J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 Jul;50(4):258-263. 10.4132/jptm.2016.04.19.
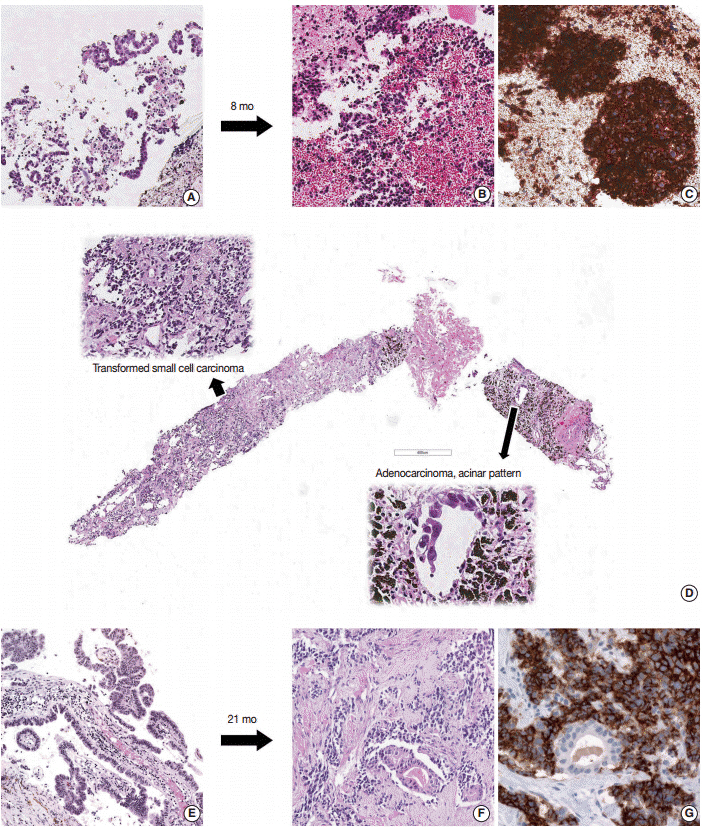
Transformation to Small Cell Lung Cancer of Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic Analysis of Six Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology and Translational Genomics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanjho@skku.edu
- 2Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Samsung Genomic Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2345547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2016.04.19
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are considered the first line treatment for a subset of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Although transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is one of the known mechanisms of resistance to EGFR TKIs, it is not certain whether transformation to SCLC is exclusively found as a mechanism of TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant tumors.
METHODS
We identified six patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma that showed transformation to SCLC on second biopsy (n = 401) during a 6-year period. Clinicopathologic information was analyzed and EGFR mutation results were compared between initial and second biopsy samples.
RESULTS
Six patients showed transformation from adenocarcinoma to SCLC, of which four were pure SCLCs and two were combined adenocarcinoma and SCLCs. Clinically, four cases were EGFR-mutant tumors from non-smoking females who underwent TKI treatment, and the EGFR mutation was retained in the transformed SCLC tumors. The remaining two adenocarcinomas were EGFR wild-type, and one of these patients received EGFR TKI treatment.
CONCLUSIONS
NSCLC can acquire a neuroendocrine phenotype with or without EGFR TKI treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Lung Adenocarcinoma after Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy
Hyung Kyu Park, Youjeong Seo, Yoon-La Choi, Myung-Ju Ahn, Joungho Han
J Pathol Transl Med. 2017;51(4):441-443. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2016.10.18.
Reference
-
1. Goldstraw P, Ball D, Jett JR, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2011; 378:1727–40.
Article2. Oser MG, Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Engelman JA. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:e165–72.
Article3. Moiseenko VM, Protsenko SA, Semenov II, et al. Effectiveness of gefitinib (Iressa) as first-line therapy for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR gene (phase II study). Vopr Onkol. 2010; 56:20–3.4. Engelman JA, Jänne PA. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:2895–9.5. Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, et al. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:2240–7.6. Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3:75ra26.
Article7. Zakowski MF, Ladanyi M, Kris MG; Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Lung Cancer OncoGenome Group. EGFR mutations in small-cell lung cancers in patients who have never smoked. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:213–5.8. van Riel S, Thunnissen E, Heideman D, Smit EF, Biesma B. A patient with simultaneously appearing adenocarcinoma and small-cell lung carcinoma harbouring an identical EGFR exon 19 mutation. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:3188–9.9. Morinaga R, Okamoto I, Furuta K, et al. Sequential occurrence of non-small cell and small cell lung cancer with the same EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer. 2007; 58:411–3.10. Norkowski E, Ghigna MR, Lacroix L, et al. Small-cell carcinoma in the setting of pulmonary adenocarcinoma: new insights in the era of molecular pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:1265–71.
Article11. Watanabe S, Sone T, Matsui T, et al. Transformation to small-cell lung cancer following treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2013; 82:370–2.
Article12. Kim WJ, Kim S, Choi H, et al. Histological transformation from non-small cell to small cell lung carcinoma after treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Thorac Cancer. 2015; 6:800–4.
Article13. Lee B, Han G, Kwon MJ, Han J, Choi YL. KRAS mutation detection in non-small cell lung cancer using a peptide nucleic acid-mediated polymerase chain reaction clamping method and comparative validation with next-generation sequencing. Korean J Pathol. 2014; 48:100–7.14. Ahn S, Lee J, Sung JY, et al. Comparison of three BRAF mutation tests in formalin-fixed paraffin embedded clinical samples. Korean J Pathol. 2013; 47:348–54.15. Pao W, Miller VA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, small-molecule kinase inhibitors, and non-small-cell lung cancer: current knowledge and future directions. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2556–68.
Article16. Miyamoto S, Ikushima S, Ono R, et al. Transformation to small-cell lung cancer as a mechanism of acquired resistance to crizotinib and alectinib. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2016; 46:170–3.
Article17. Kogo M, Shimizu R, Uehara K, et al. Transformation to large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma as acquired resistance mechanism of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Lung Cancer. 2015; 90:364–8.
Article18. Caumont C, Veillon R, Gros A, Laharanne E, Bégueret H, Merlio JP. Neuroendocrine phenotype as an acquired resistance mechanism in ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2016; 92:15–8.19. Sutherland KD, Proost N, Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Song JY, Berns A. Cell of origin of small cell lung cancer: inactivation of Trp53 and Rb1 in distinct cell types of adult mouse lung. Cancer Cell. 2011; 19:754–64.
Article20. Ham JS, Kim S, Kim HK, et al. Two cases of small cell lung cancer transformation from EGFR mutant adenocarcinoma during AZD9291 treatment. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:e1–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Combined Small Cell Carcinoma with Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma, Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Druggable Targets of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Partial Spontaneous Regression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Early Gastric Cancer Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Primary Pulmonary Lymphoepithelioma-like Carcinoma Misdiagnosed as Adenocarcinoma