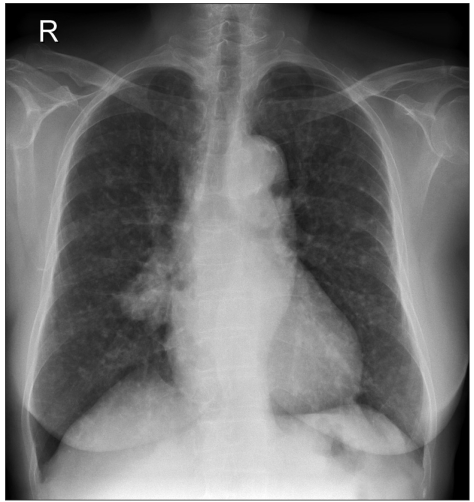
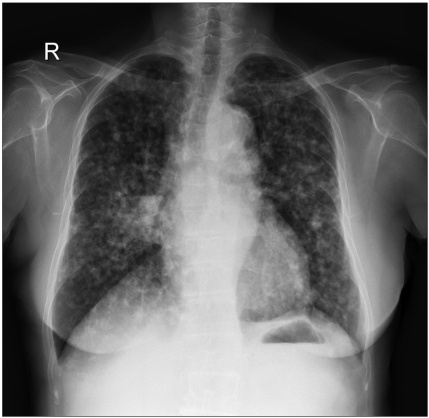
Cancer Res Treat.
2007 Mar;39(1):37-39.
Sequential Responses of Adenocarcinoma of the Lung to Erlotinib after Gefitinib in Never Smoker Korean Woman
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea. chihongk@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
Abstract
- A patient with adenocarcinoma of the lung was treated sequentially using two kinds of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, gefitinib and erlotinib. The patient was a 73-year-old female who received gefitinib as a second line treatment, which resulted in a partial response with response duration of 6 months. After progression of the disease, the patient received erlotinib, which resulted in partial response again with response duration of 11.5 months. This observation suggests that treatment with erlotinib may be effective in patients who develop progressive disease after a primary treatment with gefitinib following an initial response.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thatcher N, Chang A, Parikh P, Pereira JR, Ciuleanu T, von Pawel J, et al. Gefitinib plus best supportive care in previously treated patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer:results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicentre study (Iressa Survival Evaluation in Lung Cancer). Lancet. 2005; 366:1527–1537. PMID: 16257339.2. Han SW, Kim TY, Hwang PG, Jeong S, Kim J, Choi IS, et al. Predictive and prognostic impact of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:2493–2501. PMID: 15710947.
Article3. Lee DH, Han JY, Lee HG, Lee JJ, Lee EK, Kim HY, et al. Gefitinib as a first-line therapy of advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the lung in never-smokers. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:3032–3037. PMID: 15837758.
Article4. Shepherd FA, Pereira JR, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated nonsmall-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:123–132. PMID: 16014882.
Article5. Viswanathan A, Pillot G, Govindan R. Lack of response to erlotinib after progression on gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2005; 50:417–418. PMID: 16129510.
Article6. Garfield DH. Response to Erlotinib after failure of Gefitinib in a patient with advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:7738–7740. PMID: 16234533.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Rechallenge with Gefitinib for an Initial Erlotinib-Responder with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Comparison of the therapeutic outcome between gefitinib and erlotinib in female patients with non-small-cell lung cancer
- A Case of Gefitinib (Iressa(R))-associated Tumor Lysis Syndrome in Adenocarcinoma of the Lung
- Comparison of Gefitinib and Erlotinib for Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- Clinical efficacy of erlotinib, a salvage treatment for non-small cell lung cancer patients following gefitinib failure