Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2012 Mar;15(1):23-28.
Clinical and Endoscopic Findings in Children with Peptic Ulcer in Terms of Helicobacter pylori in Incheon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hanil General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Ilsan Dong-gu Community Health Center, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Gil Hospital, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea. onecar@gilhospital.com
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Gil Hospital, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Interest in peptic ulcer in children has been relatively low because the disease is rarer in children than in adults and there were restrictions in the application of endoscopy to children, but the recent development of pediatric endoscopy is activating research on pediatric peptic ulcer. Thus, this study compared the H. pylori infection rate and clinical and endoscopic findings among pediatric patients diagnosed with peptic ulcer.
METHODS
We analyzed retrospectively 58 pediatric patients for whom whether to be infected with H. pylori was confirmed selected out of pediatric patients diagnosed with gastric ulcer or duodenal ulcer through upper gastrointestinal endoscopy at the Department of Pediatrics of Gachon University Gil Hospital during the period from January 2002 to December 2007. A case was considered H. pylori positive if H. pylori was detected in the Giemsa stain of tissue or the results of UBT (urea breath test) and CLO (rapid urease test) were both positive.
RESULTS
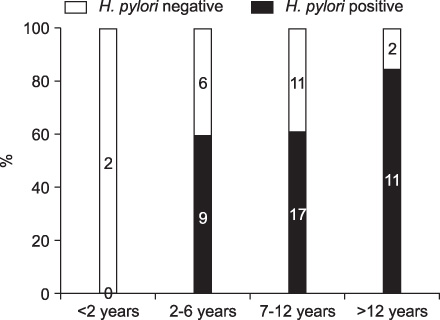
Of the pediatric patients, 37 were infected with H. pylori and 21 were not. The H. pylori infection rate increased with aging and the result was statistically significant (p<0.05). However, H. pylori infection was not in a statistically significant correlation with sex, chief complaint, and gastroduodenal ulcer (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
H. pylori infection increased with aging, but was not significantly correlated with gastroduodenal ulcer. Further research may need to examine prospectively the relation between H. pylori and gastroduodenal ulcer in the Incheon area.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee A, O'Rourke J. Gastric bacteria other than Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993. 22:21–42.2. Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984. 1:1311–1315.
Article3. Faigel DO, Furth EE, Childs M, Goin J, Metz DC. Histological predictors of active Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci. 1996. 41:937–943.4. Sarker SA, Mahmud H, Davidsson L, Alam NH, Ahmed T, Alam N, et al. Causal relationship of Helicobacter pylori with iron-deficiency anemia or failure of iron supplementation in children. Gastroenterology. 2008. 135:1534–1542.
Article5. Hill ID, Sinclair-Smith C, Lastovica AJ, Bowie MD, Emms M. Transient protein losing enteropathy associated with acute gastritis and Campylobacter pylori. Arch Dis Child. 1987. 62:1215–1219.
Article6. Kato S, Sherman PM. What is new related to Helicobacter pylori infection in children and teenagers? Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005. 159:415–421.
Article7. Sullivan PB, Thomas JE, Weight DG, Neale G, Eastham EJ, Corrah T, et al. Helicobacter pylori in Gambian children with chronic diarrhea and malnutrition. Arch Dis Child. 1990. 65:189–191.
Article8. Rhee KS, Park JO. Gastroduodenoscopic findings and effect of therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 8:12–20.
Article9. Seo JK. Recurrent abdominal pain in children. J Korean Med Assoc. 1999. 42:859–867.10. Valle J, Kekki M, Sipponen P, Ihamaki T, Siurala M. Long-term course and consequences of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Results of a 32-year follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996. 31:546–550.
Article11. Webb PM, Knight T, Greaves S, Wilson A, Newell DG, Elder J, et al. Relation between infection with Helicobacter pylori and living condition in childhood: evidence for person to person transmission in early life. BMJ. 1994. 308:750–753.
Article12. Jung MK, Kwon YS, Choe H, Choe YH, Hong YC. Relation between Helicobacter pylori infection and socioeconomic status in Korean adolescents. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000. 3:17–22.
Article13. Megraud F, Lamouliatte H. Helicobacter pylori and duodenal ulcer: Evidence suggesting causation. Dig Dis Sci. 1992. 37:769–772.14. Yom HW, Seo JW. Gastric mucosal immune response of Helicobacter pylori-infected children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:457–464.15. Barthel JS, Everett ED. Diagnosis of Campylobacter pylori infections: The "gold standard" and the alternatives. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. 12:s107–s114.16. Brown KE, Peura DA. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993. 22:105–115.17. Egbaria R, Levine A, Tamir A, Shaoul R. Peptic ulcers and erosions are common in Israel children undergoing upper endoscopy. Helicobacter. 2008. 13:62–68.
Article18. Bittencourt PF, Rocha GA, Penna FJ, Queiroz DM. Gastroduodenal peptic ulcer and Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2006. 82:325–334.19. Kim YJ. Gastrointestinal mucosal lesions in children with short-term abdominal pain. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. 9:176–182.
Article20. Lee SL, Kim YS, Suh ES, Paik TW, Kang CM. A clinical study on peptic ulcer in childhood. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1989. 32:198–205.21. Park IS, Kim NS, Jung PM. Peptic ulcer disease in infants and children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1995. 38:339–346.22. Choe YH, Ko JS, Kim SY, Yoo YM, Seo JK. The eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the duodenal ulcer in children and the duodenal recurrence. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998. 1:30–36.
Article23. Drumm B, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ. Intrafamilial clustering of Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 1990. 322:359–363.
Article24. Hassall E, Dimmick JE. Unique features of Helicobacter pylori disease in children. Dig Dis Sci. 1991. 36:417–423.25. Drumm B, O'Brien A, Cutz E, Sherman P. Campylobacter pylori-associated primary gastritis in children. Pediatrics. 1987. 80:192–195.26. Kilbridge PM, Dahms BB, Czinn SJ. Campylobacter pylori-associated gastritis and peptic ulcer disease in children. Am J Dis Child. 1988. 142:1149–1152.
Article27. Moon A, Solomon A, Beneck D, Cunningham-Rundles S. Positive association between Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 49:283–288.
Article28. Kim HJ, Han HJ, An SG, Yoo JS, Kim HS, Tchah H, et al. Clinical and endoscopic findings in children with duodenal ulcer due to Helicobacter pylori infection. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1999. 42:69–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Difference in Helicobacter pylori Eradication between Patients with Iatrogenic Ulcer after Endoscopic Resection and Patients with Peptic Ulcer
- Helicobacter pylori-negative Peptic Ulcer
- Complications and Management of Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Peptic Ulcer Disease: Present and Future Perspective
- The Effect of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Peptic Ulcer Bleeding