Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Apr;57(4):253-257. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.4.253.
A Case of Portal Hypertension after the Treatment of Oxaliplatin Based Adjuvant-Chemotherapy for Rectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. yokweon@mail.knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1718407
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.4.253
Abstract
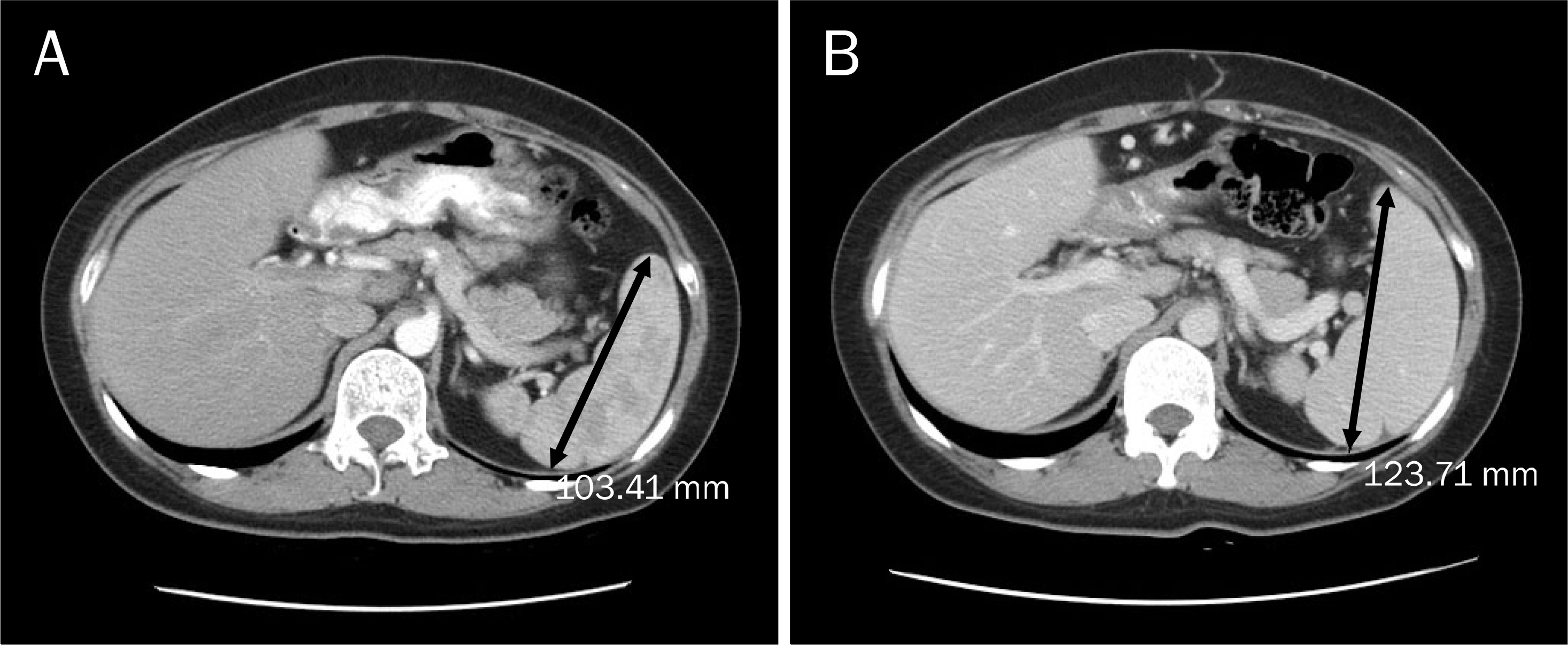
- We report herein a case of 35-years-old woman in whom portal hypertension (esophageal varix and splenomegaly) developed after 12 cycles of oxaliplatin based adjuvant chemotherapy for rectal cancer. She was transferred for the evaluation of etiology of new-onset portal hypertension. The esophageal varix and splenomegaly were absent before the oxaliplatin based adjuvant chemotherapy. Thorough history taking and serological exam revealed no evidence of chronic liver disease. Liver biopsy was done and there was no cirrhotic nodule formation. Instead, perivenular fibrosis was noted. Considering new development of esophageal varices and splenomegaly after 12 cycles of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy, we could conclude that portal hypertension in this patient were due to sinusoidal injury by oxaliplatin. Finally, we recommend regular follow-up with endoscopy and radiologic examination for checking the development of varices and for screening of varices and splenomegaly in patients with colo-rectal cancer who receive oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Antineoplastic Agents/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Chemotherapy, Adjuvant
Esophageal and Gastric Varices/chemically induced
Female
Fibrosis
Humans
Hypertension, Portal/chemically induced/*diagnosis
Liver/pathology
Organoplatinum Compounds/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Positron-Emission Tomography
Rectal Neoplasms/*drug therapy/surgery
Splenomegaly/chemically induced
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Garcia-Tsao G. Portal hypertension. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005; 21:313–322.
Article2. Lebrec D. Methods to evaluate portal hypertension. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1992; 21:41–59.
Article3. Baik SK. Assessment and current treatment of portal hypertension. Korean J Hepatol. 2005; 11:211–217.4. Kim CY, Lee HS, Han CJ. Relative etiologic role of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus in chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma among age specific groups in Korea: the possible presence of non-B, non-C agents. Seoul J Med. 1993; 34:27–33.5. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108.
Article6. Shin HR, Jung KW, Won YJ, Park JG. 139 KCCR-affiliated Hospitals. 2002 annual report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry: based on registered data from 139 hospitals. Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 36:103–114.
Article7. Jonker DJ, Maroun JA, Kocha W. Survival benefit of chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Br J Cancer. 2000; 82:1789–1794.
Article8. Erlichman C, Fine S, Wong A, Elhakim T. A randomized trial of fluorouracil and folinic acid in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1988; 6:469–475.
Article9. Douillard JY. Irinotecan-based regimens in the adjuvant therapy of colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2005; 5(Suppl 1):S34–S37.
Article10. de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:2938–2947.
Article11. Jennerwein MM, Eastman A, Khokhar A. Characterization of ad-ducts produced in DNA by isomeric 1,2-diaminocyclohex-aneplatinum(II) complexes. Chem Biol Interact. 1989; 70:39–49.
Article12. Rixe O, Ortuzar W, Alvarez M, et al. Oxaliplatin, tetraplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin: spectrum of activity in drug-resistant cell lines and in the cell lines of the National Cancer Institute's Anticancer Drug Screen panel. Biochem Pharmacol. 1996; 52:1855–1865.
Article13. Raymond E, Buquet-Fagot C, Djelloul S, et al. Antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil and the thymidy-late synthase inhibitor AG337 in human colon, breast and ovarian cancers. Anticancer Drugs. 1997; 8:876–885.
Article14. Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:460–466.
Article15. DeLeve LD, Shulman HM, McDonald GB. Toxic injury to hepatic sinusoids: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease). Semin Liver Dis. 2002; 22:27–42.
Article16. Morris-Stiff G, Tan YM, Vauthey JN. Hepatic complications following preoperative chemotherapy with oxaliplatin or irinotecan for hepatic colorectal metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:609–614.
Article17. Hubert C, Sempoux C, Horsmans Y, et al. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia: a deleterious consequence of chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases? Liver Int. 2007; 27:938–943.
Article18. Overman MJ, Maru DM, Charnsangavej C, et al. Oxaliplatin- mediated increase in spleen size as a biomarker for the development of hepatic sinusoidal injury. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:2549–2555.19. Kandutsch S, Klinger M, Hacker S, Wrba F, Gruenberger B, Gruenberger T. Patterns of hepatotoxicity after chemotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:1231–1236.
Article20. Nakano H, Oussoultzoglou E, Rosso E, et al. Sinusoidal injury increases morbidity after major hepatectomy in patients with colorectal liver metastases receiving preoperative chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 2008; 247:118–124.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adjuvant oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy effect after treatment of colorectal hepatic metastasis
- Chemotherapy for Colorectal Cancer
- Chemotherapy in Rectal Cancer
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Colon Cancer
- A Case of Liver Fibrosis with Splenomegaly after Oxaliplatin-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer