Tuberc Respir Dis.
2014 Oct;77(4):172-177. 10.4046/trd.2014.77.4.172.
Recurrent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Chronic Lung Diseases: Relapse or Reinfection?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hoho@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2320574
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.4.172
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is particularly associated with progressive and ultimately chronic recurrent respiratory infections in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchiectasis, chronic destroyed lung disease, and cystic fibrosis. Its treatment is also very complex because of drug resistance and recurrence.
METHODS
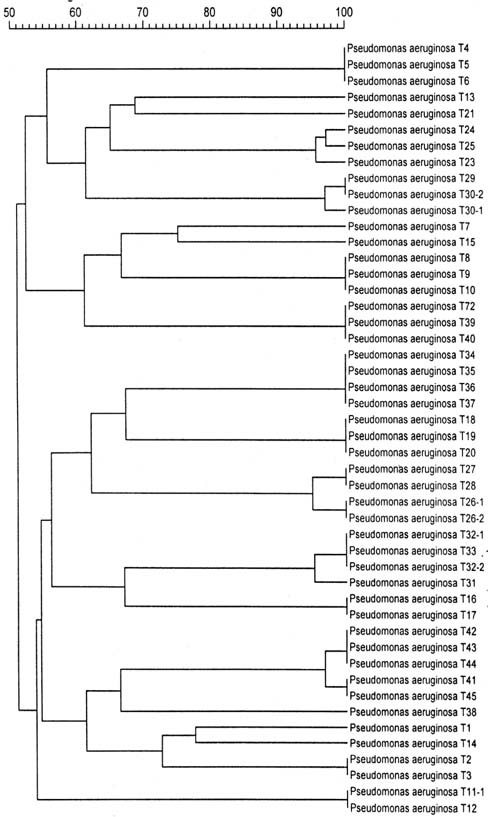
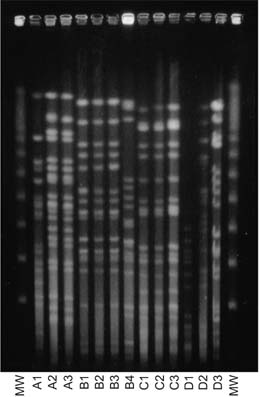
Forty eight cultures from 18 patients with recurrent P. aeruginosa pneumonia from 1998 to 2002 were included in this study. Two or more pairs of sputum cultures were performed during 2 or more different periods of recurrences. The comparison of strains was made according to the phenotypic patterns of antibiotic resistance and chromosomal fingerprinting by pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) using the genomic DNA of P. aeruginosa from the sputum culture.
RESULTS
Phenotypic patterns of antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa were not correlated with their prior antibiotic exposition. Fifteen of 18 patients (83.3%) had recurrent P. aeruginosa pneumonia caused by the strains with same PFGE pattern.
CONCLUSION
These data suggest that the most of the recurrent P. aeruginosa infections in chronic lung disease occurred due to the relapse of prior infections. Further investigations should be performed for assessing the molecular mechanisms of the persistent colonization and for determining how to eradicate clonal persistence of P. aeruginosa.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dowling RB, Wilson R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory infections. Clin Pulm Med. 1999; 6:278–286.2. Hilf M, Yu VL, Sharp J, Zuravleff JJ, Korvick JA, Muder RR. Antibiotic therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: outcome correlations in a prospective study of 200 patients. Am J Med. 1989; 87:540–546.3. Moss RB, Wunderink RG. Strategies for drug therapy in treating Pseudomonas infection. J Respir Dis. 1996; 17:806–809.4. Fink MP, Snydman DR, Niederman MS, Leeper KV Jr, Johnson RH, Heard SO, et al. The Severe Pneumonia Study Group. Treatment of severe pneumonia in hospitalized patients: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial comparing intravenous ciprofloxacin with imipenem-cilastatin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994; 38:547–557.5. Rello J, Mariscal D, March F, Jubert P, Sanchez F, Valles J, et al. Recurrent Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in ventilated patients: relapse or reinfection? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157(3 Pt 1):912–916.6. Talon D, Capellier G, Boillot A, Michel-Briand Y. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as an epidemiologic tool during an outbreak of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in an intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 1995; 21:996–1002.7. Silver DR, Cohen IL, Weinberg PF. Recurrent Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in an intensive care unit. Chest. 1992; 101:194–198.8. Crouch Brewer S, Wunderink RG, Jones CB, Leeper KV Jr. Ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chest. 1996; 109:1019–1029.9. Boukadida J, De Montalembert M, Lenoir G, Scheinmann P, Veron M, Berche P. Molecular epidemiology of chronic pulmonary colonisation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. J Med Microbiol. 1993; 38:29–33.10. Doring G, Horz M, Ortelt J, Grupp H, Wolz C. Molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an intensive care unit. Epidemiol Infect. 1993; 110:427–436.11. Poh CL, Yeo CC, Tay L. Genome fingerprinting by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and ribotyping to differentiate Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype O11 strains. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992; 11:817–822.12. Kirschke DL, Jones TF, Craig AS, Chu PS, Mayernick GG, Patel JA, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens contamination associated with a manufacturing defect in bronchoscopes. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:214–220.13. Spencker FB, Haupt S, Claros MC, Walter S, Lietz T, Schille R, et al. Epidemiologic characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2000; 6:600–607.14. Poh CL, Yeo CC. Recent advances in typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Hosp Infect. 1993; 24:175–181.15. Renders N, Romling Y, Verbrugh H, van Belkum A. Comparative typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by random amplification of polymorphic DNA or pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA macrorestriction fragments. J Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:3190–3195.16. Niederman MS, Ferranti RD, Zeigler A, Merrill WW, Reynolds HY. Respiratory infection complicating long-term tracheostomy. The implication of persistent gram-negative tracheobronchial colonization. Chest. 1984; 85:39–44.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Approach to a vaccine against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- A Case of Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Healthy Adult
- Overexpression of Efflux Pump in Multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: How You Will Discover and Treat It?
- Effect of pseudomonas aeruginosa infection on production of IL-2 and IL-6, and other parameters of immunocompetency in mice
- Activity of cefepime against enterobacter cloacae, serratin marcesc- ens, pseudomonas aeruginosa and other aerobic gram-negative bacilli