Ann Clin Microbiol.
2016 Jun;19(2):39-47. 10.5145/ACM.2016.19.2.39.
Molecular Epidemiology and Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae Isolated at a University Hospital in Korea during 4-Year Period
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance,Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jysung80@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Infection Control, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Infectious Diseases,Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2307782
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2016.19.2.39
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) has been increasingly reported worldwide in the past 10 years, which is an important infection control concern. Since the epidemiology and characteristics of these CPEs vary according to institutes, we aimed to characterize CPEs in a university hospital during the recent 4 years.
METHODS
From October 2011 to September 2015, CPE isolates from clinical specimens and hospital surveillance cultures were collected. Carbapenem resistance was confirmed by disk diffusion method and Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) was determined by agar dilution method. Carbapenemase production was tested by double disk test using aminophenylboronic acid and dipicolic acid. PCR and sequence analysis were performed to detect bla(KPC), bla(IMP-1), bla(VIM-2), bla(NDM-1)-like genes and bla(OXA-48) gene. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) were conducted for KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates.
RESULTS
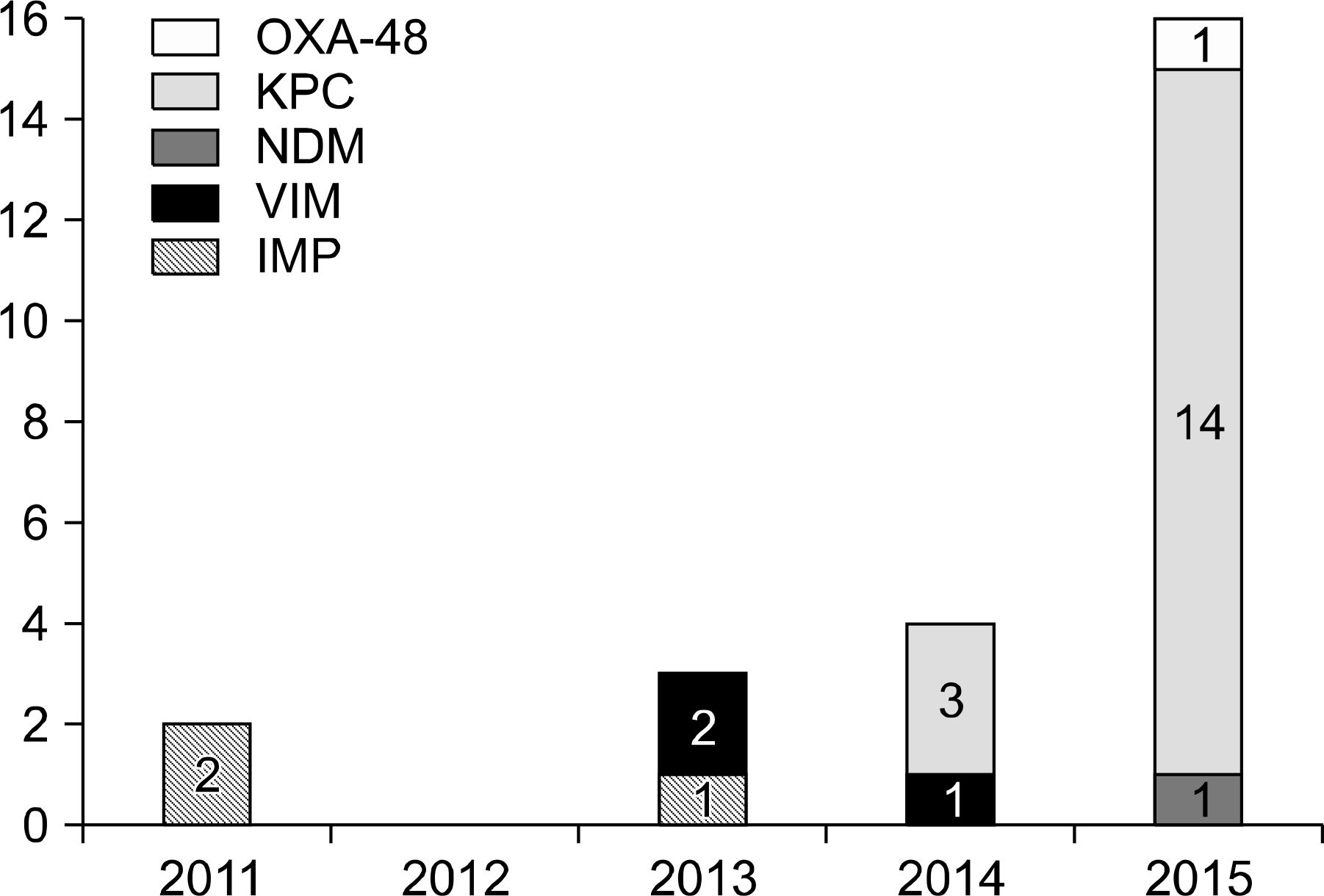
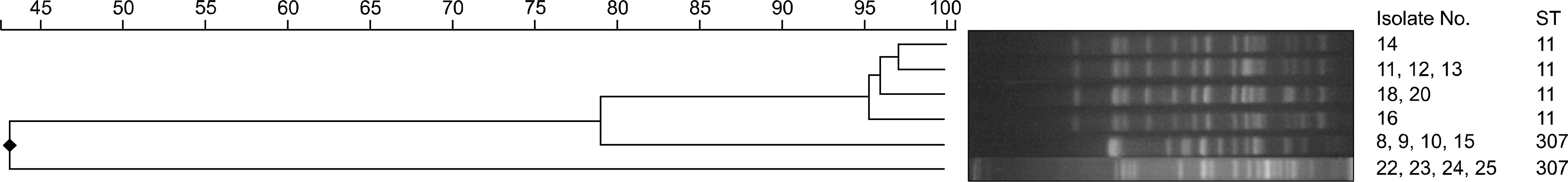
Twenty-five isolates (11%) of CPE were identified among 222 carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriacae isolates during the study period. The most prevalent CPE was KPC-producing K. pneumonia and others were IMP-1, VIM-2, NDM-1 type and OXA-48 producing CPEs. Most of these CPEs showed resistance to carbapenems with variable MICs. The sequence types (STs) of KPC-producing K. pneumoniae were ST307 and ST11. The PFGE of ST11 and ST307 showed clonality in each group suggesting the possibility of in-hospital outbreak.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of CPE has been increasing. In our institute, KPC-producing K. pneumoniae was the most frequently isolated CPE in the recent 4 years. CPE including KPC producers can easily transfer their resistance. Therefore continuous monitoring and more intensified infection control for CPE should be considered.
MeSH Terms
-
Academies and Institutes
Agar
Carbapenems
Diffusion
Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Electrophoresis, Gel, Pulsed-Field
Enterobacteriaceae*
Epidemiology
Infection Control
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Korea*
Methods
Molecular Epidemiology*
Multilocus Sequence Typing
Pneumonia
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prevalence
Sequence Analysis
Agar
Carbapenems
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Nordmann P, Naas T, Poirel L. Global spread of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:1791–8.2. Pitout JD. Infections with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: changing epidemiology and drug treatment choices. Drugs. 2010; 70:313–33.3. CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013. http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/. [Online] (last visited on 1 November 2015).4. Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T. The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009; 9:228–36.
Article5. Tzouvelekis LS, Markogiannakis A, Psichogiou M, Tassios PT, Daikos GL. Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae: an evolving crisis of global dimensions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25:682–707.
Article6. Park JW, Lee EJ, Lee DH. Status of carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae in Korea, 2014. Public Health Weekly Report. 2016; 9:9–13.7. Ko KS, Lee JY, Baek JY, Suh JY, Lee MY, Choi JY, et al. Predominance of an ST11 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae clone causing bacteraemia and urinary tract infections in Korea. J Med Microbiol. 2010; 59:822–8.8. Kim SY, Shin J, Shin SY, Ko KS. Characteristics of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from Korea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013; 76:486–90.
Article9. Kim MN, Yong D, An D, Chung HS, Woo JH, Lee K, et al. Nosocomial clustering of NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 340 strains in four patients at a South Korean tertiary care hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:1433–6.
Article10. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: twenty-fifth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S25. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2015.11. Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. EUCAST (The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing). http://www.eucast.org/[Online. ] (last visited on 1 November 2015).12. Diancourt L, Passet V, Verhoef J, Grimont PA, Brisse S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:4178–82.13. Gona F, Barbera F, Pasquariello AC, Grossi P, Gridelli B, Mezzatesta ML, et al. In vivo multiclonal transfer of bla KPC-3 from Klebsiella pneumoniae to Escherichia coli in surgery patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014; 20:O633–5.14. Goren MG, Carmeli Y, Schwaber MJ, Chmelnitsky I, Schechner V, Navon-Venezia S. Transfer of carbapenem-resistant plasmid from Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 to Escherichia coli in patient. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010; 16:1014–7.15. Tijet N, Muller MP, Matukas LM, Khan A, Patel SN, Melano RG. Lateral dissemination and inter-patient transmission of bla KPC-3: role of a conjugative plasmid in spreading carbapenem resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016; 71:344–7.16. Mathers AJ, Cox HL, Kitchel B, Bonatti H, Brassinga AK, Carroll J, et al. Molecular dissection of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae reveals intergenus KPC carbapenemase transmission through a promiscuous plasmid. MBio. 2011; 2:e00204–11.
Article17. Richter SN, Frasson I, Bergo C, Parisi S, Cavallaro A, Palù G. Transfer of KPC-2 carbapenemase from Klebsiella pneumoniae to Escherichia coli in a patient: first case in Europe. J Clin Microbiol. 2011; 49:2040–2.
Article18. Chen L, Mathema B, Chavda KD, DeLeo FR, Bonomo RA, Kreiswirth BN. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: molecular and genetic decoding. Trends Microbiol. 2014; 22:686–96.
Article19. Monaco M, Giani T, Raffone M, Arena F, Garcia-Fernandez A, Pollini S. Colistin resistance superimposed to endemic carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: a rapidly evolving problem in Italy, November 2013 to April 2014. Euro Surveill. 2014; 19.
Article20. Tumbarello M, Trecarichi EM, De Rosa FG, Giannella M, Giacobbe DR, Bassetti M, et al. Infections caused by KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: differences in therapy and mortality in a multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015; 70:2133–43.
Article21. Miriagou V, Cornaglia G, Edelstein M, Galani I, Giske CG, Gniadkowski M, et al. Acquired carbapenemases in Gram-negative bacterial pathogens: detection and surveillance issues. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010; 16:112–22.
Article22. Docquier JD, Calderone V, De Luca F, Benvenuti M, Giuliani F, Bellucci L, et al. Crystal structure of the OXA-48 beta-lactamase reveals mechanistic diversity among class D carbapenemases. Chem Biol. 2009; 16:540–7.23. Doi Y and Paterson DL. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 36:74–84.
Article24. Song W, Jeong SH, Lee J, Lee SS, Lee K. Emergence and spread of OXA-48-like carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 2015; 20:7–18.
Article25. Chen L, Chavda KD, Mediavilla JR, Zhao Y, Fraimow HS, Jenkins SG, et al. Multiplex realtime PCR for detection of an epidemic KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 clone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56:3444–7.
Article26. Wang Q, Li B, Tsang AK, Yi Y, Woo PC, Liu CH. Genotypic analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a Beijing Hospital reveals high genetic diversity and clonal population structure of drug-resistant isolates. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e57091.
Article27. Damjanova I, Tóth A, Pászti J, Hajbel-Vékony G, Jakab M, Berta J, et al. Expansion and countrywide dissemination of ST11, ST15 and ST147 ciprofloxacin-resistant CTX-M-15-type beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae epidemic clones in Hungary in 2005–the new ‘MRSAs’? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008; 62:978–85.28. Qi Y, Wei Z, Ji S, Du X, Shen P, Yu Y. ST11, the dominant clone of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:307–12.
Article29. Castanheira M, Farrell SE, Wanger A, Rolston KV, Jones RN, Mendes RE. Rapid expansion of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in two Texas hospitals due to clonal spread of ST258 and ST307 lineages. Microb Drug Resist. 2013; 19:295–7.
Article30. Park DJ, Yu JK, Park KG, Park YJ. Genotypes of ciprofloxacin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Korea and their characteristics according to the genetic lineages. Microb Drug Resist. 2015; 21:622–30.31. Johnson JK, Arduino SM, Stine OC, Johnson JA, Harris AD. Multilocus sequence typing compared to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for molecular typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:3707–12.32. Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, et al. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995; 33:2233–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Seoul, Korea
- Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Korea
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Performance of RAPIDEC CARBA NP Test for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae
- Rapid Identification of OXA-48-like, KPC, NDM, and VIM Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae From Culture: Evaluation of the RESIST-4 O.K.N.V. Multiplex Lateral Flow Assay
- Characterization of Carbapenemase Genes in Enterobacteriaceae Species Exhibiting Decreased Susceptibility to Carbapenems in a University Hospital in Chongqing, China