Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2014 Apr;18(2):155-161. 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.2.155.
Regulatory B Subunits of Protein Phosphatase 2A Are Involved in Site-specific Regulation of Tau Protein Phosphorylation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul 158-710, Korea. ahnj@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Colorectal Cancer Branch, Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang 410-768, Korea.
- KMID: 2285505
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.2.155
Abstract
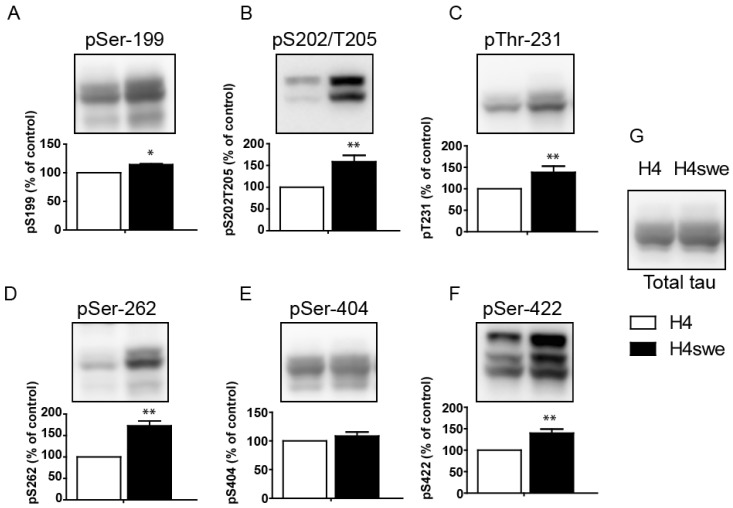
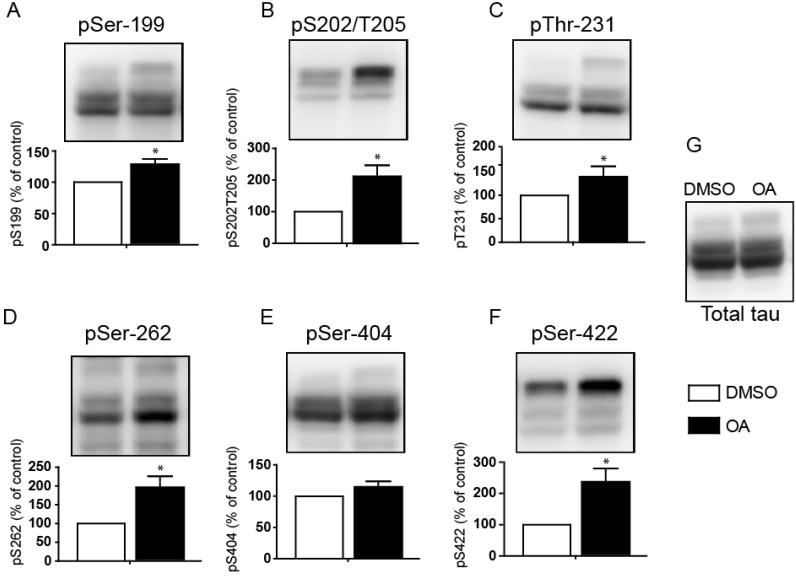
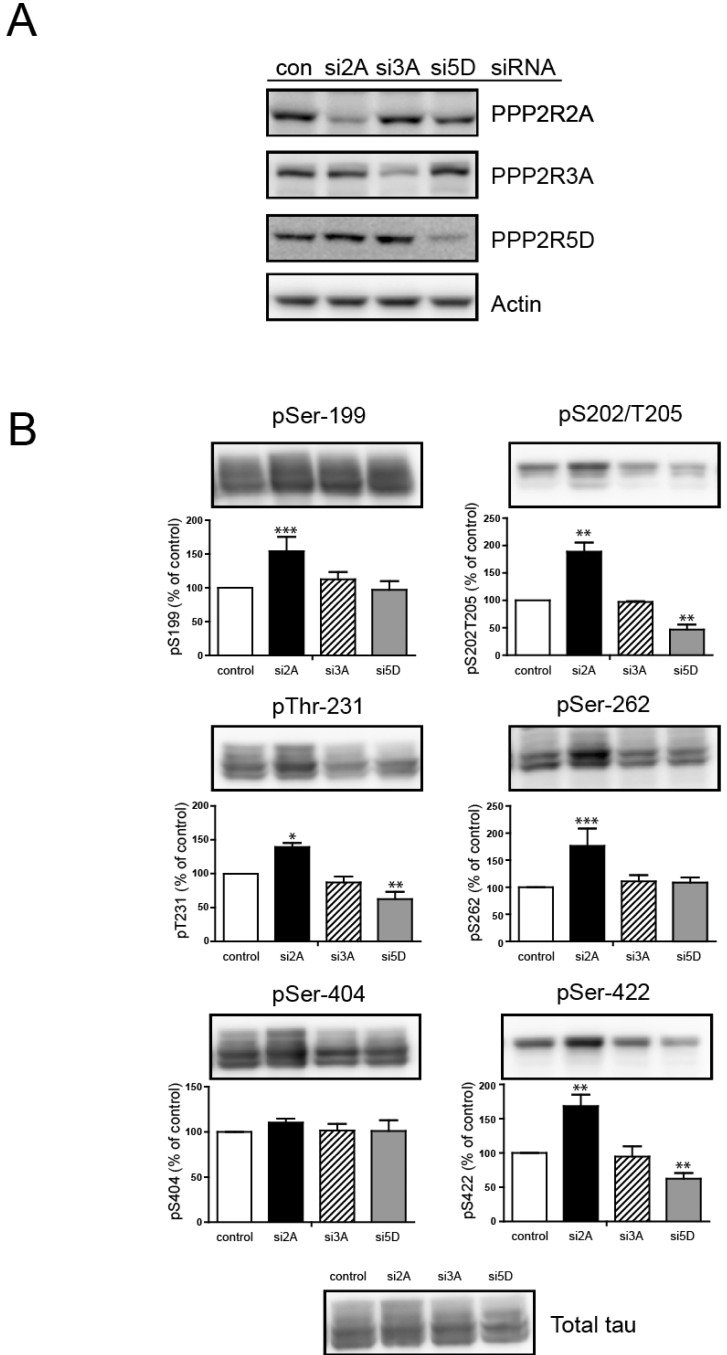
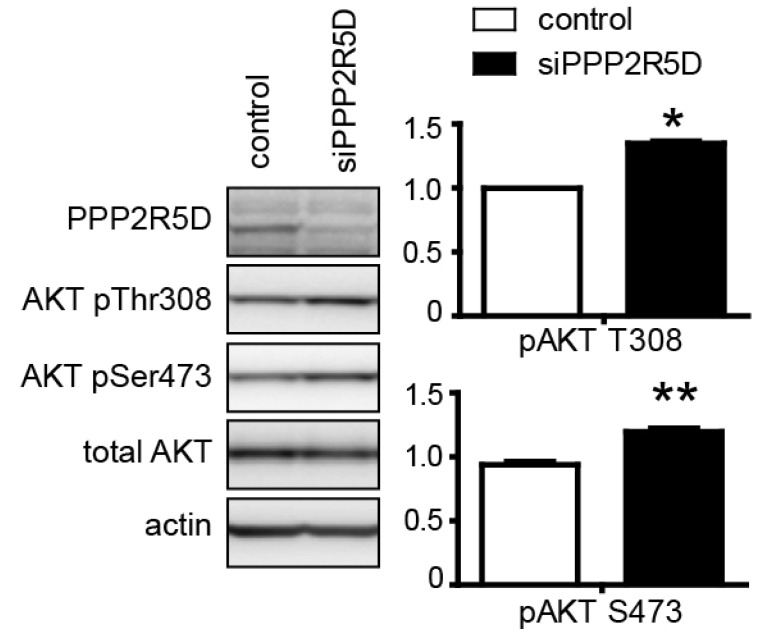
- Overexpression of amyloid precursor protein with the Swedish mutation causes abnormal hyperphosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau. Hyperphosphorylated isoforms of tau are major components of neurofibrillary tangles, which are histopathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), a major tau protein phosphatase, consists of a structural A subunit, catalytic C subunit, and a variety of regulatory B subunits. The B subunits have been reported to modulate function of the PP2A holoenzyme by regulating substrate binding, enzyme activity, and subcellular localization. In the current study, we characterized regulatory B subunit-specific regulation of tau protein phosphorylation. We showed that the PP2A B subunit PPP2R2A mediated dephosphorylation of tau protein at Ser-199, Ser-202/Thr-205, Thr-231, Ser-262, and Ser-422. Down-regulation of PPP2R5D expression decreased tau phosphorylation at Ser-202/Thr-205, Thr-231, and Ser-422, which indicates activation of the tau kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3beta) by PP2A with PPP2R5D subunit. The level of activating phosphorylation of the GSK3beta kinase Akt at Thr-308 and Ser-473 were both increased by PPP2R5D knockdown. We also characterized B subunit-specific phosphorylation sites in tau using mass spectrometric analysis. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry revealed that the phosphorylation status of the tau protein may be affected by PP2A, depending on the specific B subunits. These studies further our understanding of the function of various B subunits in mediating site-specific regulation of tau protein phosphorylation.
MeSH Terms
-
Alzheimer Disease
Amyloid
Catalytic Domain
Down-Regulation
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
Negotiating
Neurofibrillary Tangles
Phosphorylation*
Phosphotransferases
Protein Isoforms
Protein Phosphatase 2*
Spectrum Analysis
tau Proteins*
Amyloid
Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3
Phosphotransferases
Protein Isoforms
Protein Phosphatase 2
tau Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alonso AC, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Alzheimer's disease hyperphosphorylated tau sequesters normal tau into tangles of filaments and disassembles microtubules. Nat Med. 1996; 2:783–787. PMID: 8673924.
Article2. Mairet-Coello G, Courchet J, Pieraut S, Courchet V, Maximov A, Polleux F. The CAMKK2-AMPK kinase pathway mediates the synaptotoxic effects of Aβ oligomers through Tau phosphorylation. Neuron. 2013; 78:94–108. PMID: 23583109.
Article3. Louis JV, Martens E, Borghgraef P, Lambrecht C, Sents W, Longin S, Zwaenepoel K, Pijnenborg R, Landrieu I, Lippens G, Ledermann B, Götz J, Van Leuven F, Goris J, Janssens V. Mice lacking phosphatase PP2A subunit PR61/B'delta (Ppp2r5d) develop spatially restricted tauopathy by deregulation of CDK5 and GSK3beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:6957–6962. PMID: 21482799.4. Liu Y, Su Y, Sun S, Wang T, Qiao X, Run X, Liang Z. Tau phosphorylation and µ-calpain activation mediate the dexamethasone-induced inhibition on the insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e35783. PMID: 22536436.
Article5. Choe MA, Koo BS, An GJ, Jeon S. Effects of treadmill exercise on the recovery of dopaminergic neuron loss and muscle atrophy in the 6-ohda lesioned parkinson's disease rat model. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012; 16:305–312. PMID: 23129977.
Article6. Mercado-Gómez O, Hernández-Fonseca K, Villavicencio-Queijeiro A, Massieu L, Chimal-Monroy J, Arias C. Inhibition of Wnt and PI3K signaling modulates GSK-3beta activity and induces morphological changes in cortical neurons: role of tau phosphorylation. Neurochem Res. 2008; 33:1599–1609. PMID: 18461448.7. Kuo YC, Huang KY, Yang CH, Yang YS, Lee WY, Chiang CW. Regulation of phosphorylation of Thr-308 of Akt, cell proliferation, and survival by the B55alpha regulatory subunit targeting of the protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme to Akt. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:1882–1892. PMID: 18042541.8. Qian W, Shi J, Yin X, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Gong CX, Liu F. PP2A regulates tau phosphorylation directly and also indirectly via activating GSK-3beta. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010; 19:1221–1229. PMID: 20308788.9. Zhang H, Sun S, Herreman A, De Strooper B, Bezprozvanny I. Role of presenilins in neuronal calcium homeostasis. J Neurosci. 2010; 30:8566–8580. PMID: 20573903.
Article10. Ahn JH, Sung JY, McAvoy T, Nishi A, Janssens V, Goris J, Greengard P, Nairn AC. The B"PR72 subunit mediates Ca2+-dependent dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 by protein phosphatase 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:9876–9881. PMID: 17535922.11. Ahn JH, McAvoy T, Rakhilin SV, Nishi A, Greengard P, Nairn AC. Protein kinase A activates protein phosphatase 2A by phosphorylation of the B56delta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104:2979–2984. PMID: 17301223.12. Margolis SS, Perry JA, Forester CM, Nutt LK, Guo Y, Jardim MJ, Thomenius MJ, Freel CD, Darbandi R, Ahn JH, Arroyo JD, Wang XF, Shenolikar S, Nairn AC, Dunphy WG, Hahn WC, Virshup DM, Kornbluth S. Role for the PP2A/B56delta phosphatase in regulating 14-3-3 release from Cdc25 to control mitosis. Cell. 2006; 127:759–773. PMID: 17110335.13. Yu UY, Ahn JH. Phosphorylation on the PPP2R5D B regulatory subunit modulates the biochemical properties of protein phosphatase 2A. BMB Rep. 2010; 43:263–267. PMID: 20423611.
Article14. Sontag JM, Nunbhakdi-Craig V, White CL 3rd, Halpain S, Sontag E. The protein phosphatase PP2A/Bα binds to the microtubule-associated proteins Tau and MAP2 at a motif also recognized by the kinase Fyn: implications for tauopathies. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:14984–14993. PMID: 22403409.15. Salcedo-Tello P, Hernández-Ortega K, Arias C. Susceptibility to GSK3β-induced tau phosphorylation differs between the young and aged hippocampus after wnt signaling inhibition. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014; 39:775–785. PMID: 24270208.
Article16. Shin J, Yu SB, Yu UY, Jo SA, Ahn JH. Swedish mutation within amyloid precursor protein modulates global gene expression towards the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. BMB Rep. 2010; 43:704–709. PMID: 21034535.
Article17. Park JH, Sung HY, Lee JY, Kim HJ, Ahn JH, Jo I. B56α subunit of protein phosphatase 2A mediates retinoic acid-induced decreases in phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase at serine 1179 and nitric oxide production in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 430:476–481. PMID: 23237802.
Article18. Wang JZ, Xia YY, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau: sites, regulation, and molecular mechanism of neurofibrillary degeneration. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013; 33(Suppl 1):S123–S139. PMID: 22710920.
Article19. Kamat PK, Rai S, Swarnkar S, Shukla R, Ali S, Najmi AK, Nath C. Okadaic acid-induced Tau phosphorylation in rat brain: role of NMDA receptor. Neuroscience. 2013; 238:97–113. PMID: 23415789.
Article20. Janssens V, Longin S, Goris J. PP2A holoenzyme assembly: in cauda venenum (the sting is in the tail). Trends Biochem Sci. 2008; 33:113–121. PMID: 18291659.
Article21. Li X, Virshup DM. Two conserved domains in regulatory B subunits mediate binding to the A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Eur J Biochem. 2002; 269:546–552. PMID: 11856313.
Article22. Ahn JH, Kim Y, Kim HS, Greengard P, Nairn AC. Protein kinase C-dependent dephosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase requires the B56δ heterotrimeric form of protein phosphatase 2A. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e26292. PMID: 22046270.
Article23. Creyghton MP, Roël G, Eichhorn PJ, Hijmans EM, Maurer I, Destrée O, Bernards R. PR72, a novel regulator of Wnt signaling required for Naked cuticle function. Genes Dev. 2005; 19:376–386. PMID: 15687260.
Article24. Cho US, Xu W. Crystal structure of a protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimeric holoenzyme. Nature. 2007; 445:53–57. PMID: 17086192.
Article25. Longin S, Zwaenepoel K, Louis JV, Dilworth S, Goris J, Janssens V. Selection of protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits is mediated by the C terminus of the catalytic Subunit. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:26971–26980. PMID: 17635907.
Article26. Arif M, Kazim SF, Grundke-Iqbal I, Garruto RM, Iqbal K. Tau pathology involves protein phosphatase 2A in Parkinsonism-dementia of Guam. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:1144–1149. PMID: 24395787.
Article27. Sontag JM, Nunbhakdi-Craig V, Montgomery L, Arning E, Bottiglieri T, Sontag E. Folate deficiency induces in vitro and mouse brain region-specific downregulation of leucine carboxyl methyltransferase-1 and protein phosphatase 2A B(alpha) subunit expression that correlate with enhanced tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:11477–11487. PMID: 18987184.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Regulation of chicken protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 and human protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activity by casein kinase II- and p56lck-mediated phosphorylation
- Phosphorylation of chicken protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 by casein kinase II in vitro
- Opening of ATP-sensitive K+ channel by pinacidil requires serine/threonine phosphorylation in rat ventricular myocytes
- Regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylation: complexity of multiple phosphorylation sites and kinases
- Effect of serum and hydrogen peroxide on the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2(eEF-2) in Chinese hamster ovary cells