Nutr Res Pract.
2008 Jun;2(2):134-137.
Chemokine Lkn-1/CCL15 enhances matrix metalloproteinase-9 release from human macrophages and macrophage-derived foam cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea. rinayu@ulsan.ac.kr
- 2Biomedical Research Center, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea.
- 3Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejon 302-718, Korea.
Abstract
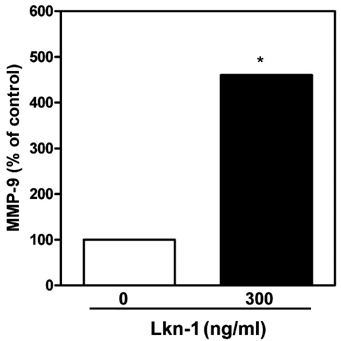
- Atherosclerosis is characterized by a chronic inflammatory disease, and chemokines play an important role in both initiation and progression of atherosclerosis development. Leukotactin-1 (Lkn-1/CCL15), a new member of the human CC chemokine family, is a potent chemoattractant for leukocytes. Our previous study has demonstrated that Lkn-1/CCL15 plays a role in the initiation of atherosclerosis, however, little is currently known whether Lkn-1/CCL15 is associated with the progression of atherosclerosis. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions play a crucial role in the progression of atherosclerosis by altering the vulnerability of plaque rupture. In the present study, we examined whether Lkn-1/CCL15 modulates MMP-9 release, which is a prevalent form expressed by activated macrophages and foam cells. Human THP-1 monocytic cells and/or human peripheral blood monocytes (PBMC) were treated with phorbol myristate acetate to induce their differentiation into macrophages. Foam cells were prepared by the treatment of THP-1 macrophages with human oxidized LDL. The macrophages and foam cells were treated with Lkn-1/CCL15, and the levels of MMP-9 release were measured by Gelatin Zymography. Lkn-1/CCL15 significantly enhanced the levels of MMP-9 protein secretion from THP-1 monocytic cells-derived macrophages, human PBMC-derived macrophages, as well as macrophage-derived foam cell in a dose dependent manner. Our data suggest that the action of Lkn-1/CCL15 on macrophages and foam cells to release MMP-9 may contribute to plaque destabilization in the progression of atherosclerosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Atherosclerosis
Chemokines
Foam Cells
Gelatin
Humans
Leukocytes
Lipoproteins, LDL
Macrophages
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Monocytes
Phorbols
Rupture
Tetradecanoylphorbol Acetate
Chemokines
Gelatin
Lipoproteins, LDL
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9
Matrix Metalloproteinases
Phorbols
Tetradecanoylphorbol Acetate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boyle JJ. Macrophage activation in atherosclerosis: pathogenesis and pharmacology of plaque rupture. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2005. 3:63–68.
Article2. Galis ZS, Khatri JJ. Matrix metalloproteinases in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Circ Res. 2002. 90:251–262.3. Kodali R, Hajjou M, Berman AB, Bansal MB, Zhang S, Pan JJ, Schecter AD. Chemokines induce matrix metalloproteinase-2 through activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in arterial smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. 69:706–715.
Article4. Lee WH, Kim SH, Jeong EM, Choi YH, Kim DI, Lee BB, Cho YS, Kwon BS, Park JE. A novel chemokine, Leukotactin-1, induces chemotaxis, pro-atherogenic cytokines, and tissue factor expression in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2002. 161:255–260.
Article5. Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002. 420:868–874.
Article6. Mann JM, Davies MJ. Vulnerable plaque. Relation of characteristics to degree of stenosis in human coronary arteries. Circulation. 1996. 94:928–931.7. Newby AC. Dual role of matrix metalloproteinases (matrixins) in intimal thickening and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Physiol Rev. 2005. 85:1–31.
Article8. Pasterkamp G, Schoneveld AH, Hijnen DJ, de Kleijn DP, Teepen H, van der Wal AC, Borst C. Atherosclerotic arterial remodeling and the localization of macrophages and matrix metalloproteases 1, 2 and 9 in the human coronary artery. Atherosclerosis. 2000. 150:245–253.
Article9. Reape TJ, Groot PH. Chemokines and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1999. 147:213–225.
Article10. Sheikine Y, Hansson GK. Chemokines and atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2004. 36:98–118.
Article11. Shin WS, Szuba A, Rockson SG. The role of chemokines in human cardiovascular pathology: enhanced biological insights. Atherosclerosis. 2002. 160:91–102.
Article12. Yu R, Kim CS, Kawada T, Kwon TW, Lim TH, Kim YW, Kwon BS. Involvement of leukotactin-1, a novel CC chemokine, in human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2004. 174:35–42.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Human LZIP induces monocyte CC chemokine receptor 2 expression leading to enhancement of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1/CCL2-induced cell migration
- LIGHT is Expressed in Foam Cells and Involved in Destabilization of Atherosclerotic Plaques through Induction of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and IL-8
- Regulation of Macrophage Activation and Differentiation in Atherosclerosis
- The Role of Macrophage Lipophagy in Reverse Cholesterol Transport
- Macrophage Infiltrations and Expressions of Matrix Metallproteinases in Intervertebral Disc