Lab Med Online.
2016 Jan;6(1):31-35. 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.1.31.
Evaluation of Real-time PCR Kits for Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Assays
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimhs54@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Health Insurance Corporation, Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2312289
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2016.6.1.31
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is known to be the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis and EBV-related malignancies. In this study, we compared the results of three real-time PCR kits for EBV DNA assays.
METHODS
A total of 300 whole blood samples submitted for quantitative EBV PCR between January 2013 and September 2014 at Severance Hospital were included. The samples were tested by using the Artus EBV RG PCR Kit (Qiagen, Germany), AccuPower EBV Quantitative PCR Kit (Bioneer, Korea), and Real-Q EBV Kit (BioSewoom, Korea). Samples with discordant results between the three kits were confirmed by direct sequencing.
RESULTS
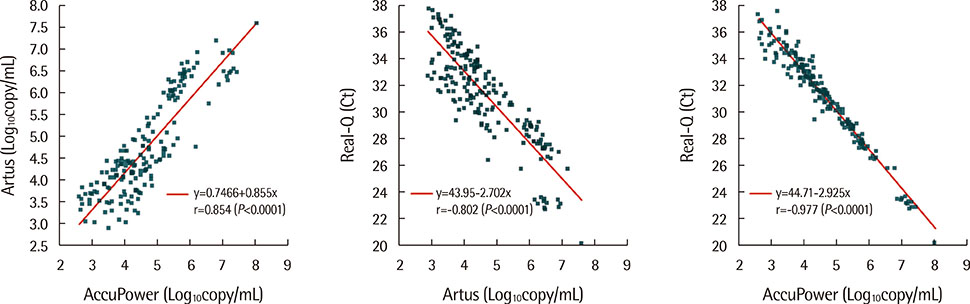
The result concordance rate and kappa coefficient (K) were 86.3% and 0.69 for Artus-AccuPower, 93.3% and 0.85 for Artus-Real-Q, and 92.3% and 0.83 for AccuPower-Real-Q, respectively. The correlations between the three kits were found to be significant, with a correlation coefficient of r=0.854 for Artus-AccuPower, -0.802 for Artus-Real-Q, and -0.977 for AccuPower-Real-Q, respectively (P<0.0001). If the real-time PCR concordant results of 258 samples and the direct sequencing results of 42 real-time PCR discordant samples were assumed to be true, the sensitivity/specificity values were 0.921/0.976 for Artus, 0.902/0.965 for AccuPower, and 0.967/1.000 for Real-Q.
CONCLUSIONS
The three real-time PCR kits showed excellent sensitivities and specificities. All these kits would be acceptable for clinical and therapeutic management of EBV. However, some discordant results between the kits indicate the need for caution in clinical diagnosis and staging. Further implementation of standardized methodology would be needed for EBV DNA assays.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus Particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 1964; 1:702–703.
Article2. Young LS, Murray PG. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene. 2003; 22:5108–5121.
Article3. Rooney CM, Loftin SK, Holladay MS, Brenner MK, Krance RA, Heslop HE. Early identification of Epstein-Barr virus-associated post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disease. Br J Haematol. 1995; 89:98–103.
Article4. James JA, Neas BR, Moser KL, Hall T, Bruner GR, Sestak AL, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in adults is associated with previous Epstein-Barr virus exposure. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44:1122–1126.
Article5. Chung JL, Kim HS. Clinical usefulness of EBV-specific antibody panel test and PCR genotyping in the diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infection. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000; 20:320–329.6. Rowe DT, Webber S, Schauer EM, Reyes J, Green M. Epstein-Barr virus load monitoring: its role in the prevention and management of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Transpl Infect Dis. 2001; 3:79–87.
Article7. Cinque P, Brytting M, Wahren B, Linde A, Castagna A, Lazzarin A, et al. Epstein-Barr virus DNA in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with AIDS-related primary lymphoma of the central nervous system. Lancet. 1993; 342:398–401.
Article8. Lo YM, Chan AT, Chan LY, Leung SF, Lam CW, Huang DP, et al. Molecular prognostication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by quantitative analysis of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:6878–6881.9. Chan AT, Lo YM, Zee B, Chan LY, Ma BB, Leung SF, et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and residual disease after radiotherapy for undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94:1614–1619.
Article10. Kimura H, Morita M, Yabuta Y, Kuzushima K, Kato K, Kojima S, et al. Quantitative analysis of Epstein-Barr virus load by using a real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:132–136.
Article11. Brengel-Pesce K, Morand P, Schmuck A, Bourgeat MJ, Buisson M, Barguès G, et al. Routine use of real-time quantitative PCR for laboratory diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus infections. J Med Virol. 2002; 66:360–369.
Article12. Patel S, Zuckerman M, Smith M. Real-time quantitative PCR of Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 DNA using the LightCycler. J Virol Methods. 2003; 109:227–233.
Article13. Hayden RT, Hokanson KM, Pounds SB, Bankowski MJ, Belzer SW, Carr J, et al. Multicenter comparison of different real-time PCR assays for quantitative detection of Epstein-Barr virus. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:157–163.
Article14. Aalto SM, Juvonen E, Tarkkanen J, Volin L, Haario H, Ruutu T, et al. Epstein-Barr viral load and disease prediction in a large cohort of allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:1305–1309.
Article15. Styczynski J, Reusser P, Einsele H, de la Camara R, Cordonnier C, Ward KN, et al. Management of HSV, VZV and EBV infections in patients with hematological malignancies and after SCT: guidelines from the Second European Conference on Infections in Leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009; 43:757–770.
Article16. Ruiz G, Peña P, de Ory F, Echevarría JE. Comparison of commercial real-time PCR assays for quantification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:2053–2057.
Article17. Le QT, Jones CD, Yau TK, Shirazi HA, Wong PH, Thomas EN, et al. A comparison study of different PCR assays in measuring circulating plasma epstein-barr virus DNA levels in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:5700–5707.
Article18. Meijerink J, Mandigers C, van de Locht L, Tönnissen E, Goodsaid F, Raemaekers J. A novel method to compensate for different amplification efficiencies between patient DNA samples in quantitative real-time PCR. J Mol Diagn. 2001; 3:55–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Performance of the Real-Q EBV Quantification Kit for Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Quantification in Whole Blood
- Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction Systems for Detecting Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus Using Real-Time PCR: A Comparison Study Between the QIAsymphony RGQ and QIAcube Systems
- Evaluation of Two Commercial HLA-B27 Real-Time PCR Kits
- Performance Evaluation of the ELITe InGenius System for Detecting Cytomegalovirus, EpsteinBarr Virus, and BK Virus Infections
- Diagnostic Performance and Comparative Evaluation of the Architect, Liaison, and Platelia Epstein-Barr Virus Antibody Assays