Article26. Kaul N, Siveski-Iliskovic N, Hill M, Khaper N, Seneviratne C, Singal PK. Probucol treatment reverses antioxidant and functional deficit in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem. 1996; 160-161:283–288.
Article27. Ha H, Lee HB. Reactive oxygen species as glucose signaling molecules in mesangial cells cultured under high glucose. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000; 77:S19–S25.
Article28. Oh JH, Ha H, Yu MR, Lee HB. Sequential effects of high glucose on mesangial cell transforming growth factor-beta 1 and fibronectin synthesis. Kidney Int. 1998; 54:1872–1878.
Article29. Iglesias-De La, Ruiz-Torres P, Alcamí J, Díez-Marqués L, Ortega-Velázquez R, Chen S, et al. Hydrogen peroxide increases extracellular matrix mRNA through TGF-beta in human mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2001; 59:87–95.30. Ravid M, Brosh D, Ravid-Safran D, Levy Z, Rachmani R. Main risk factors for nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus are plasma cholesterol levels, mean blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:998–1004.
Article31. Haxsen V, Adam-Stitah S, Ritz E, Wagner J. Retinoids inhibit the actions of angiotensin II on vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2001; 88:637–644.
Article32. Andersen AR, Christiansen JS, Andersen JK, Kreiner S, Deckert T. Diabetic nephropathy in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: an epidemiological study. Diabetologia. 1983; 25:496–501.
Article33. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–986.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Anti-inflammatory Effect of Retinoid on Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Nephropathy
- The Effect of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid on the Activity and the Gene Expression of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes in Rat Skin
- The Effect of Retinoids in Medulloblastoma Cell Culture
- The Effects of All-trans and 13-cis Retinoic Acid on C6 Cell Line Cultures
- All-trans Retinoic Acid induced Myositis in a Patient with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia