Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 May;68(5):259-266.
Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Factors in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Admitted to Intensive Care Units
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdlee@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), requiring the intensive care unit (ICU) care, has been a high-mortality condition until now. In the present study, we aimed to investigate clinical features and parameters associated with TB mortality.
METHODS
From August 2003 to December 2008, patients with microbiologically or histologically confirmed pulmonary TB then admitted to the ICU, were retrospectively enrolled into the study. Upon enrollment, their medical records were reviewed.
RESULTS
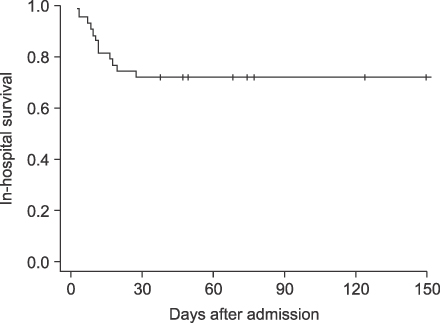
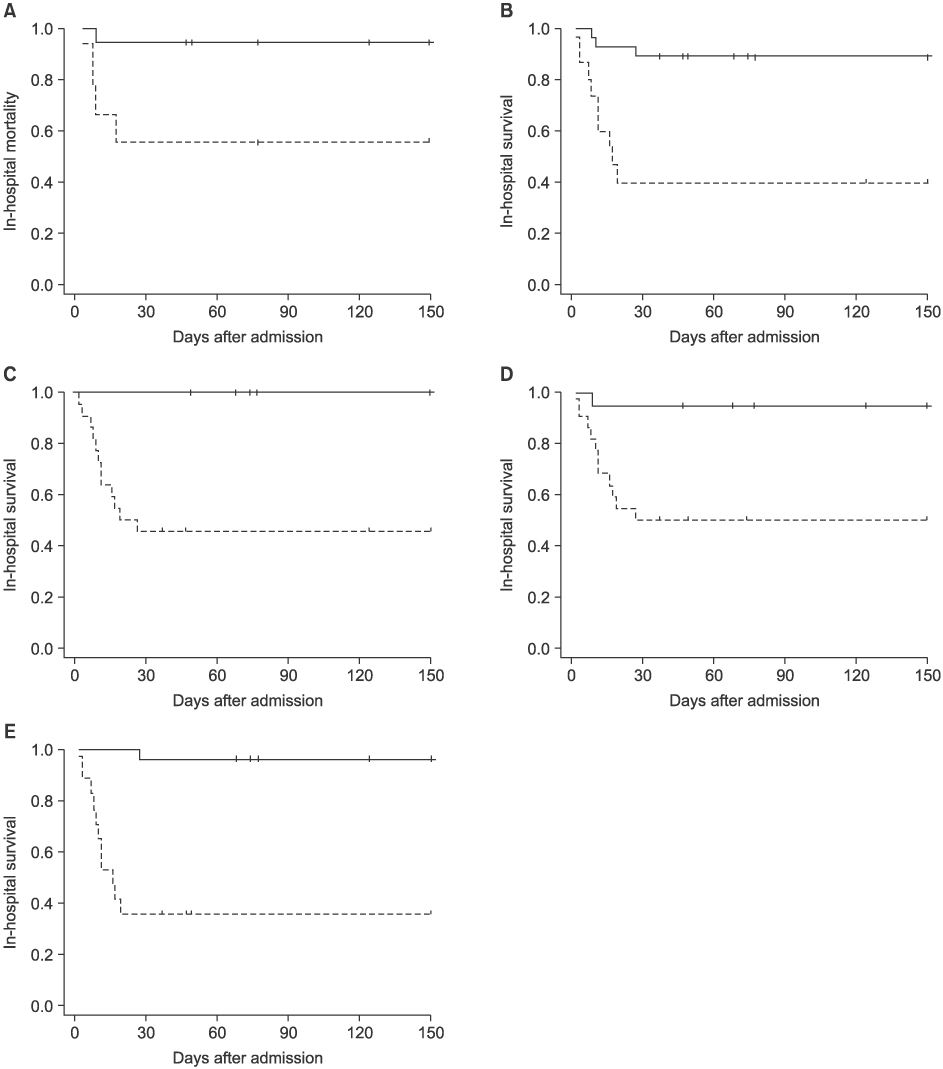
Forty three patients (30 males, 13 females) were included and their mean age was 63.8 years (range: 17~87 years). Twelve patients died, an overall in-hospital mortality of 27.8%. The main reason for the ICU care was dyspnea or hypoxemia requiring mechanical ventilation (n=17). Other diagnoses for ICU care were hemoptysis, monitoring after procedures, neurologic dysfunction, shock, and gastrointestinal bleeding. On univariate analysis, the factors affecting the mortality were malnutrition-related parameters including low body mass index, hypoalbuminemia, lymphocytopenia, and hypocholersterolemia, as well as severity-related variables such as high acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE) score, number of involved lobes, and high C-reactive protein. In addition, respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation and acute respiratory distress syndrome contributed to patient fatality. It was shown on multivariate analysis that respiratory failure and hypoalbuminemia were significantly independent variables associated with the mortality.
CONCLUSION
Acute respiratory failure is the most common reason for the ICU care and also the most important factor in predicting poor outcome. In addition, our data suggest that the parameters associated with malnutrition could be possible factors contributing to mortality.
MeSH Terms
-
Anoxia
APACHE
Body Mass Index
C-Reactive Protein
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Hemorrhage
Hospital Mortality
Humans
Hypoalbuminemia
Critical Care
Intensive Care Units
Lymphopenia
Male
Malnutrition
Medical Records
Multivariate Analysis
Neurologic Manifestations
Nutritional Status
Respiration, Artificial
Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Adult
Respiratory Insufficiency
Retrospective Studies
Shock
Tuberculosis, Pulmonary
C-Reactive Protein
Figure
Reference
-
1. Männle C, Wiedemann K, Ruchalla E. The incidence of tuberculosis at an intensive care unit. Anasth Intensivther Notfallmed. 1989. 24:334–340.2. Frame RN, Johnson MC, Eichenhorn MS, Bower GC, Popovich J Jr. Active tuberculosis in the medical intensive care unit: a 15-year retrospective analysis. Crit Care Med. 1987. 15:1012–1014.3. Zahar JR, Azoulay E, Klement E, De Lassence A, Lucet JC, Regnier B, et al. Delayed treatment contributes to mortality in ICU patients with severe active pulmonary tuberculosis and acute respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med. 2001. 27:513–520.4. Lee PL, Jerng JS, Chang YL, Chen CF, Hsueh PR, Yu CJ, et al. Patient mortality of active pulmonary tuberculosis requiring mechanical ventilation. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:141–147.5. Erbes R, Oettel K, Raffenberg M, Mauch H, Schmidt-Ioanas M, Lode H. Characteristics and outcome of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis requiring intensive care. Eur Respir J. 2006. 27:1223–1228.6. Lin SM, Wang TY, Liu WT, Chang CC, Lin HC, Liu CY, et al. Predictive factors for mortality among non-HIV-infected patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and respiratory failure. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009. 13:335–340.7. Cegielski JP, McMurray DN. The relationship between malnutrition and tuberculosis: evidence from studies in humans and experimental animals. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004. 8:286–298.8. Ryu YJ, Koh WJ, Kang EH, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kim H, et al. Prognostic factors in pulmonary tuberculosis requiring mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory failure. Respirology. 2007. 12:406–411.9. Park JH, Na JO, Kim EK, Lim CM, Shim TS, Lee SD, et al. The prognosis of respiratory failure in patients with tuberculous destroyed lung. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001. 5:963–967.10. Confalonieri M, Potena A, Carbone G, Porta RD, Tolley EA, Umberto Meduri G. Acute respiratory failure in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia: a prospective randomized evaluation of noninvasive ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:1585–1591.11. Lin SM, Huang CD, Lin HC, Liu CY, Wang CH, Kuo HP. A modified goal-directed protocol improves clinical outcomes in intensive care unit patients with septic shock: a randomized controlled trial. Shock. 2006. 26:551–557.12. Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med. 2003. 31:1250–1256.13. Kim YJ, Pack KM, Jeong E, Na JO, Oh YM, Lee SD, et al. Pulmonary tuberculosis with acute respiratory failure. Eur Respir J. 2008. 32:1625–1630.14. Rao VK, Iademarco EP, Fraser VJ, Kollef MH. The impact of comorbidity on mortality following in-hospital diagnosis of tuberculosis. Chest. 1998. 114:1244–1252.15. Penner C, Roberts D, Kunimoto D, Manfreda J, Long R. Tuberculosis as a primary cause of respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:867–872.16. Hopewell PC. Mason RJ, Courtney Broaddus V, Murrary JF, Nadel JA, editors. Chapter 33. Tuberculosis and other mycobacterial diseases. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, Inc.;998.17. Scrimshaw NS, SanGiovanni JP. Synergism of nutrition, infection, and immunity: an overview. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997. 66:464S–477S.18. Yoneda T. Relation between malnutrition and cell-mediated immunity in pulmonary tuberculosis. Kekkaku. 1989. 64:633–640.19. Madebo T, Nysaeter G, Lindtjørn B. HIV infection and malnutrition change the clinical and radiological features of pulmonary tuberculosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1997. 29:355–359.20. Shin SR, Kim CH, Kim SE, Park YB, Lee JY, Mo EK, et al. Predictors on in-hospital mortality following in-hospital diagnosis of tuberculosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006. 61:233–238.21. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985. 13:818–829.22. Del Bufalo C, Morelli A, Bassein L, Fasano L, Quarta CC, Pacilli AM, et al. Severity scores in respiratory intensive care: APACHE II predicted mortality better than SAPS II. Respir Care. 1995. 40:1042–1047.23. Lee JH, Ryu YJ, Chun EM, Chang JH. Outcomes and prognostic factors for severe community-acquired pneumonia that requires mechanical ventilation. Korean J Intern Med. 2007. 22:157–163.24. Afessa B, Morales IJ, Scanlon PD, Peters SG. Prognostic factors, clinical course, and hospital outcome of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease admitted to an intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:1610–1615.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Severe Sepsis in Patients Who Were Admitted to a Medical Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital
- Rehabilitation in Intensive Care Unit
- The Authors Reply: Should Very Old Patients Be Admitted to the Intensive Care Units?
- Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Admitted to Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Differences between Patients with TB-Destroyed Lung and Patients with COPD Admitted to the ICU