Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Jan;72(1):93-97.
A Case of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage with Glomerulonephritis after Propylthiouracil Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea. kangkw9@naver.com
Abstract
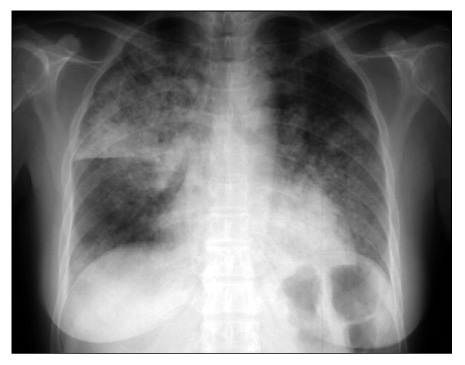
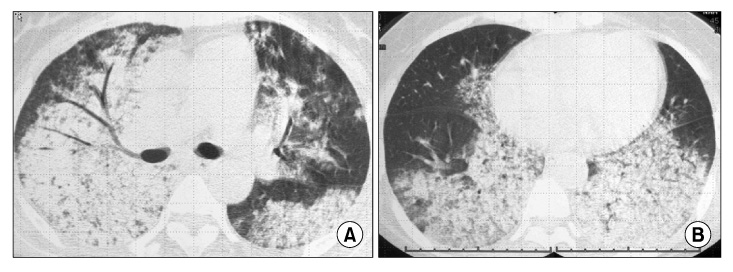
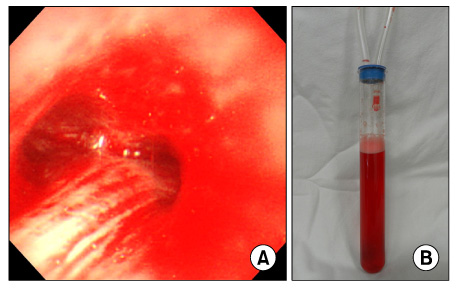
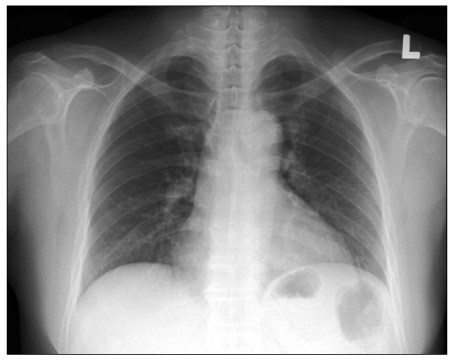
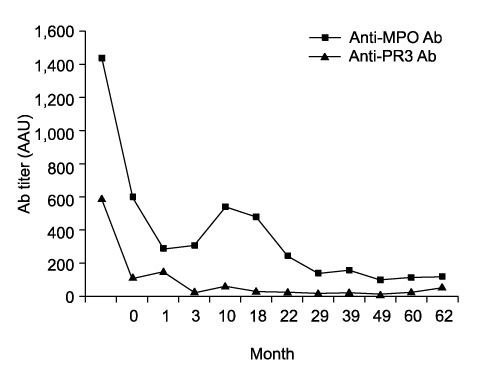
- Propylthiouracil (PTU) is one of the most common drugs used in the treatment of Graves' disease. There are a number of side effects found with PTU use including fever, rash, arthralgia, and flu-like symptoms. Recently antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) positive vasculitis after PTU treatment was reported as a rare side effect, which can cause diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and glomerulonephritis. A 45-year-old woman with Graves' disease had been treated with PTU for five months, complained of hemoptysis due to pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage causing anemia, and also had hematuria. Simple chest X-ray and HRCT showed bilateral consolidation and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid revealed alveolar hemorrhage. A serologic test was positive for ANCA against myeloperoxidase and proteinase-3. Such findings suggested that the presence of PTU induced ANCA positive vasculitis. Cessation of PTU and the administration of high dose steroids improved the clinical manifestation, radiologic and serologic findings. We observed ANCA titer serially for 6 years. During the follow up period, ANCA titer decreased slowly and stayed within the acceptable upper normal limit.
MeSH Terms
-
Anemia
Antibodies, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic
Arthralgia
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
Exanthema
Female
Fever
Follow-Up Studies
Glomerulonephritis
Graves Disease
Hematuria
Hemoptysis
Hemorrhage
Humans
Middle Aged
Peroxidase
Propylthiouracil
Serologic Tests
Steroids
Thorax
Vasculitis
Antibodies, Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic
Peroxidase
Propylthiouracil
Steroids
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SY, Jung JY, Lee KJ, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Lee EJ, et al. A case of propylthiouracil induced diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 58:78–82.2. Sun DS, Kim DK, Lee HJ, Lee HY, Kim DJ, Kim ES, et al. A case of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) positive, propylthiouracil-induced diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in Graves' disease. J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007. 22:215–219.3. Park YK, Yun YW, Sung SS, Park US, Park SH, Woo JH, et al. Propylthiouracil-associated p-ANCA positive vasculitis with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Korean J Nephrol. 2004. 23:997–1003.4. Kim JH, Kim HW, Jang EC, Jung WR, Ko SH, Shin YS, et al. A case of ANCA-positive crescentic glomerulonephritis after propylthiouracil treatment in Graves' disease. Korean J Nephrol. 2005. 24:305–312.5. Dolman KM, Gans RO, Vervaat TJ, Zevenbergen G, Maingay D, Nikkels RE, et al. Vasculitis and antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies associated with propylthiouracil therapy. Lancet. 1993. 342:651–652.6. Gunton JE, Stiel J, Caterson RJ, McElduff A. Clinical case seminar: Anti-thyroid drugs and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positive vasculitis. A case report and review of the literature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:13–16.7. Fujieda M, Hattori M, Kurayama H, Koitabashi Y. Members and Coworkers of the Japanese Society for Pediatric Nephrology. Clinical features and outcomes in children with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-positive glomerulonephritis associated with propylthiouracil treatment. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002. 13:437–445.8. Dhillon SS, Singh D, Doe N, Qadri AM, Ricciardi S, Schwarz MI. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and pulmonary capillaritis due to propylthiouracil. Chest. 1999. 116:1485–1488.9. Jiang X, Khursigara G, Rubin RL. Transformation of lupus-inducing drugs to cytotoxic products by activated neutrophils. Science. 1994. 266:810–813.10. Harper L, Cockwell P, Savage CO. Case of propylthiouracil-induced ANCA associated small vessel vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998. 13:455–458.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Propylthiouracil Induced Diffuse Pulmonary Hemorrhage
- Propylthiouracil-Induced ANCA-Positive Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Patient with Thyroid Storm
- A Case of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA) Positive, Propylthiouracil-Induced Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Graves' Disease
- Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Associated with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody levels in a Pregnant Woman Taking Propylthiouracil
- A Case of Microscopic Polyangiitis Presenting As Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage