Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 Aug;69(2):115-118.
A Case of Ischemic Colitis Associated with Paclitaxel Loaded Polymeric Micelle (Genexol-PM(R)) Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. cyberkks@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
Abstract
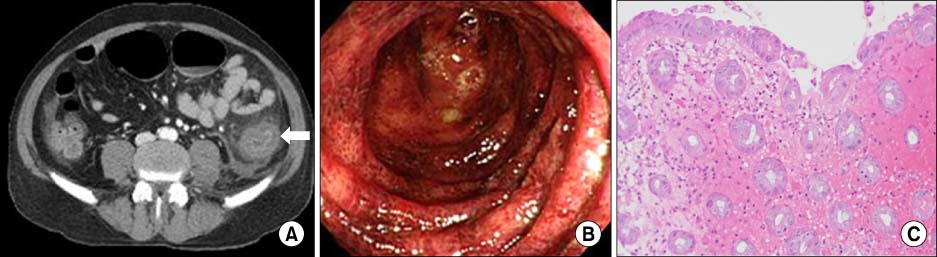
- Paclitaxel has been widely used for treating many solid tumors. Although colonic toxicity is an unusual complication of paclitaxel-based chemotherapy, the reported toxicities include pseudomembranous colitis, neutropenic enterocolitis and on rare occasions ischemic colitis. Genexol-PM(R), which is a recently developed cremophor-free, polymeric micelle-formulated paclitaxel, has shown a more potent antitumor effect because it can increase the usual dose of paclitaxel due to that Genexol-PM(R) does not include the toxic cremophor compound. We report here on a case of a 57-year-old man with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and who developed ischemic colitis after chemotherapy with Genexol-PM(R) and cisplatin. He complained of hematochezia with abdominal pain on the left lower quadrant. Colonoscopy revealed diffuse mucosal hemorrhage and edema from the sigmoid colon to the splenic flexure. After bowel rest, he recovered from his symptoms and the follow-up colonoscopic findings showed that the mucosa was healing. Since then, he was treated with pemetrexed monotherapy instead of a paclitaxel compound and platinum.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abdominal Pain
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Cisplatin
Colitis, Ischemic
Colon
Colon, Sigmoid
Colon, Transverse
Colonoscopy
Edema
Enterocolitis, Neutropenic
Enterocolitis, Pseudomembranous
Follow-Up Studies
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
Glutamates
Guanine
Hemorrhage
Humans
Middle Aged
Mucous Membrane
Paclitaxel
Platinum
Polyethylene Glycols
Polymers
Pemetrexed
Cisplatin
Glutamates
Guanine
Paclitaxel
Platinum
Polyethylene Glycols
Polymers
Figure
Reference
-
1. Johnson DH, Paul DM, Hande KR, Shyr Y, Blanke C, Murphy B, et al. Paclitaxel plus carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol. 1996. 14:2054–2060.2. Tashiro M, Yoshikawa I, Kume K, Otsuki M. Ischemic colitis associated with paclitaxel and carboplatin chemotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98:231–232.3. Kim TY, Kim DW, Chung JY, Shin SG, Kim SC, Heo DS, et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of Genexol-PM, a cremophor-free, polymeric micelle-formulated paclitaxel, in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:3708–3716.4. Kim DW, Kim SY, Kim HK, Kim SW, Shin SW, Kim JS, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of Genexol-PM, a novel Cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel, with cisplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007. 18:2009–2014.5. Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A. Cremophor EL: the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer. 2001. 37:1590–1598.6. Kim SC, Kim DW, Shim YH, Bang JS, Oh HS, Wan Kim S, et al. In vivo evaluation of polymeric micellar paclitaxel formulation: toxicity and efficacy. J Control Release. 2001. 72:191–202.7. Sreenarasimhaiah J. Diagnosis and management of ischemic colitis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2005. 7:421–426.8. Seewaldt VL, Cain JM, Goff BA, Tamimi H, Greer B, Figge D. A retrospective review of paclitaxel-associated gastrointestinal necrosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1997. 67:137–140.9. Sollott SJ, Cheng L, Pauly RR, Jenkins GM, Monticone RE, Kuzuya M, et al. Taxol inhibits neointimal smooth muscle cell accumulation after angioplasty in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1995. 95:1869–1876.10. Klauber N, Parangi S, Flynn E, Hamel E, D'Amato RJ. Inhibition of angiogenesis and breast cancer in mice by the microtubule inhibitors 2-methoxyestradiol and taxol. Cancer Res. 1997. 57:81–86.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Safety and Tolerability of Weekly Genexol-PM, a Cremophor-Free Polymeric Micelle Formulation of Paclitaxel, with Carboplatin in Gynecologic Cancer: A Phase I Study
- An Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel, Phase III Trial Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Polymeric Micelle-Formulated Paclitaxel Compared to Conventional Cremophor EL-Based Paclitaxel for Recurrent or Metastatic HER2-Negative Breast Cancer
- Cost-Effectiveness of Genexol-PM for Treating Metastatic Breast Cancer
- An Open-Label, Randomized, Parallel, Phase II Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Cremophor-Free Polymeric Micelle Formulation of Paclitaxel as First-Line Treatment for Ovarian Cancer: A Korean Gynecologic Oncology Group Study (KGOG-3021)
- Non-convulsive seizure related to Cremophor ELâ„¢-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel: a case report