Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Jun;20(2):105-113. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.105.
Susceptibility Vessel Sign for the Detection of Hyperacute MCA Occlusion: Evaluation with Susceptibility-weighted MR Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. choids@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2327422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.105
Abstract
- PURPOSE
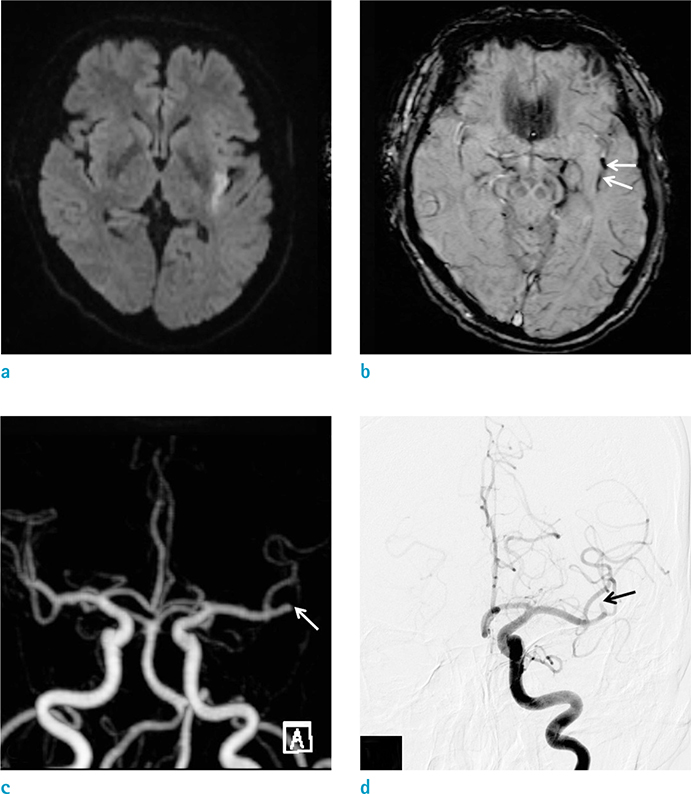
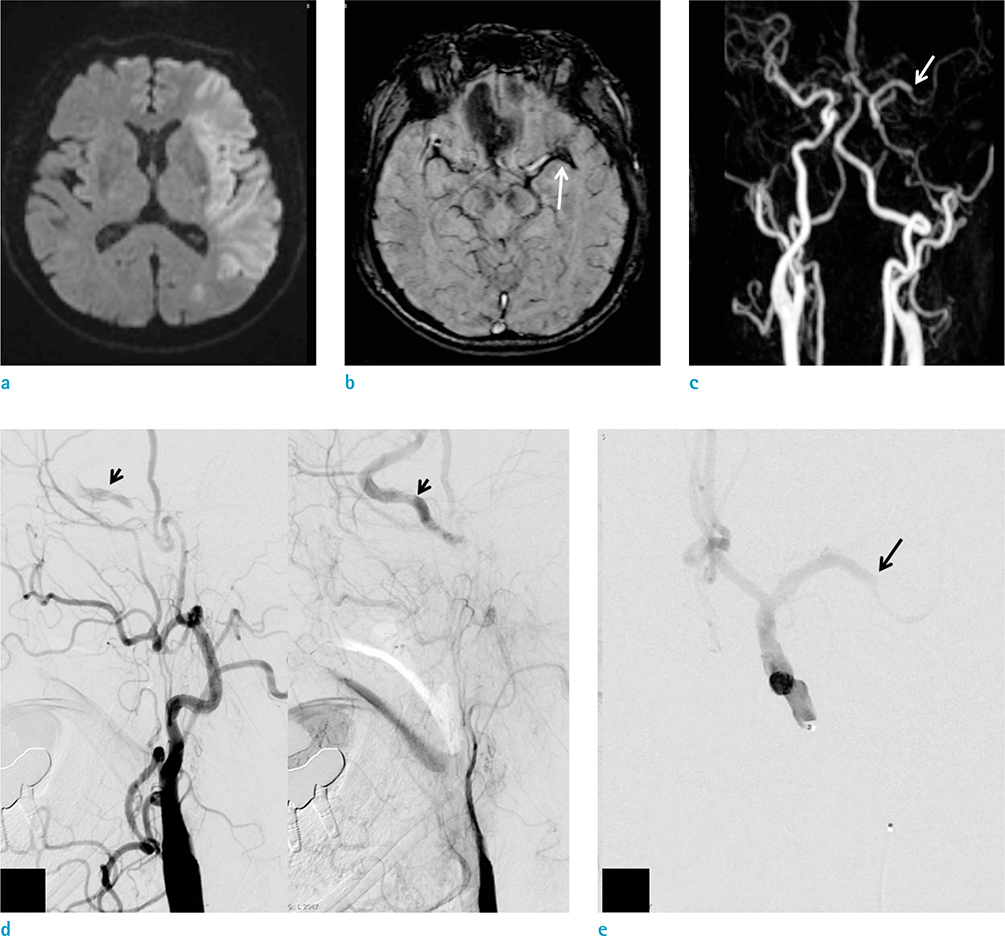
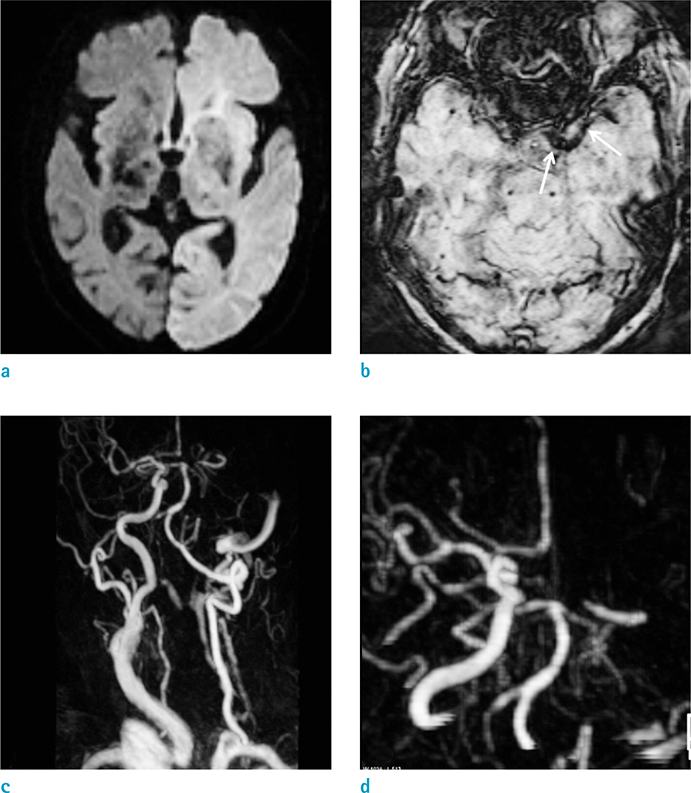
Susceptibility vessel sign (SVS) on gradient echo image, which is caused by MR signal loss due to arterial thrombosis, has been reported in acute middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarction. However, the reported sensitivity and diagnostic accuracy of SVS have been variable. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) is a newly developed MR sequence. Recent studies have found that SWI may be useful in the field of cerebrovascular diseases, especially for detecting the presence of prominent veins, microbleeds and the SVS. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic values of SWI for the detection of hyperacute MCA occlusion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-nine patients (37 males, 32 females; 46-89 years old [mean, 69.1]) with acute stroke involving the MCA territory underwent MR imaging within 6 hours after the symptom onset. MR examination included T2, FLAIR (fluid-attenuated inversion recovery), DWI, SWI, PWI (perfusion-weighted imaging), contrast-enhanced MR angiography (MRA) and contrast-enhanced T1. Of these patients, 28 patients also underwent digital subtraction angiography (DSA) within 2 hours after MR examination. Presence or absence of SVS on SWI was assessed without knowledge of clinical, DSA and other MR imaging findings.
RESULTS
On MRA or DSA, 34 patients (49.3%) showed MCA occlusion. Of these patients, SVS was detected in 30 (88.2%) on SWI. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy of SWI were 88.2%, 97.1%, 96.8%, 89.5% and 92.8%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
SWI was sensitive, specific and accurate for the detection of hyperacute MCA occlusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Flacke S, Urbach H, Keller E, et al. Middle cerebral artery (MCA) susceptibility sign at susceptibility-based perfusion MR imaging: clinical importance and comparison with hyperdense MCA sign at CT. Radiology. 2000; 215:476–482.2. Rovira A, Orellana P, Alvarez-Sabin J, et al. Hyperacute ischemic stroke: middle cerebral artery susceptibility sign at echo-planar gradient-echo MR imaging. Radiology. 2004; 232:466–473.3. Adams HP Jr, Adams RJ, Brott T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: a scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2003; 34:1056–1083.4. Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR. Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med. 2004; 52:612–618.5. Santhosh K, Kesavadas C, Thomas B, Gupta AK, Thamburaj K, Kapilamoorthy TR. Susceptibility weighted imaging: a new tool in magnetic resonance imaging of stroke. Clin Radiol. 2009; 64:74–83.6. Huang P, Chen CH, Lin WC, Lin RT, Khor GT, Liu CK. Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted imaging in patients with major stroke. J Neurol. 2012; 259:1426–1432.7. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.8. Cho KH, Kim JS, Kwon SU, Cho AH, Kang DW. Significance of susceptibility vessel sign on T2*-weighted gradient echo imaging for identification of stroke subtypes. Stroke. 2005; 36:2379–2383.9. Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YC. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:19–30.10. Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:232–252.11. Hermier M, Nighoghossian N. Contribution of susceptibility-weighted imaging to acute stroke assessment. Stroke. 2004; 35:1989–1994.12. Ishimaru H, Ochi M, Morikawa M, et al. Accuracy of pre- and postcontrast 3D time-of-flight MR angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke: correlation with catheter angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:923–926.13. Kinoshita T, Ogawa T, Kado H, Sasaki N, Okudera T. CT angiography in the evaluation of intracranial occlusive disease with collateral circulation: comparison with MR angiography. Clin Imaging. 2005; 29:303–306.14. Le Bras A, Raoult H, Ferre JC, Ronziere T, Gauvrit JY. Optimal MRI sequence for identifying occlusion location in acute stroke: which value of time-resolved contrast-enhanced MRA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; 36:1081–1088.15. Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:11–20.16. Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM. Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology. 1997; 204:272–277.17. Rauscher A, Sedlacik J, Barth M, Mentzel HJ, Reichenbach JR. Magnetic susceptibility-weighted MR phase imaging of the human brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:736–742.18. Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Thomas B, Shroff MM, Haacke EM. Principles, techniques, and applications of T2*-based MR imaging and its special applications. Radiographics. 2009; 29:1433–1449.19. Radbruch A, Mucke J, Schweser F, et al. Comparison of susceptibility weighted imaging and TOF-angiography for the detection of Thrombi in acute stroke. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63459.20. Park MG, Oh SJ, Baik SK, Jung DS, Park KP. Susceptibility-weighted imaging for detection of thrombus in acute cardioembolic stroke. J Stroke. 2016; 18:73–79.21. Agarwal A, Vijay K, Thamburaj K, Kanekar S, Kalapos P. Sensitivity of 3D gradient recalled echo susceptibility-weighted imaging technique compared to computed tomography angiography for detection of middle cerebral artery thrombus in acute stroke. Neurol Int. 2014; 6:5521.22. Kim HS, Lee DH, Choi CG, Kim SJ, Suh DC. Progression of middle cerebral artery susceptibility sign on T2*-weighted images: its effect on recanalization and clinical outcome after thrombolysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:W650–W657.23. Rohan V, Baxa J, Tupy R, et al. Length of occlusion predicts recanalization and outcome after intravenous thrombolysis in middle cerebral artery stroke. Stroke. 2014; 45:2010–2017.24. Soize S, Batista AL, Rodriguez Regent C, et al. Susceptibility vessel sign on T2* magnetic resonance imaging and recanalization results of mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers: a multicentre cohort study. Eur J Neurol. 2015; 22:967–972.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypointensity on Susceptibility-Weighted Images Prior to Signal Change on Diffusion-Weighted Images in a Hyperacute Ischemic Infarction: a Case Study
- A newly Developed Hyperintensity Within a Posterior Cerebral Artery Susceptibility Vessel Sign in T2*-Weighted Gradient-Echo Imaging: a Case Report and Correlation with Magnetic Resonance Angiography and Black-Blood Imaging
- Intraarterial therapy for middle cerebral artery dissection with intramural hematoma detection on susceptibility-weighted imaging
- Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging for the Detection of Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Arterial Spin Labelling Perfusion, Proton MR Spectroscopy and Susceptibility-Weighted MR Findings of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: a Case Report