Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Dec;75(6):231-235.
Druggable Targets of Squamous Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. cheol@kcch.re.kr
Abstract
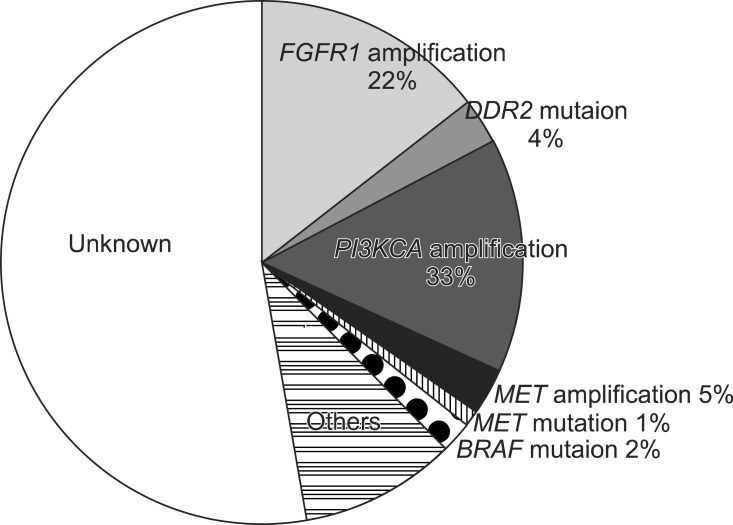
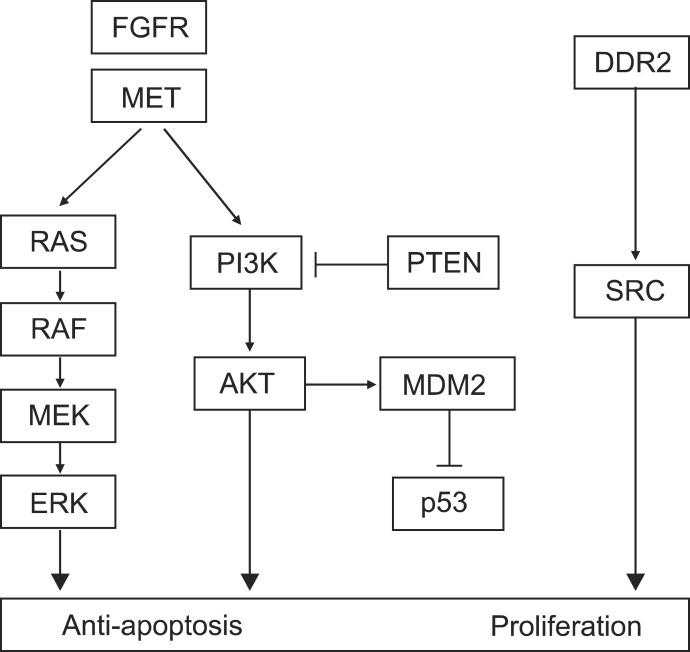
- Knowledge of molecular pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer has increased remarkably and changed the principles of treatment, especially during the past decade. These advancements have been limited mainly to adenocarcinoma of the lung. Recently, genetic alterations in squamous cell lung cancer (SQCLC) have been detailed and positive results of clinical trials using agents targeting these changes have indicated the potential for improved treatment outcomes for SQCLC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pao W, Girard N. New driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011; 12:175–180. PMID: 21277552.
Article2. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature. 2012; 489:519–525. PMID: 22960745.3. Drilon A, Rekhtman N, Ladanyi M, Paik P. Squamous-cell carcinomas of the lung: emerging biology, controversies, and the promise of targeted therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:e418–e426. PMID: 23026827.
Article4. Perez-Moreno P, Brambilla E, Thomas R, Soria JC. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: molecular subtypes and therapeutic opportunities. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:2443–2451. PMID: 22407829.
Article5. Semrad TJ, Mack PC. Fibroblast growth factor signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2012; 13:90–95. PMID: 21959109.
Article6. Weiss J, Sos ML, Seidel D, Peifer M, Zander T, Heuckmann JM, et al. Frequent and focal FGFR1 amplification associates with therapeutically tractable FGFR1 dependency in squamous cell lung cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2:62ra93.
Article7. Dutt A, Ramos AH, Hammerman PS, Mermel C, Cho J, Sharifnia T, et al. Inhibitor-sensitive FGFR1 amplification in human non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20351. PMID: 21666749.8. Ford CE, Lau SK, Zhu CQ, Andersson T, Tsao MS, Vogel WF. Expression and mutation analysis of the discoidin domain receptors 1 and 2 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007; 96:808–814. PMID: 17299390.
Article9. Hammerman PS, Sos ML, Ramos AH, Xu C, Dutt A, Zhou W, et al. Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011; 1:78–89. PMID: 22328973.10. Heist RS, Sequist LV, Engelman JA. Genetic changes in squamous cell lung cancer: a review. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:924–933. PMID: 22722794.
Article11. Spigel DR, Ervin TJ, Ramlau R, Daniel DB, Goldschmidt JH, Blumenschein GR, et al. Final efficacy results from OAM4558g, a randomized phase II study evaluating Met-MAb or placebo in combination with erlotinib in advanced NSCLC. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29(Suppl):7505.
Article12. Bass AJ, Watanabe H, Mermel CH, Yu S, Perner S, Verhaak RG, et al. SOX2 is an amplified lineage-survival oncogene in lung and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:1238–1242. PMID: 19801978.13. Goss GD, Arnold A, Shepherd FA, Dediu M, Ciuleanu TE, Fenton D, et al. Randomized, double-blind trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel with either daily oral cediranib or placebo in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: NCIC clinical trials group BR24 study. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:49–55. PMID: 19917841.
Article14. Reck M, Kaiser R, Eschbach C, Stefanic M, Love J, Gatzemeier U, et al. A phase II double-blind study to investigate efficacy and safety of two doses of the triple angiokinase inhibitor BIBF 1120 in patients with relapsed advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2011; 22:1374–1381. PMID: 21212157.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The change of squamous cell cancer antigen(SCC Ag) level as a tumor marker in squamous cell lung cancer
- Multiple primary lung cancer: Synchronous small cell lung carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung: Two Case Reports with CT Imaging Findings
- Synchronous Primary Lung Cancer with Differrent Squamous cell Carcinoma: One Case Report
- Breast Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Lung