Nutr Res Pract.
2009 Jun;3(2):84-88.
The inhibition of inflammatory molecule expression on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by berberine is not mediated by leptin signaling
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Life Science, Handong Global University, Heunghae-eup, Buk-gu, Pohang, Gyeongbuk 791-708, Korea. msdo@handong.edu
Abstract
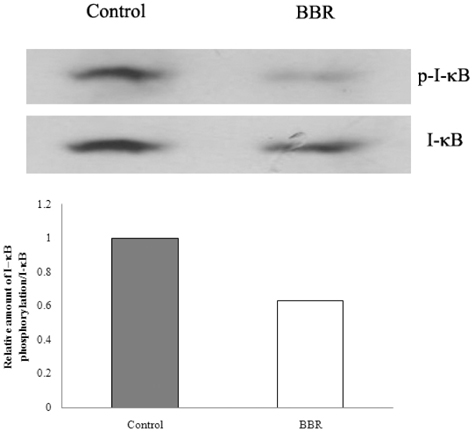
- In our previous study, we have shown that berberine has both anti-adipogenic and anti-inflammatory effects on 3T3-L1 adipocytes, and the anti-adipogenic effect is due to the down-regulation of adipogenic enzymes and transcription factors. Here we focused more on anti-inflammatory effect of berberine using real time RT-PCR and found it changes expressions of adipokines. We hypothesized that anti-adipogenicity of berberine mediates anti-inflammtory effect and explored leptin as a candidate mediator of this signaling. We studied this hypothesis by western blot analysis, but our results showed that berberine has no effect on the phosphorylations of STAT-3 and ERK which have important roles on leptin signaling. These results led us to conclude that the anti-inflammatory effect of berberine is not mediated by the inhibition of leptin signal transduction. Moreover, we have found that berberine down-regulates NF-kappaB signaling, one of the inflammation-related signaling pathway, through western blot analysis. Taken together, the anti-inflammatory effect of berberine is not mediated by leptin, and berberine induces anti-inflammatory effect independent of leptin signaling.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Capeau J, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006. 17:4–12.2. Baumann H, Morella KK, White DW, Dembski M, Bailon PS, Kim H, Lai CF, Tartaglia LA. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. 93:8374–8378.
Article3. Choi BH, Ahn IS, Kim YH, Park JW, Lee SY, Hyun CK, Do MS. Berberine reduces the expression of adipogenic enzymes and inflammatory molecules of 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Exp Mol Med. 2006. 38:599–605.
Article4. Enk R, Ehehalt R, Graham JE, Bierhaus A, Remppis A, Greten HJ. Differential effect of Rhizoma coptidis and its main alkaloid compound berberine on TNF-alpha induced NFkappaB translocation in human keratinocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007. 109:170–175.
Article5. Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. 115:911–919.
Article6. Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998. 16:225–260.
Article7. Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993. 259:87–91.
Article8. Hu JP, Nishishita K, Sakai E, Yoshida H, Kato Y, Tsukuba T, Okamoto K. Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB and Akt pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. 580:70–79.
Article9. Ikram M. A review on the chemical and pharmacological aspects of genus Berberis. Planta Med. 1975. 28:353–358.
Article10. Kim S, Kim Y, Kim JE, Cho KH, Chung JH. Berberine inhibits TPA-induced MMP-9 and IL-6 expression in normal human keratinocytes. Phytomedicine. 2008. 15:340–347.
Article11. Kong W. Berberine is a novel cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism distinct from statins. Nat Med. 2004. 10:1344–1351.
Article12. Kuo CL, Chi CW, Liu TY. The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2004. 203:127–137.13. La Cava A, Matarese G. The weight of leptin in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004. 4:371–379.
Article14. Lam QL, Lu L. Role of leptin in immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2007. 4:1–13.15. Lee CH, Chen JC, Hsiang CY, Wu SL, Wu HC, Ho TY. Berberine suppresses inflammatory agents-induced interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha productions via the inhibition of IkappaB degradation in human lung cells. Pharmacol Res. 2007. 56:193–201.
Article16. Machinal-Quélin F, Dieudonné MN, Leneveu MC, Pecquery R, Giudicelli Y. Proadipogenic effect of leptin on rat adipocytes in vitro: activation of MAPK and STAT3 signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. 282:C853–C863.17. Otero M, Lago R, Gomez R, Dieguez C, Lago F, Gómez-Reino J, Gualillo O. Towards a pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory emerging role of leptin. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. 45:944–950.
Article18. Trayhurn P, Wood IS. Adipokines. Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr. 2004. 92:347–355.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Berberine reduces the expression of adipogenic enzymes and inflammatory molecules of 3T3-L1 adipocyte
- B-cell-activating factor is a regulator of adipokines and a possible mediator between adipocytes and macrophages
- The Effect of IGFBP-3 on Adipokines and Gene Expression in Differentiated 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- Role of heat shock protein 70 in regulation of anti-inflammatory response to curcumin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- The Effects of Ginseng Saponin-Re, Rc and Green Tea Catechine; ECGC (Epigallocatechin Gallate) on Leptin, Hormone Sensitive Lipase and Resistin mRNA Expressions in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes