J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Aug;75(2):151-156. 10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.151.
Thoracic Air-Leakage Syndrome in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients as a Late Complication of Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: Case Reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. haneul88@hanmail.net
- 2Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2344807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.151
Abstract
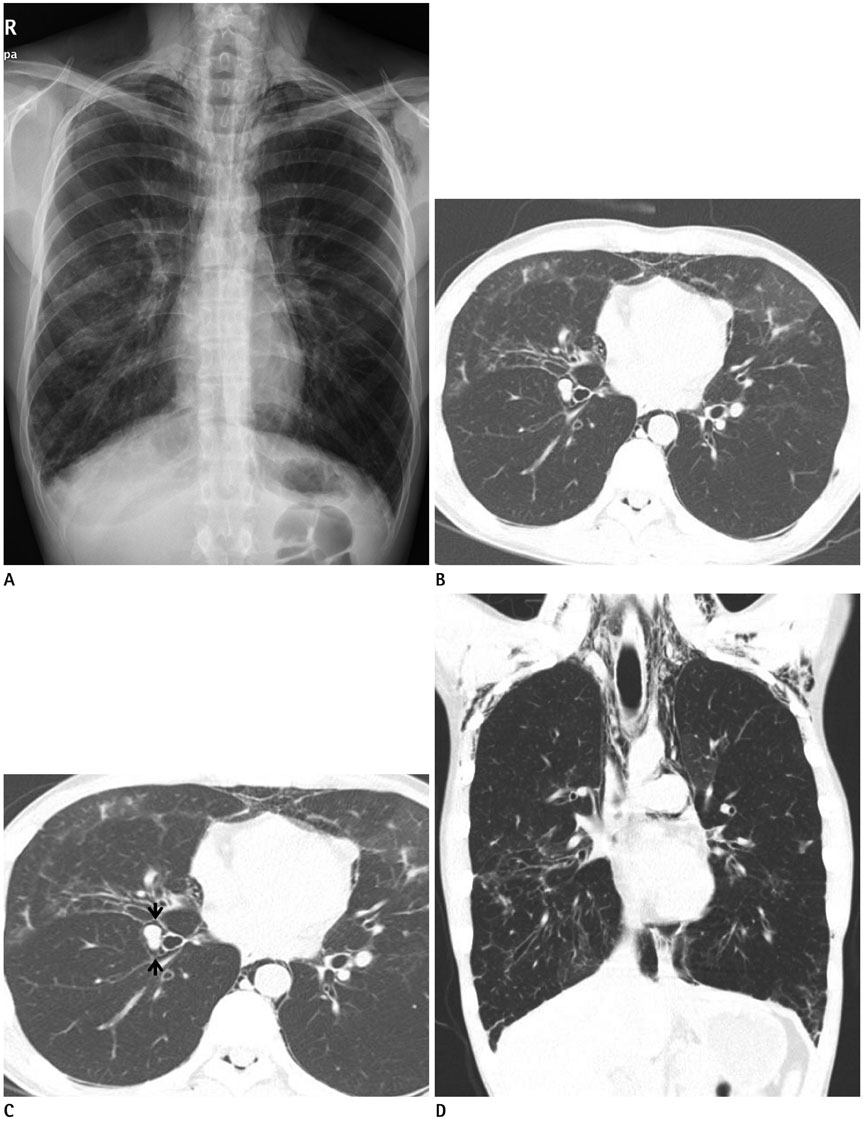
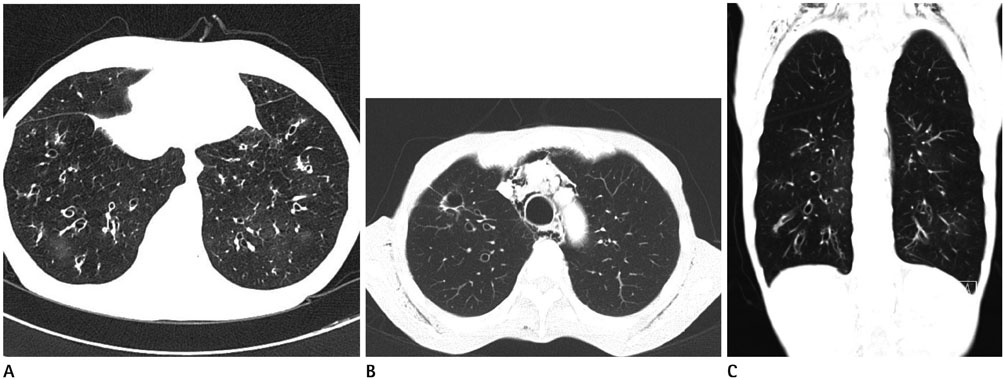
- Air-leakage syndrome associated with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a rare complication, but it is also reported as an independent predictor of a worse survival rate after stem cell transplantation. We report two cases of air-leakage syndrome associated with GVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute leukemia patients who presented with spontaneous pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema, and finally death due to respiratory failure seven to eight months later.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shin HJ, Park CY, Park YH, Kim YJ, Min CK, Lee S, et al. Spontaneous pneumothorax developed in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans after unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: case report and review of the literature. Int J Hematol. 2004; 79:298–302.2. Soubani AO, Uberti JP. Bronchiolitis obliterans following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur Respir J. 2007; 29:1007–1019.3. Sakai R, Kanamori H, Nakaseko C, Yoshiba F, Fujimaki K, Sakura T, et al. Air-leak syndrome following allo-SCT in adult patients: report from the Kanto Study Group for Cell Therapy in Japan. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011; 46:379–384.4. Hildebrandt GC, Fazekas T, Lawitschka A, Bertz H, Greinix H, Halter J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary chronic GVHD: report from the consensus conference on clinical practice in chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011; 46:1283–1295.5. Afessa B, Litzow MR, Tefferi A. Bronchiolitis obliterans and other late onset non-infectious pulmonary complications in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001; 28:425–434.6. Franquet T, Rodríguez S, Hernández JM, Martino R, Giménez A, Hidalgo A, et al. Air-leak syndromes in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with chronic GVHD: high-resolution CT findings. J Thorac Imaging. 2007; 22:335–340.7. Moon MH, Sa YJ, Cho KD, Jo KH, Lee SH, Sim SB. Thoracic air-leak syndromes in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with graft-versus-host disease: a possible sign for poor response to treatment and poor prognosis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:658–662.8. Vogel M, Brodoefel H, Bethge W, Faul C, Hartmann J, Schimmel H, et al. Spontaneous thoracic air-leakage syndrome in patients following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: causes, CT-follow up and patient outcome. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 60:392–397.9. Toubai T, Tanaka J, Kobayashi N, Honda T, Miura Y, Ogawa T, et al. Mediastinal emphysema and bilateral pneumothoraces with chronic GVHD in patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004; 33:1159–1163.10. Wintermark M, Schnyder P. The Macklin effect: a frequent etiology for pneumomediastinum in severe blunt chest trauma. Chest. 2001; 120:543–547.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Air-leakage syndrome after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from unrelated donor
- A case of pneumomediastinum combined with chronic graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Dermatomyositis in an Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipient with Graft-Versus-Host Disease
- Chronic graft versus host disease with small bowel obstruction after unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia
- Thoracic Air-leak Syndromes In Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients with Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Possible Sign for Poor Response to Treatment and Poor Prognosis