Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Mar;15(1):38-43.
Plasma Real Time-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction of Epstein-Barr Virus in Immunocompetent Patients with Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea. khm9120@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) hepatitis is a usually asymptomatic and self-limiting disease in immunocompetent patients. However, the range of severity is wide, and the serological diagnosis is typically difficult until the convalescent phase. Thus, we examined the value of plasma EBV DNA real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) in EBV hepatitis for the timely diagnosis and the relationship between EBV viral load and clinical severity.
METHODS
Sixty samples were confirmed as having EBV infection by RT-qPCR with the EBV BALF5 gene sequence. We examined the clinical characteristics of EBV hepatitis by reviewing medical records.
RESULTS
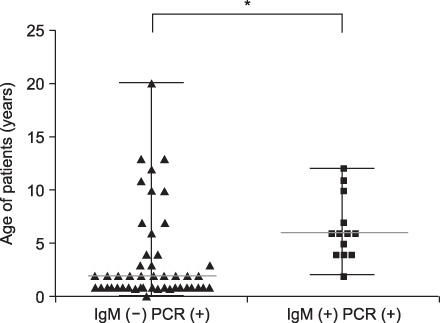
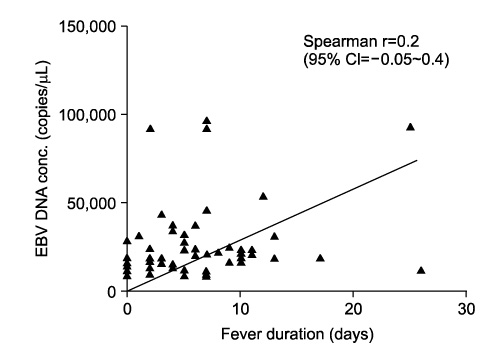
The median total duration of fever was 8 days (range: 0-13 days). The mean peak value of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was 241+/-214 U/L, and the mean peak value of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) was 298+/-312 U/L. There was no correlation between the serum levels of liver enzyme and plasma EBV DNA titer (p=0.1) or between median total duration of fever and EBV DNA titer (p=0.056). The median age of the EBV VCA IgM-negative group was lower compared with the EBV VCA IgM-positive group in EBV hepatitis (2 years vs. 6 years, p=0.0009).
CONCLUSION
The severity of EBV hepatitis does not correlate with circulating EBV DNA load according to our data. Furthermore, we suggest that plasma EBV PCR may be valuable in young infants in whom the results of serology test for EBV infection commonly are negative.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Odumade OA, Hogquist KA, Balfour HH. Progress and problems in understanding and managing primary Epstein-Barr virus infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2011. 24:193–209.
Article2. Kofteridis DP, Koulentaki M, Valachis A, Christofaki M, Mazokopakis E, Papazoglou G, et al. Epstein Barr virus hepatitis. Eur J Intern Med. 2011. 22:73–76.
Article3. Kimura H, Nagasaka T, Hoshino Y, Hayashi N, Tanaka N, Xu JL, et al. Severe hepatitis caused by Epstein-Barr virus without infection of hepatocytes. Hum Pathol. 2001. 32:757–762.
Article4. Palanduz A, Yildirmak Y, Telhan L, Arapoglu M, Urganci N, Tufekci S, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure and autoimmune hemolytic anemia associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Infect. 2002. 45:96–98.
Article5. Cheng CC, Chang LY, Shao PL, Lee PI, Chen JM, Lu CY, et al. Clinical manifestations and quantitative analysis of virus load in Taiwanese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2007. 40:216–221.6. Teramura T, Tabata Y, Yagi T, Morimoto A, Hibi S, Imashuku S. Quantitative analysis of cell-free Epstein-Barr virus genome copy number in patients with EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2002. 43:173–179.
Article7. Kasztelewicz B, Jankowska I, Pawlowska J, Teisseyre J, Grenda R, Pronicki M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and whole blood from pediatric transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011. 13:471–479.
Article8. Baek SH, Kim SY, Koh H. Effect of reactivation of latent Epstein-Barr virus using polymerase chain-reaction on acute hepatitis A in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. 14:59–66.
Article9. Kimura H, Morita M, Yabuta Y, Kuzushima K, Kato K, Kojima S, et al. Quantitative analysis of Epstein-Barr virus load by using a real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:132–136.
Article10. Markin RS. Manifestations of Epstein-Barr virus-associated disorders in liver. Liver. 1994. 14:1–13.
Article11. Petrova M, Kamburov V. Epstein-Barr virus: silent companion or causative agent of chronic liver disease? World J Gastroenterol. 2010. 16:4130–4134.
Article12. Jo DS, Han JH, Kim SY, Kim MS, Yi HK, Lee DY, et al. Changes in the expression of cytokines and apoptosis-related genes in children with infectious mononucleosis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:1348–1357.
Article13. Gulley ML, Tang W. Laboratory assays for Epstein-Barr virus-related disease. J Mol Diagn. 2008. 10:279–292.
Article14. Luderer R, Kok M, Niesters HG, Schuurman R, de Weerdt O, Thijsen SF. Real-time Epstein-Barr virus PCR for the diagnosis of primary EBV infections and EBV reactivation. Mol Diagn. 2005. 9:195–200.
Article15. Pitetti RD, Laus S, Wadowsky RM. Clinical evaluation of a quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction assay for diagnosis of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:736–739.
Article16. Bauer CC, Aberle SW, Popow-Kraupp T, Kapitan M, Hofmann H, Puchhammer-Stockl E. Serum Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Med Virol. 2005. 75:54–58.
Article17. Maurmann S, Fricke L, Wagner HJ, Schlenke P, Hennig H, Steinhoff J, et al. Molecular parameters for precise diagnosis of asymptomatic Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in healthy carriers. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:5419–5428.
Article18. Liu Y, Fang Z, Liu L, Yang S, Zhang L. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in serum or plasma for nasopharyngeal cancer: a meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2011. 15:495–502.
Article19. Hara S, Hoshino Y, Naitou T, Nagano K, Iwai M, Suzuki K, et al. Association of virus infected-t cell in severe hepatitis caused by primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Virol. 2006. 35:250–256.
Article20. Drebber U, Kasper HU, Krupacz J, Haferkamp K, Kern MA, Steffen HM, et al. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in acute and chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol. 2006. 44:879–885.
Article21. Cameron B, Bharadwaj M, Burrows J, Fazou C, Wakefield D, Hickie I, et al. Prolonged illness after infectious mononucleosis is associated with altered immunity but not with increased viral load. J Infect Dis. 2006. 193:664–671.
Article22. Suh N, Liapis H, Misdraji J, Brunt EM, Wang HL. Epstein-Barr virus hepatitis: diagnostic value of in situ hybridization, polymerase chain reaction, and immunohistochemistry on liver biopsy from immunocompetent patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007. 31:1403–1409.
Article23. Yuge A, Kinoshita E, Moriuchi M, Ohno Y, Haga H, Moriuchi H. Persistent hepatitis associated with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. 23:74–76.
Article24. Ma C, Wong CK, Wong BC, Chan KC, Lun SW, Lee N, et al. Cytokine responses in a severe case of glandular fever treated successfully with foscarnet combined with prednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulin. J Med Virol. 2009. 81:99–105.
Article25. Ghosal R, Lewis KE, Chandramouli S. Infectious mononucleosis complicated by acute hepatitis and myocarditis: a response to corticosteroids. BMJ Case Rep. 2009. published on line 10.1136/bcr.10.2008.1083.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Real-time PCR Kits for Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Assays
- A Case of Epstein Barr Virus-Associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome Confirmed by mRNA In Situ Hybridization and Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Several Cases of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Hepatitis
- Effects of Reactivation of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus Using Polymerase Chain Reaction on Acute Hepatitis A in Children
- Quantifing the Circulating Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) DNA to Monitor a Case of Aggressive Natural Killer Cell Leukemia