World J Mens Health.
2013 Aug;31(2):136-140.
The Role of Androgen in the Adipose Tissue of Males
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. belong@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
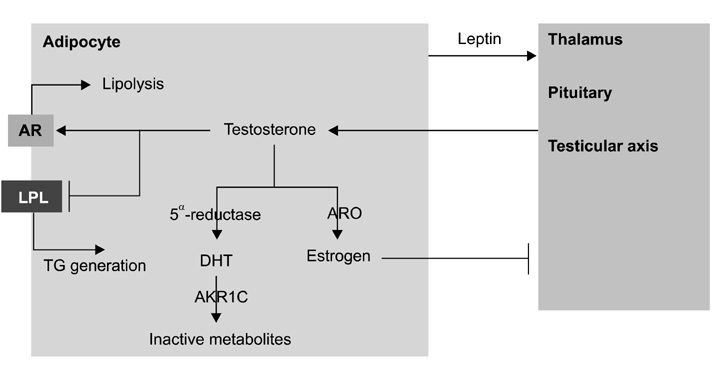
- Adipose tissue, where various metabolic hormones are secreted, plays a role in metabolizing different substances including androgen. Within fat tissue, enzymes such as aromatase and aldo-keto reductase 1C are responsible for metabolizing testosterone into estrogen and 5-dihydrotestosterone into inactive metabolites. Adipose tissue can also affect the secretion of gonadotropin, which influences the formation of androgen in the testes. At the same time, androgen has an impact on the distribution and proliferation of adipose tissue. The adrenoreceptors for catecholamines, which have been proven to play an essential role in controlling lipolysis, function by being up-regulated by androgens. Furthermore, androgens regulate the activity of lipoprotein lipase, a key enzyme involved in intracellular esterification of adipose tissue.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:2548–2556.
Article2. Galic S, Oakhill JS, Steinberg GR. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010; 316:129–139.
Article3. Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:10697–10703.
Article4. Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001; 409:307–312.
Article5. Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005; 436:356–362.
Article6. Sopasakis VR, Sandqvist M, Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Schmelz M, Yang X, et al. High local concentrations and effects on differentiation implicate interleukin-6 as a paracrine regulator. Obes Res. 2004; 12:454–460.
Article7. Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 280:E745–E751.
Article8. Fontana L, Eagon JC, Trujillo ME, Scherer PE, Klein S. Visceral fat adipokine secretion is associated with systemic inflammation in obese humans. Diabetes. 2007; 56:1010–1013.
Article9. Rotter V, Nagaev I, Smith U. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:45777–45784.10. Rebuffé-Scrive M, Brönnegard M, Nilsson A, Eldh J, Gustafsson JA, Björntorp P. Steroid hormone receptors in human adipose tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990; 71:1215–1219.11. Muller M, Grobbee DE, den Tonkelaar I, Lamberts SW, van der Schouw YT. Endogenous sex hormones and metabolic syndrome in aging men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90:2618–2623.
Article12. Blouin K, Boivin A, Tchernof A. Androgens and body fat distribution. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008; 108:272–280.
Article13. Kennedy GC. The role of depot fat in the hypothalamic control of food intake in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1953; 140:578–596.14. Coleman DL. Obese and diabetes: two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice. Diabetologia. 1978; 14:141–148.
Article15. Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994; 372:425–432.
Article16. Chen H, Charlat O, Tartaglia LA, Woolf EA, Weng X, Ellis SJ, et al. Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell. 1996; 84:491–495.
Article17. Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:292–295.
Article18. Barash IA, Cheung CC, Weigle DS, Ren H, Kabigting EB, Kuijper JL, et al. Leptin is a metabolic signal to the reproductive system. Endocrinology. 1996; 137:3144–3147.
Article19. Mounzih K, Lu R, Chehab FF. Leptin treatment rescues the sterility of genetically obese ob/ob males. Endocrinology. 1997; 138:1190–1193.
Article20. Chehab FF, Lim ME, Lu R. Correction of the sterility defect in homozygous obese female mice by treatment with the human recombinant leptin. Nat Genet. 1996; 12:318–320.
Article21. Banks WA, McLay RN, Kastin AJ, Sarmiento U, Scully S. Passage of leptin across the blood-testis barrier. Am J Physiol. 1999; 276:E1099–E1104.
Article22. Caprio M, Isidori AM, Carta AR, Moretti C, Dufau ML, Fabbri A. Expression of functional leptin receptors in rodent Leydig cells. Endocrinology. 1999; 140:4939–4947.23. Tena-Sempere M, Pinilla L, González LC, Diéguez C, Casanueva FF, Aguilar E. Leptin inhibits testosterone secretion from adult rat testis in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1999; 161:211–218.
Article24. Yu WH, Kimura M, Walczewska A, Karanth S, McCann SM. Role of leptin in hypothalamic-pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94:1023–1028.
Article25. El-Hefnawy T, Ioffe S, Dym M. Expression of the leptin receptor during germ cell development in the mouse testis. Endocrinology. 2000; 141:2624–2630.
Article26. Bhat GK, Sea TL, Olatinwo MO, Simorangkir D, Ford GD, Ford BD, et al. Influence of a leptin deficiency on testicular morphology, germ cell apoptosis, and expression levels of apoptosis-related genes in the mouse. J Androl. 2006; 27:302–310.
Article27. Dunn JF, Nisula BC, Rodbard D. Transport of steroid hormones: binding of 21 endogenous steroids to both testosterone-binding globulin and corticosteroid-binding globulin in human plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981; 53:58–68.
Article28. Vermeulen A, Andó S. Metabolic clearance rate and interconversion of androgens and the influence of the free androgen fraction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979; 48:320–326.
Article29. Hammes A, Andreassen TK, Spoelgen R, Raila J, Hubner N, Schulz H, et al. Role of endocytosis in cellular uptake of sex steroids. Cell. 2005; 122:751–762.
Article30. Russell DW, Wilson JD. Steroid 5 alpha-reductase: two genes/two enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994; 63:25–61.31. Simpson ER, Mahendroo MS, Means GD, Kilgore MW, Hinshelwood MM, Graham-Lorence S, et al. Aromatase cytochrome P450, the enzyme responsible for estrogen biosynthesis. Endocr Rev. 1994; 15:342–355.
Article32. Cleland WH, Mendelson CR, Simpson ER. Aromatase activity of membrane fractions of human adipose tissue stromal cells and adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1983; 113:2155–2160.
Article33. Calle EE, Kaaks R. Overweight, obesity and cancer: epidemiological evidence and proposed mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:579–591.
Article34. Vermeulen A, Kaufman JM, Deslypere JP, Thomas G. Attenuated luteinizing hormone (LH) pulse amplitude but normal LH pulse frequency, and its relation to plasma androgens in hypogonadism of obese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993; 76:1140–1146.
Article35. Jones TH. Testosterone deficiency: a risk factor for cardiovascular disease? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 21:496–503.
Article36. Blouin K, Richard C, Bélanger C, Dupont P, Daris M, Laberge P, et al. Local androgen inactivation in abdominal visceral adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:5944–5950.
Article37. Blouin K, Richard C, Brochu G, Hould FS, Lebel S, Marceau S, et al. Androgen inactivation and steroid-converting enzyme expression in abdominal adipose tissue in men. J Endocrinol. 2006; 191:637–649.
Article38. Zhang Y, Dufort I, Rheault P, Luu-The V. Characterization of a human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Mol Endocrinol. 2000; 25:221–228.
Article39. Dufort I, Labrie F, Luu-The V. Human types 1 and 3 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: differential lability and tissue distribution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:841–846.40. Ibrahim MM. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes Rev. 2010; 11:11–18.
Article41. Bouloumie A, Valet P, Dauzats M, Lafontan M, Saulnier-Blache JS. In vivo upregulation of adipocyte alpha 2-adrenoceptors by androgens is consequence of direct action on fat cells. Am J Physiol. 1994; 267:C926–C931.
Article42. Xu X, De Pergola G, Björntorp P. The effects of androgens on the regulation of lipolysis in adipose precursor cells. Endocrinology. 1990; 126:1229–1234.
Article43. Hansson P, Saggerson D, Nilsson-Ehle P. Sex difference in triglyceride/fatty acid substrate cycling of rat adipose tissue: indirect regulation by androgens. Horm Metab Res. 1991; 23:465–468.
Article44. Eckel RH. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320:1060–1068.45. Wang H, Eckel RH. Lipoprotein lipase: from gene to obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 297:E271–E288.
Article46. Ramirez ME, McMurry MP, Wiebke GA, Felten KJ, Ren K, Meikle AW, et al. Evidence for sex steroid inhibition of lipoprotein lipase in men: comparison of abdominal and femoral adipose tissue. Metabolism. 1997; 46:179–185.
Article47. Mårin P, Odén B, Björntorp P. Assimilation and mobilization of triglycerides in subcutaneous abdominal and femoral adipose tissue in vivo in men: effects of androgens. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995; 80:239–243.
Article48. Mårin P, Lönn L, Andersson B, Odén B, Olbe L, Bengtsson BA, et al. Assimilation of triglycerides in subcutaneous and intraabdominal adipose tissues in vivo in men: effects of testosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996; 81:1018–1022.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Vitamin D in Adipose Tissue Biology: Adipocyte Differentiation, Energy Metabolism, and Inflammation
- The Effects of Androgen on Androgen Receptor, Apoptosis and Proliferation in the Penile Erectile Tissue of Adult Rat
- Sex-dependent Depot Differences in Adipose Tissue Development and Function; Role of Sex Steroids
- Partial Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome Presenting with Gynecomastia
- A Case Report of Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome