Korean J Urol.
2006 Nov;47(11):1185-1190. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.11.1185.
Comparison of the Efficacy of Transperineal Intraprostatic Injection and Oral Administration of Fluoroquinolone in Men with Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis-Seminal Vesiculitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Urology, Social and Preventive Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2294277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.11.1185
Abstract
- Purpose
Although oral antibiotic therapy remains the most common treatment modality for chronic bacterial prostatitis (CBP), it is known to have problems, such as potential adverse effects and the development of bacterial resistance. We compared the effects of oral and local injection therapies, with fluoroquinolones, in patients diagnosed as having chronic bacterial prostatitis/seminal vesiculitis, from Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging.
Materials and Methods
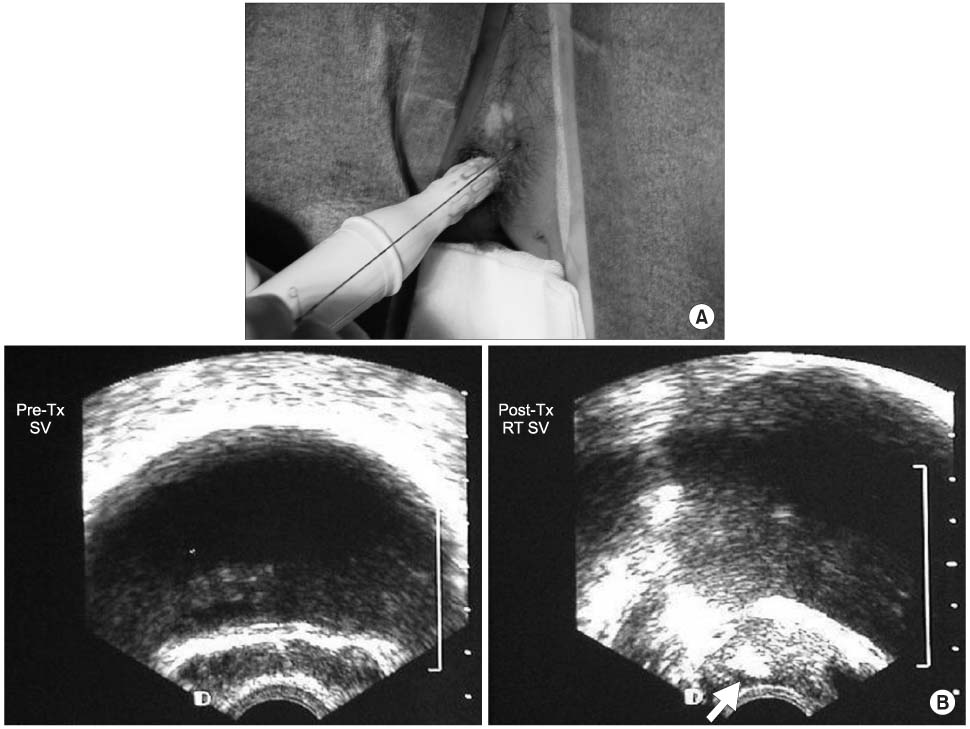
The study randomly included 79 patients with symptom of prostatitis, who also showed hot uptake in the prostate or seminal vesicle on Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging. A total of 53 patients received oral antibiotics for 3 months. In 26 patients, a local injection of ciprofloxacin into the prostate and/or seminal vesicle was performed via the transperineal route, with transrectal ultrasonography guidance. Four- glass tests and Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging were performed, and the patients were asked to complete National institute of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) questionnaires at the baseline and 3 months after the initiation of therapy.
Results
The total score or subscores from the NIH-CPSI and bacteriological study after treatment was significantly decreased in both groups compared to that before treatment. The complete cure rate, based on the Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging findings, was significantly higher in the local injection (23.1%) than the oral therapy group (16.9%, p<0.024). In the local injection group, 15 men (57.7%) showed transient hematuria and/or bloody ejaculation, but without any serious side effects.
Conclusions
A transperineal lesional injection of fluoroquinolone will be a valuable therapeutic alternative in men with chronic bacterial prostatitis/ seminal vesiculitis; although a long term outcome study will be required.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lipsky BA. Urinary tract infections in men. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1989. 110:138–135.2. Krieger JN, Nyberg L Jr, Nickel JC. NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis. JAMA. 1999. 292:236–237.3. Nickel JC. Walsh PC, Reik AB, Vaughan ED, Wein AJ, editors. Prostatitis and related conditions. Campbell's urology. 2002. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;604–630.4. Nickel JC. Antibiotics for bacterial prostatitis. J Urol. 2000. 163:1407.5. Ritter SJ, Lippow C. Pathological and bacteriological processes present in prostatitis and tissue reaction to therapy. J Urol. 1938. 39:111–114.6. Jimenez-Cruz JF, Tormo FB, Gomez JG. Treatment of chronic prostatitis: intraprostatic antibiotic injections under echography control. J Urol. 1988. 139:967–970.7. Yamamoto M, Hibi H, Satoshi K, Miyake K. Chronic bacterial prostatitis treated with intraprostatic injection of antibiotics. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1996. 30:199–202.8. Park JH, Lee YT, Hong YK, Shin JS. Treatment of chronic bacterial and nonbacterial prostatitis by local injection of Amikacin sulfate. Korean J Androl. 2000. 18:63–67.9. Hu WL, Zhong SZ, He HX. Treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis with amikacin through anal submucosal injection. Asian J Androl. 2002. 4:163–167.10. Yavascaoglu I, Camlikiyi H, Oktay B, Simsek U, Ozyurt M. Percutaneous suprapubic transvesical route: a new and comfortable method of intraprostatic injection. Urol Int. 1998. 60:229–234.11. Shafik A. Anal submucosal injection: a new route for drug administration. VI. Chronic prostatitis: a new modality of treatment with report of eleven cases. Urology. 1991. 37:61–64.12. Tillotson GS. Quinolones: structure-activity relationships and future predictions. J Med Microbiol. 1996. 44:320–324.13. Naber KG. Weider W, Madsen PO, Schiefer HG, editors. The role of quinolones in the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis. Prostatitis. 1994. 1st ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;175–190.14. Ryu JK, Lee SM, Seong DW, Suh JK, Kim SG, Choe W, et al. Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging in diagnosis of chronic bacterial prostatitis. Asian J Androl. 2003. 5:179–183.15. Lee SM, Ryu JK, Suh JK. Role of Tc-99m ciprofloxacin imaging in the diagnosis of bacterial prostatitis. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:861–865.16. Choe W, Chung MH, Kim WH, Kim SG, Ryu JK, Kang JK, et al. Imaging prostatitis with Tc-99m ciprofloxacin. Clin Nucl Med. 2002. 27:527–529.17. Choe W, Ryu JK, Kim WH, Chung MH, Suh JK. Imaging seminal vesiculitis with Tc-99m ciprofloxacin. Clin Nucl Med. 2003. 28:501–502.18. Solanki KK, Bomanji J, Siraj Q, Small M, Britton KE. Tc-99m Infecton: a new class of radiopharmaceutical for imaging infection. J Nucl Med. 1993. 34:119.19. Choe W, Im MH, Chung JK, Jeong JM. Imaging pelvic inflammatory disease with Tc-99m ciprofloxacin. Clin Nucl Med. 2000. 25:842–844.20. Hall AV, Solanki KK, Vinjamuri S, Britton KE, Das SS. Evaluation of the efficacy of 99mTc-infecton: a novel agent for detecting sites of infection. J Clin Pathol. 1998. 51:215–219.21. Vinjamuri S, Hall AV, Solanki KK, Bomanji J, Siraj Q, O'Shaughnessy E, et al. Comparison of 99mTc-infecton imaging with radiolabelled white-cell imaging in the evaluation of bacterial infection. Lancet. 1996. 347:233–235.22. Meares EM, Stamey TA. Bacteriologic localization patterns in bacterial prostatitis and urethritis. Invest Urol. 1968. 5:492–518.23. Schaeffer AJ, Knauss JS, Landis JR, Propert KJ, Alexander RB, Litwin MS, et al. National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Cohort Study. Leukocyte and bacterial counts do not correlate with severity of symptoms in men with chronic prostatitis. J Urol. 2002. 168:1048–1053.24. Nickel JC, Downey J, Johnston B, Clark J. Predictors of patient response to antibiotic therapy for the chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. J Urol. 2001. 165:1539–1544.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis by Intraprostatic Injection of Fosfomycin: 6 Years' Experience
- The Comparison of the Effects of Oral Antibiotic Ingestion and Intraprostatic Antibiotic Injection in a Rat Model of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
- Treatment of Chronic Bacterial and Nonbacterial Prostatitis by Local Injection of Amikacin Sulfate
- Comparative Study of Oral Minocycline Treatment and Intraprostatic Fosfomycin Injection on Nonbacterial Prostatitis
- Chronic Prostatitis Patient with Seminal Vesiculitis and Elevated PSA