Tuberc Respir Dis.
2013 Mar;74(3):129-133.
Repeated Favorable Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in a Case of Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Lung and Esophageal Cancer Clinic, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea. droij@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
Abstract
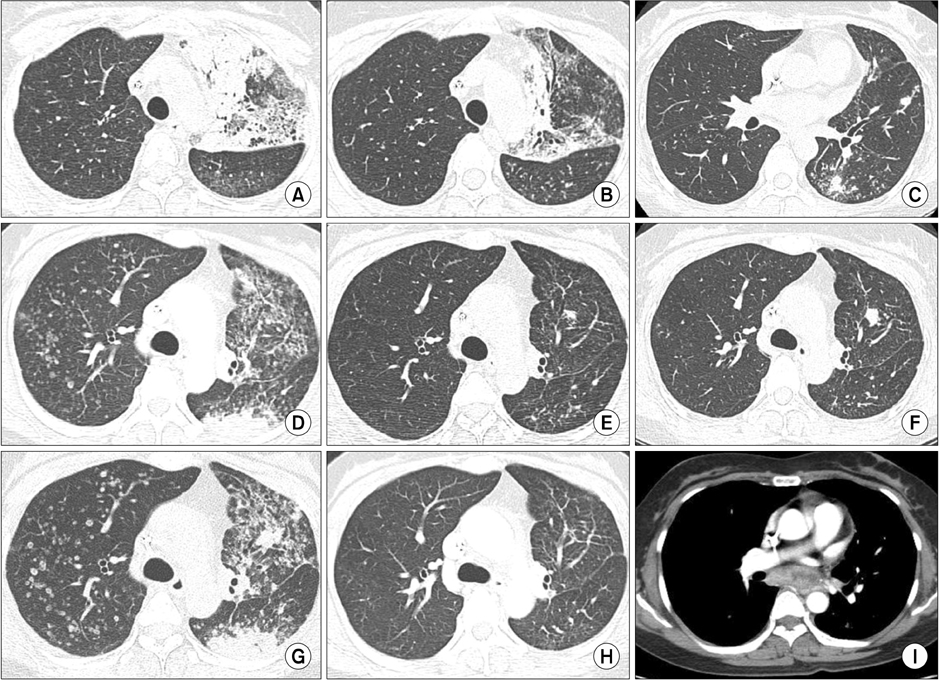
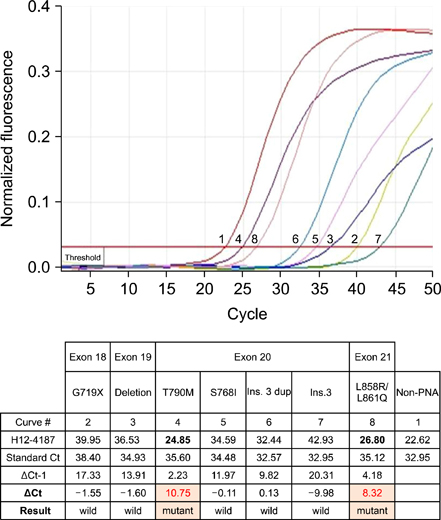
- The presence of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation is a prognostic and predictive marker for EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy. However, inevitably, relapse occurs due to the development of acquired resistance, such as T790M mutation. We report a case of repeated responses to EGFR-TKIs in a never-smoked woman with adenocarcinoma. After six cycles of gemcitabine and cisplatin, the patient was treated by gefitinib for 4 months until progression. Following the six cycles of third-line pemetrexed, gefitinib retreatment was initiated and continued with a partial response for 6 months. After progression, she was recruited for an irreversible EGFR inhibitor trial, and the time to progression was 11 months. Although EGFR direct sequencing on the initial diagnostic specimen revealed a wild-type, we performed a rebiopsy from the progressed subcarinal node at the end of the trial. The result of peptide nucleic acid clamping showed L858R/L861Q.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma
Cisplatin
Constriction
Deoxycytidine
Epidermal Growth Factor
Female
Glutamates
Guanine
Humans
Lung
Lung Neoplasms
Phosphotransferases
Quinazolines
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Recurrence
Retreatment
Pemetrexed
Adenocarcinoma
Cisplatin
Deoxycytidine
Epidermal Growth Factor
Glutamates
Guanine
Lung Neoplasms
Phosphotransferases
Quinazolines
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim KS, Jeong JY, Kim YC, Na KJ, Kim YH, Ahn SJ, et al. Predictors of the response to gefitinib in refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11:2244–2251.2. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2129–2139.3. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:947–957.4. Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S, Costa DB. Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. 10:281–289.5. Kim HJ, Lee KY, Kim YC, Kim KS, Lee SY, Jang TW, et al. Detection and comparison of peptide nucleic acid-mediated real-time polymerase chain reaction clamping and direct gene sequencing for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012. 75:321–325.6. Oh IJ, Ban HJ, Kim KS, Kim YC. Retreatment of gefitinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who previously controlled to gefitinib: a single-arm, open-label, phase II study. Lung Cancer. 2012. 77:121–127.7. Watanabe S, Tanaka J, Ota T, Kondo R, Tanaka H, Kagamu H, et al. Clinical responses to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor retreatment in non-small cell lung cancer patients who benefited from prior effective gefitinib therapy: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer. 2011. 11:1.8. Yokouchi H, Yamazaki K, Kinoshita I, Konishi J, Asahina H, Sukoh N, et al. Clinical benefit of readministration of gefitinib for initial gefitinib-responders with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007. 7:51.9. Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Gale CM, Lifshits E, Gonzales AJ, Shimamura T, et al. PF00299804, an irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor, is effective in lung cancer models with EGFR and ERBB2 mutations that are resistant to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007. 67:11924–11932.10. Miller VA, Hirsh V, Cadranel J, Chen YM, Park K, Kim SW, et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): a phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012. 13:528–538.11. Doebele RC, Oton AB, Peled N, Camidge DR, Bunn PA Jr. New strategies to overcome limitations of reversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010. 69:1–12.12. Ercan D, Zejnullahu K, Yonesaka K, Xiao Y, Capelletti M, Rogers A, et al. Amplification of EGFR T790M causes resistance to an irreversible EGFR inhibitor. Oncogene. 2010. 29:2346–2356.13. Han HS, Lim SN, An JY, Lee KM, Choe KH, Lee KH, et al. Detection of EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma specimens with different proportions of tumor cells using two methods of differential sensitivity. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. 7:355–364.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance: Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors
- Mechanisms of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance and Strategies to Overcome Resistance in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Successful Rechallenge with Gefitinib for an Initial Erlotinib-Responder with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
- A Case of Favorable Responses after Gefitinib in a Patient with EGFR Mutated Adenosquamous Lung Carcinoma
- Does the efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor differ according to the type of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer?