Antioxidative effects of Kimchi under different fermentation stage on radical-induced oxidative stress
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition and Kimchi Research Institute, Pusan National University, 2, Busandaehak-ro 63beon-gil, Geumjeong-gu, Busan 609-735, Korea. ejcho@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Conversing Technology, Graduate School of Venture, Hoseo University, Seoul 137-867, Korea.
- KMID: 2313790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2014.8.6.638
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Kimchi is a traditional Korean fermented vegetable containing several ingredients. We investigated the protective activity of methanol extract of kimchi under different fermentation stages against oxidative damage.
MATERIALS/METHODS
Fresh kimchi (Fresh), optimally ripened kimchi (OptR), and over ripened kimchi (OvR) were fermented until the pH reached pH 5.6, pH 4.3, and pH 3.8, respectively. The radical scavenging activity and protective activity from oxidative stress of kimchi during fermentation were investigated under in vitro and cellular systems using LLC-PK1 cells.
RESULTS
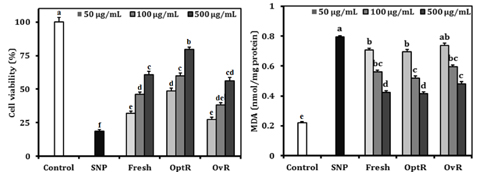
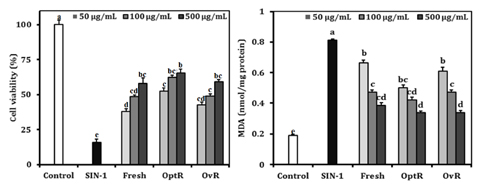
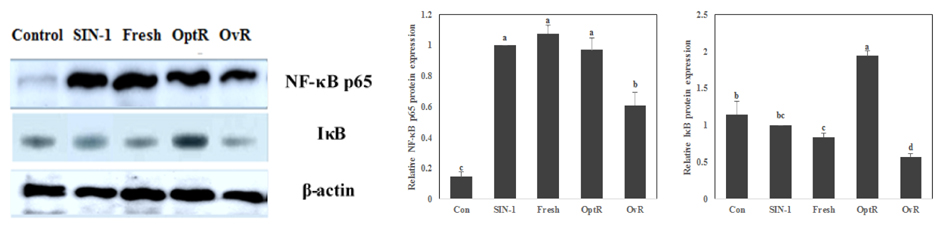
Kimchi exhibited strong radical scavenging activities against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, nitric oxide, superoxide anion, and hydroxyl radical. In addition, the free radical generators led to loss of cell viability and elevated lipid peroxidation, while treatment with kimchi resulted in significantly increased cell viability and decreased lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, the protective effect against oxidative stress was related to regulation of cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, nuclear factor-kappaB p65, and IkappaB expression. In particular, OvR showed the strongest protective effect from cellular oxidative stress among other kimchi.
CONCLUSION
The current study indicated that kimchi, particularly OptR and OvR, played a protective role against free radical-induced oxidative stress. These findings suggest that kimchi is a promising functional food with an antioxidative effect and fermentation of kimchi led to elevation of antioxidative activity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Cell Survival
Cyclooxygenase 2
Fermentation*
Functional Food
Hydrogen-Ion Concentration
Hydroxyl Radical
Lipid Peroxidation
LLC-PK1 Cells
Methanol
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
Oxidative Stress*
Superoxides
Swine
Vegetables
Cyclooxygenase 2
Hydroxyl Radical
Methanol
Nitric Oxide
Nitric Oxide Synthase Type II
Superoxides
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Kimchi attenuates fatty streak formation in the aorta of low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
Minji Woo, Mijeong Kim, Jeong Sook Noh, Chan Hum Park, Yeong Ok Song
Nutr Res Pract. 2017;11(6):445-451. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.6.445.Antioxidant effects of kimchi supplemented with black raspberry during fermentation protect against liver cirrhosis-induced oxidative stress in rats
Eun-Hye Ryu, Ji-Su Yang, Min-Jung Lee, Sung Hyun Kim, Hye-Young Seo, Ji-Hye Jung
Nutr Res Pract. 2019;13(2):87-94. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.87.A survey of research papers on the health benefits of kimchi and kimchi lactic acid bacteria
Bohkyung Kim, Eun-Gyung Mun, Doyeon Kim, Young Kim, Yongsoon Park, Hae-Jeung Lee, Youn-Soo Cha
J Nutr Health. 2018;51(1):1-13. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2018.51.1.1.Antioxidant activities of brown teff hydrolysates produced by protease treatment
Ye-Rang Yun, Sung-Hee Park
J Nutr Health. 2018;51(6):599-606. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2018.51.6.599.
Reference
-
1. Nakamura T, Cho DH, Lipton SA. Redox regulation of protein misfolding, mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic damage, and cell death in neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Neurol. 2012; 238:12–21.
Article2. Zhang Y, Tocchetti CG, Krieg T, Moens AL. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in the maintenance of myocardial function. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 53:1531–1540.
Article3. Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A, Chandra N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: impact on human health. Pharmacogn Rev. 2010; 4:118–126.
Article4. Singh B, Bhat TK, Singh B. Potential therapeutic applications of some antinutritional plant secondary metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. 2003; 51:5579–5597.
Article5. Park KY, Rhee SH. Functional foods from fermented vegetable products: Kimchi (Korean fermented vegetables) and functionality. In : Shi J, Ho CT, Shahidi F, editors. Asian Functional Foods. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press;2006. p. 341–380.6. Kong CS, Bahn YE, Kim BK, Lee KY, Park KY. Antiproliferative effect of chitosan-added Kimchi in HT-29 human colon carcinoma cells. J Med Food. 2010; 13:6–12.
Article7. Kim EK, An SY, Lee MS, Kim TH, Lee HK, Hwang WS, Choe SJ, Kim TY, Han SJ, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW. Fermented Kimchi reduces body weight and improves metabolic parameters in overweight and obese patients. Nutr Res. 2011; 31:436–443.
Article8. Noh JS, Choi YH, Song YO. Beneficial effects of the active principle component of Korean cabbage Kimchi via increasing nitric oxide production and suppressing inflammation in the aorta of apoE knockout mice. Br J Nutr. 2013; 109:17–24.
Article9. Cho EJ, Lee SM, Rhee SH, Park KY. Studies on standardization of Chinese cabbage Kimchi. Korean J Food Sci Technol. 1998; 30:324–332.10. Hatano T, Edamatsu R, Hiramatsu M, Mori A, Fujita Y, Yasuhara T, Yoshida T, Okuda T. Effects of the interaction of tannins with co-existing substances. VI.: effects of tannins and related polyphenols on superoxide anion radical, and on 1, 1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1989; 37:2016–2021.
Article11. Sreejayan , Rao MN. Nitric oxide scavenging by curcuminoids. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997; 49:105–107.
Article12. Kim BK, Choi MJ, Park KY, Cho EJ. Protective effects of Korean mistletoe lectin on radical-induced oxidative stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010; 33:1152–1158.
Article13. Kim JW, Minamikawa T. Hydroxyl radical-scavenging effects of spices and scavengers from brown mustard (Brassica nigra). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1997; 61:118–123.
Article14. Yokozawa T, Satoh A, Cho EJ, Kashiwada Y, Ikeshiro Y. Protective role of Coptidis Rhizoma alkaloids against peroxynitrite-induced damage to renal tubular epithelial cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005; 57:367–374.
Article15. Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Mitchell JB. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:936–942.16. Yokode M, Kita T, Kikawa Y, Ogorochi T, Narumiya S, Kawai C. Stimulated arachidonate metabolism during foam cell transformation of mouse peritoneal macrophages with oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1988; 81:720–729.
Article17. Lee HA, Song YO, Jang MS, Han JS. Alleviating effects of Baechu Kimchi added Ecklonia cava on postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2013; 18:163–168.
Article18. Park KY, Cho EJ, Rhee SH, Jung KO, Yi SJ, Jhun BH. Kimchi and an active component, beta-sitosterol, reduce oncogenic H-Ras(v12)-induced DNA synthesis. J Med Food. 2003; 6:151–156.
Article19. Choi IH, Noh JS, Han JS, Kim HJ, Han ES, Song YO. Kimchi, a fermented vegetable, improves serum lipid profiles in healthy young adults: randomized clinical trial. J Med Food. 2013; 16:223–229.
Article20. Kalyanaraman B. Teaching the basics of redox biology to medical and graduate students: oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2013; 1:244–257.
Article21. Yokozawa T, Kim YA, Kim HY, Lee YA, Nonaka G. Protective effect of persimmon peel polyphenol against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in LLC-PK(1) cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007; 45:1979–1987.
Article22. Yokozawa T, Cho EJ, Rhyu DY, Shibahara N, Aoyagi K. Glycyrrhizae Radix attenuates peroxynitrite-induced renal oxidative damage through inhibition of protein nitration. Free Radic Res. 2005; 39:203–211.
Article23. Schreck R, Albermann K, Baeuerle PA. Nuclear factor κB: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun. 1992; 17:221–237.
Article24. Oh YC, Cho WK, Im GY, Jeong YH, Hwang YH, Liang C, Ma JY. Anti-inflammatory effect of Lycium Fruit water extract in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012; 13:181–189.
Article25. Aktan F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004; 75:639–653.
Article26. Biswas SK, Lopes de Faria JB. Does peroxynitrite sustain nuclear factor-κB? Cardiovasc Res. 2005; 67:745–746.
Article27. Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996; 87:13–20.
Article28. Salminen A, Kaarniranta K. Genetics vs. entropy: longevity factors suppress the NF-κB-driven entropic aging process. Ageing Res Rev. 2010; 9:298–314.
Article29. Salminen A, Huuskonen J, Ojala J, Kauppinen A, Kaarniranta K, Suuronen T. Activation of innate immunity system during aging: NF-κB signaling is the molecular culprit of inflamm-aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2008; 7:83–105.
Article30. Yokozawa T, Cho EJ, Rhyu DY, Nakagawa T. Novel approaches to oxidative stress-induced renal failure: therapeutic potentials of Sanguisorbae Radix, Wen-Pi-Tang and green tea. J Trad Med. 2003; 20:83–101.31. Park JM, Shin JH, Gu JG, Yoon SJ, Song JC, Jeon WM, Suh HJ, Chang UJ, Yang CY, Kim JM. Effect of antioxidant activity in Kimchi during a short-term and over-ripening fermentation period. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011; 112:356–359.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antioxidant effects of kimchi supplemented with black raspberry during fermentation protect against liver cirrhosis-induced oxidative stress in rats
- The effects of physical training on antioxidative status under exercise-induced oxidative stress
- A Study on Use State and Satisfaction for Commercial Brand Kimchi of Women in Seoul Area
- Effect of vitamin B6 deficiency on antioxidative status in rats with exercise-induced oxidative stress
- Antioxidative effects of fermented sesame sauce against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in LLC-PK1 porcine renal tubule cells