Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jul;48(3):990-997. 10.4143/crt.2015.296.
Splenomegaly and Its Associations with Genetic Polymorphisms and Treatment Outcome in Colorectal Cancer Patients Treated with Adjuvant FOLFOX
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. saewon1@snu.ac.kr
- 2Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Center for Gastric Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology and Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2344072
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.296
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Splenomegaly is a clinical surrogate of oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS). We investigated development of splenomegaly and its association with treatment outcome and genetic polymorphisms following adjuvant 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Splenomegaly was determined by spleen volumetry using computed tomography images obtained before initiation of chemotherapy and after completion of adjuvant FOLFOX in CRC patients. Ten genetic polymorphisms in 4 SOS-related genes (VEGFA, MMP9, NOS3, and GSTP1) were analyzed using DNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
RESULTS
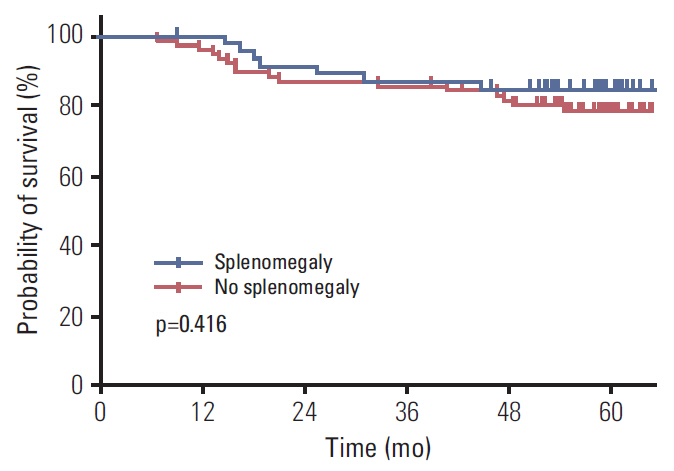
Of 124 patients included, increase in spleen size was observed in 109 (87.9%). Median change was 31% (range, -42% to 168%). Patients with splenomegaly had more severe thrombocytopenia compared to patients without splenomegaly during the chemotherapy period (p < 0.0001). The cumulative dose of oxaliplatin and the lowest platelet count during the chemotherapy period were clinical factors associated with splenomegaly. However, no significant associations were found between genetic polymorphisms and development of splenomegaly. Disease-free survival was similar regardless of the development of splenomegaly.
CONCLUSION
Splenomegaly was frequently observed in patients receiving adjuvant FOLFOX and resulted in more severe thrombocytopenia but did not influence treatment outcome. Examined genetic polymorphisms did not predict development of splenomegaly.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Protective effect of Korean red ginseng on oxaliplatin-mediated splenomegaly in colon cancer
Jeonghyun Kang, Joon Seong Park, Sung Gwe Ahn, Jin Hong Lim, Seung Hyuk Baik, Dong Sup Yoon, Kang Young Lee, Joon Jeong
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2018;95(3):161-167. doi: 10.4174/astr.2018.95.3.161.
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012; 62:10–29.
Article2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Lee DH, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2011. Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 46:109–23.
Article3. Choti MA, Sitzmann JV, Tiburi MF, Sumetchotimetha W, Rangsin R, Schulick RD, et al. Trends in long-term survival following liver resection for hepatic colorectal metastases. Ann Surg. 2002; 235:759–66.
Article4. de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:2938–47.
Article5. Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–51.
Article6. Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, Roth AD, Brezault C, Le Charpentier M, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:460–6.
Article7. Nakano H, Oussoultzoglou E, Rosso E, Casnedi S, Chenard-Neu MP, Dufour P, et al. Sinusoidal injury increases morbidity after major hepatectomy in patients with colorectal liver metastases receiving preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:118–24.
Article8. Angitapalli R, Litwin AM, Kumar PR, Nasser E, Lombardo J, Mashtare T, et al. Adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy and splenomegaly in patients with stages II-III colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2009; 76:363–8.
Article9. Overman MJ, Maru DM, Charnsangavej C, Loyer EM, Wang H, Pathak P, et al. Oxaliplatin-mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2549–55.
Article10. Vreuls CP, Olde Damink SW, Koek GH, Winstanley A, Wisse E, Cloots RH, et al. Glutathione S-transferase M1-null genotype as risk factor for SOS in oxaliplatin-treated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013; 108:676–80.
Article11. Levitsky J, Sorrell MF. Hepatic complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2007; 9:60–5.
Article12. Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Ribero D, Wu TT, Zorzi D, Hoff PM, et al. Chemotherapy regimen predicts steatohepatitis and an increase in 90-day mortality after surgery for hepatic colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2065–72.
Article13. Rubbia-Brandt L. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Clin Liver Dis. 2010; 14:651–68.
Article14. Rubbia-Brandt L, Lauwers GY, Wang H, Majno PE, Tanabe K, Zhu AX, et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and nodular regenerative hyperplasia are frequent oxaliplatin-associated liver lesions and partially prevented by bevacizumab in patients with hepatic colorectal metastasis. Histopathology. 2010; 56:430–9.
Article15. Soubrane O, Brouquet A, Zalinski S, Terris B, Brezault C, Mallet V, et al. Predicting high grade lesions of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome related to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: correlation with post-hepatectomy outcome. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:454–60.16. van den Broek MA, Vreuls CP, Winstanley A, Jansen RL, van Bijnen AA, Dello SA, et al. Hyaluronic acid as a marker of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome secondary to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:1462–9.
Article17. DeLeve LD, McCuskey RS, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, Epstein RB, et al. Characterization of a reproducible rat model of hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Hepatology. 1999; 29:1779–91.
Article18. Iguchi A, Kobayashi R, Yoshida M, Kobayashi K, Matsuo K, Kitajima I, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is one of the cytokines causative and predictive of hepatic venoocclusive disease (VOD) in stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001; 27:1173–80.
Article19. Ribero D, Wang H, Donadon M, Zorzi D, Thomas MB, Eng C, et al. Bevacizumab improves pathologic response and protects against hepatic injury in patients treated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases. Cancer. 2007; 110:2761–7.
Article20. Jung EJ, Ryu CG, Kim G, Kim SR, Park HS, Kim YJ, et al. Splenomegaly during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2012; 32:3357–62.21. Jardim DL, Rodrigues CA, Novis YA, Rocha VG, Hoff PM. Oxaliplatin-related thrombocytopenia. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:1937–42.
Article22. Rubbia-Brandt L, Tauzin S, Brezault C, Delucinge-Vivier C, Descombes P, Dousset B, et al. Gene expression profiling provides insights into pathways of oxaliplatin-related sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in humans. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011; 10:687–96.
Article23. Agostini J, Benoist S, Seman M, Julie C, Imbeaud S, Letourneur F, et al. Identification of molecular pathways involved in oxaliplatin-associated sinusoidal dilatation. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:869–76.
Article24. Tamandl D, Klinger M, Eipeldauer S, Herberger B, Kaczirek K, Gruenberger B, et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome impairs long-term outcome of colorectal liver metastases treated with resection after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:421–30.
Article25. Vreuls CP, Van Den Broek MA, Winstanley A, Koek GH, Wisse E, Dejong CH, et al. Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) reduces the effect of oxaliplatin in colorectal liver metastases. Histopathology. 2012; 61:314–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Dietary Vitamin D and Calcium With Genetic Polymorphisms in Colorectal Neoplasia
- The Colorectal Cancer Risk of Meat Intake, Smoking, and CYP2E1 Polymorphisms: The Comparison of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Controls
- Analysis of reduced-dose administration of oxaliplatin as adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy for colorectal cancer
- Protective effect of Korean red ginseng on oxaliplatin-mediated splenomegaly in colon cancer
- Clinical value of an adenosine triphosphate-based chemotherapy response assay in resectable stage III colorectal cancer