Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Oct;71(4):286-290.
Successful Rechallenge with Gefitinib for an Initial Erlotinib-Responder with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jinhwalee@ewha.ac.kr
Abstract
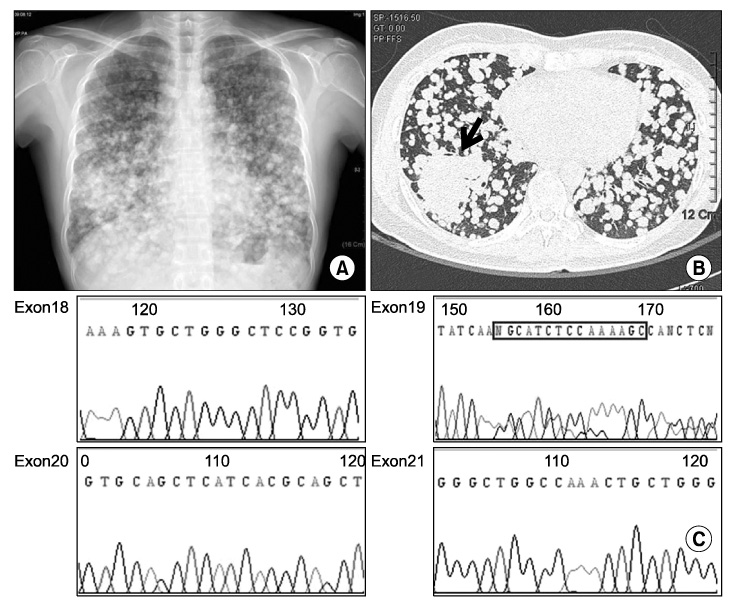
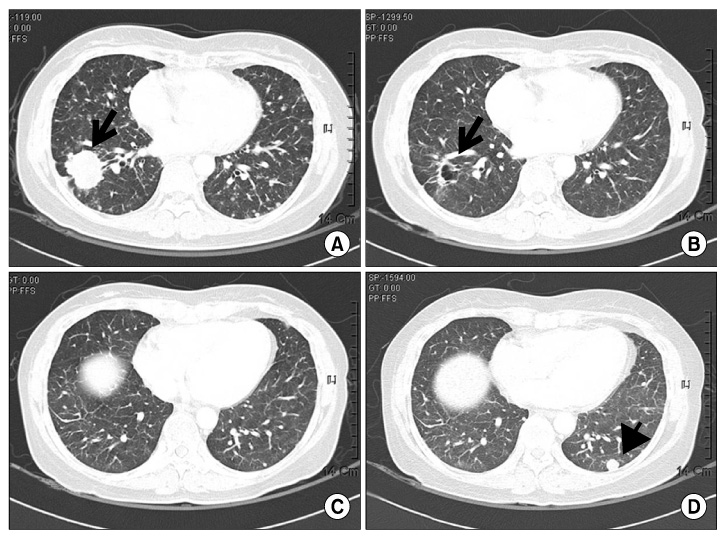
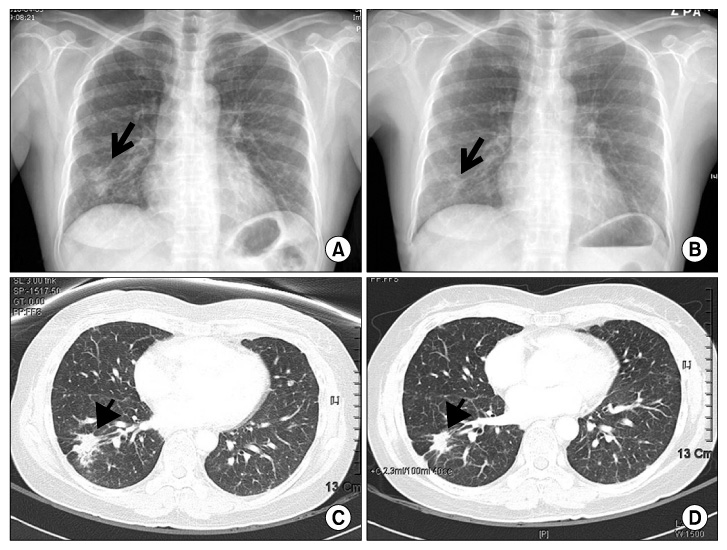
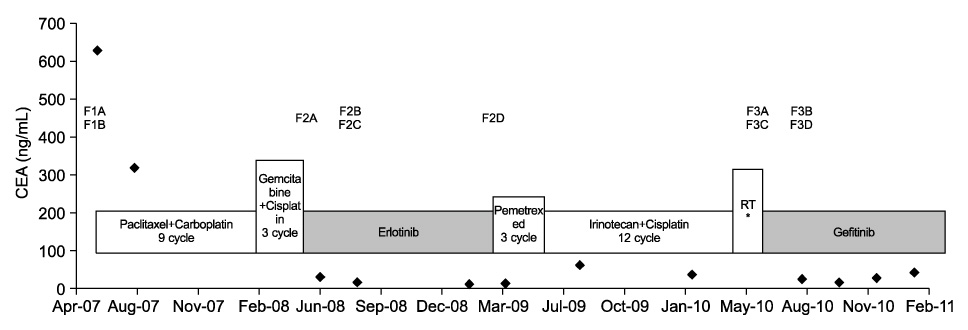
- Although failure of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKI) is generally believed to be associated with cross-resistance to other EGFR TKI, the benefit of administering erlotinib as a second EGFR TKI after resistance of gefitinib as the first TKI has been well known. However, good response to gefitinib after an initial response to erlotinib has been rare. We report that a 45-year-old woman (never smoked), with lung adenocarcinoma and EGFR mutation, showed an initial response to erlotinib, and then responded to gefitinib again.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor under-lying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2129–2139.2. Cho BC, Im CK, Park MS, Kim SK, Chang J, Park JP, et al. Phase II study of erlotinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:2528–2533.3. Wong AS, Soong R, Seah SB, Lim SW, Chuah KL, Nga ME, et al. Evidence for disease control with erlotinib after gefitinib failure in typical gefitinib-sensitive Asian patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. 3:400–404.4. Chang JW, Chou CL, Huang SF, Wang HM, Hsieh JJ, Hsu T, et al. Erlotinib response of EGFR-mutant gefitinib-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2007. 58:414–417.5. Gridelli C, Maione P, Galetta D, Colantuoni G, Del Gaizo F, Ferrara C, et al. Three cases of long-lasting tumor control with erlotinib after progression with gefitinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2007. 2:758–761.6. Kim HK, Ahn MI, Yoo J, Kim CH, Yang HJ, Shim BY. Sequential responses of adenocarcinoma of the lung to erlotinib after gefitinib in never smoker Korean woman. Cancer Res Treat. 2007. 39:37–39.7. Wong AS, Seto KY, Chin TM, Soo RA. Lung cancer response to gefitinib, then erlotinib, then gefitinib again. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. 3:1077–1078.8. Wu SG, Shih JY, Yu CJ, Yang PC. Lung adenocarcinoma with good response to erlotinib after gefitinib treatment failure and acquired T790M mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. 3:451–452.9. Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:786–792.10. Viswanathan A, Pillot G, Govindan R. Lack of response to erlotinib after progression on gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2005. 50:417–418.11. Fukui T, Otani S, Hataishi R, Jiang SX, Nishii Y, Igawa S, et al. Successful rechallenge with erlotinib in a patient with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma who developed gefitinib-related interstitial lung disease. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. 65:803–806.12. Yokouchi H, Yamazaki K, Kinoshita I, Konishi J, Asahina H, Sukoh N, et al. Clinical benefit of read-ministration of gefitinib for initial gefitinib-responders with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007. 7:51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sequential Responses of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung to Erlotinib after Gefitinib in Never Smoker Korean Woman
- Comparison of the therapeutic outcome between gefitinib and erlotinib in female patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
- Comparison of Gefitinib and Erlotinib for Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- Clinical efficacy of erlotinib, a salvage treatment for non-small cell lung cancer patients following gefitinib failure
- Erlotinib-Related Spontaneous Pneumothorax in Patient with Primary Lung Cancer