Ann Surg Treat Res.
2018 Sep;95(3):161-167. 10.4174/astr.2018.95.3.161.
Protective effect of Korean red ginseng on oxaliplatin-mediated splenomegaly in colon cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gsjjoon@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2419447
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.95.3.161
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study investigated how adding Korean red ginseng extract (KRG) to folinic acid, fluorouracil and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) chemotherapy affected the rate of splenomegaly in colon cancer.
METHODS
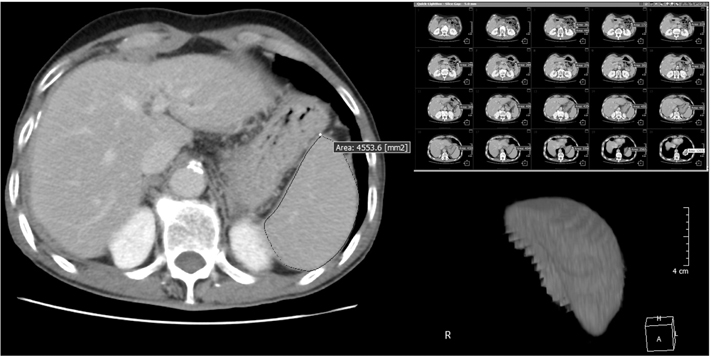
This retrospective study analyzed 42 patients who were randomly assigned to receive a FOLFOX regimen with or without KRG. Spleen volume change was assessed by computed tomography scans measured before surgery (presurgery volume) and 3 weeks after cessation of the 12th cycle of FOLFOX (postchemotherapy volume).
RESULTS
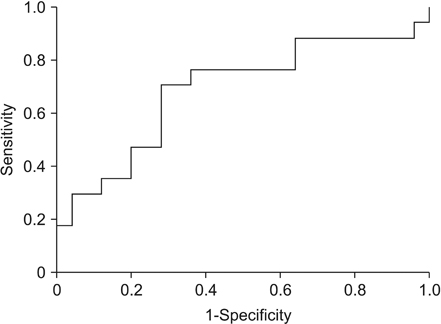
All patients showed increased spleen volume. No difference was observed in median presurgery and postchemotherapy volume between the KRG and control groups. However, a ratio defined as postchemotherapy volume divided by presurgery volume was significantly lower in the KRG group than the control group (median, 1.38 [range, 1.0-2.8] in KRG group vs. median, 1.89 [range, 1.1-3.0] in control group, P = 0.028). When splenomegaly was defined as a >61% increase in spleen volume, the rate of splenomegaly was significantly lower in the KRG group than the control group (28.6% vs. 61.9%, P = 0.03). KRG consumption was inversely associated with developing splenomegaly in multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
Adding KRG during FOLFOX chemotherapy for colon cancer might protect against oxaliplatin-induced splenomegaly. The protective effect of Korean red ginseng should be investigated with further research.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.
Article2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Cho H, Lee DH, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2012. Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 47:127–141.
Article3. André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–2351.
Article4. Yothers G, O'Connell MJ, Allegra CJ, Kuebler JP, Colangelo LH, Petrelli NJ, et al. Oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: updated results of NSABP C-07 trial, including survival and subset analyses. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3768–3774.5. Haller DG, Tabernero J, Maroun J, de Braud F, Price T, Van Cutsem E, et al. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil and folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:1465–1471.
Article6. Jeong WK, Shin JW, Baek SK. Oncologic outcomes of early adjuvant chemotherapy initiation in patients with stage III colon cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 89:124–130.
Article7. Nam SJ, Cho JY, Lee HS, Choe G, Jang JJ, Yoon YS, et al. Chemotherapy-associated hepatopathy in korean colorectal cancer liver metastasis patients: oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy and sinusoidal injury. Korean J Pathol. 2012; 46:22–29.
Article8. Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, Roth AD, Brezault C, Le Charpentier M, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:460–466.
Article9. Mehta NN, Ravikumar R, Coldham CA, Buckels JA, Hubscher SG, Bramhall SR, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on liver resection for colorectal liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:782–786.
Article10. Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Ribero D, Wu TT, Zorzi D, Hoff PM, et al. Chemotherapy regimen predicts steatohepatitis and an increase in 90-day mortality after surgery for hepatic colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2065–2072.
Article11. Overman MJ, Maru DM, Charnsangavej C, Loyer EM, Wang H, Pathak P, et al. Oxaliplatin-mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2549–2555.
Article12. Angitapalli R, Litwin AM, Kumar PR, Nasser E, Lombardo J, Mashtare T, et al. Adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy and splenomegaly in patients with stages II-III colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2009; 76:363–368.
Article13. Jung EJ, Ryu CG, Kim G, Kim SR, Park HS, Kim YJ, et al. Splenomegaly during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2012; 32:3357–3362.14. Kim MJ, Han SW, Lee DW, Cha Y, Lee KH, Kim TY, et al. Splenomegaly and its associations with genetic polymorphisms and treatment outcome in colorectal cancer patients treated with adjuvant FOLFOX. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:990–997.
Article15. Robinson SM, Mann J, Vasilaki A, Mathers J, Burt AD, Oakley F, et al. Pathogenesis of FOLFOX induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in a murine chemotherapy model. J Hepatol. 2013; 59:318–326.
Article16. Park HM, Kim SJ, Mun AR, Go HK, Kim GB, Kim SZ, et al. Korean red ginseng and its primary ginsenosides inhibit ethanol-induced oxidative injury by suppression of the MAPK pathway in TIB-73 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012; 141:1071–1076.
Article17. Han JY, Lee S, Yang JH, Kim S, Sim J, Kim MG, et al. Korean red ginseng attenuates ethanol-induced steatosis and oxidative stress via AMPK/Sirt1 activation. J Ginseng Res. 2015; 39:105–115.
Article18. Shin KS, Lee JJ, Kim YI, Yu JY, Park ES, Im JH, et al. Effect of Korean red ginseng extract on blood circulation in healthy volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Ginseng Res. 2007; 31:109–116.19. Boo YJ, Park JM, Kim J, Suh SO. Prospective study for Korean red ginseng extract as an immune modulator following a curative surgery in patients with advanced colon cancer. J Ginseng Res. 2007; 31:54–59.20. Masi G, Loupakis F, Pollina L, Vasile E, Cupini S, Ricci S, et al. Long-term outcome of initially unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan (FOLFOXIRI) followed by radical surgery of metastases. Ann Surg. 2009; 249:420–425.
Article21. Nakano H, Oussoultzoglou E, Rosso E, Casnedi S, Chenard-Neu MP, Dufour P, et al. Sinusoidal injury increases morbidity after major hepatectomy in patients with colorectal liver metastases receiving preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:118–124.
Article22. Soubrane O, Brouquet A, Zalinski S, Terris B, Brézault C, Mallet V, et al. Predicting high grade lesions of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome related to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: correlation with post-hepatectomy outcome. Ann Surg. 2010; 251:454–460.23. Yuan HD, Kim JT, Kim SH, Chung SH. Ginseng and diabetes: the evidences from in vitro, animal and human studies. J Ginseng Res. 2012; 36:27–39.
Article24. Seo SJ, Cho JY, Jeong YH, Choi YS. Effect of Korean red ginseng extract on liver damage induced by short-term and long-term ethanol treatment in rats. J Ginseng Res. 2013; 37:194–200.
Article25. Ki SH, Yang JH, Ku SK, Kim SC, Kim YW, Cho IJ. Red ginseng extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. J Ginseng Res. 2013; 37:45–53.
Article26. Imai K, Emi Y, Iyama KI, Beppu T, Ogata Y, Kakeji Y, et al. Splenic volume may be a useful indicator of the protective effect of bevacizumab against oxaliplatin-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014; 40:559–566.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Experimental Study on the Protective Effects of Ginseng Extract to Oxygen Toxicity
- Colon Cancer Chemoprevention With Ginseng and Other Botanicals
- Inhibition by Ginseng of Colon Carcinogenesis in Rats
- Oxaliplatin-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report
- A Case of Portal Hypertension after the Treatment of Oxaliplatin Based Adjuvant-Chemotherapy for Rectal Cancer