Ann Rehabil Med.
2011 Jun;35(3):405-411. 10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.405.
The Additional Effect of Hyaluronidase in Lumbar Interlaminar Epidural Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan 602-715, Korea. kwlee65@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.3.405
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
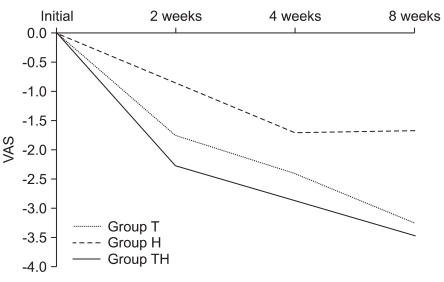
To evaluate the effect of hyaluronidase in lumbar interlaminar epidural injection (LIEI) for low back pain and sciatica. METHOD: Sixty-one patients suffering from severe low back pain and sciatica were randomly allocated into three groups. Group T (n=18, mean duration of illness: 2.12+/-1.16 months) received lumbar interlaminar epidural injection (LIEI) with 2 ml triamcinolone (40 mg/ml) and 5 ml bupivacaine (0.25%). Group H (n=16, mean duration of illness: 2.05+/-1.12 months) received LIEI with 1,500 IU hyaluronidase and 5 ml bupivacaine (0.25%). Group TH (n=27, mean duration of illness: 2.16+/-1.65 months) received LIEI with 1,500 IU hyaluronidase, 2 ml triamcinolone (40 mg/ml), and 5 ml bupivacaine (0.25%). The effects were evaluated using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) at preinjection and 2 weeks, 4 weeks, and 8 weeks after LIEI.
RESULTS
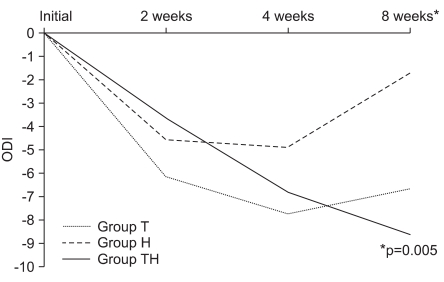
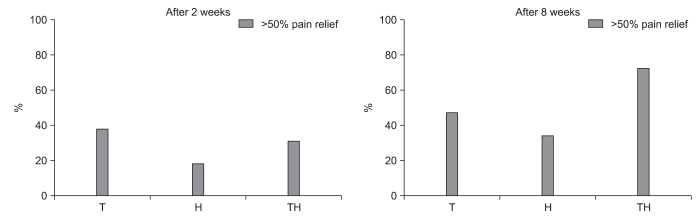
Pain improved in all groups after 2 weeks (p<0.05). After 8 weeks, there was no significant difference in VAS improvement among the 3 groups. However, pain improved in 70.4% of Group TH compared with preinjection, in contrast to 44.4% of Group T and 31.3% of Group H. The ODI improved significantly only in Group TH after 8 weeks (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
LIEI with triamcinolone and hyaluronidase is more effective for reducing pain after 8 weeks than injection with triamcinolone or hyaluronidase alone.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Effect of Hyaluronidase in Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Injection for Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
Sang Beom Kim, Kyeong Woo Lee, Jong Hwa Lee, Min Ah Kim, Byoung Woo An
Ann Rehabil Med. 2012;36(4):466-473. doi: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.466.Percutaneous Adhesiolysis Versus Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Chronic Radicular Pain Caused by Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Yongbum Park, Woo Yong Lee, Jae Ki Ahn, Hee-Seung Nam, Ki Hoon Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(6):941-949. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.941.Epidural Lysis of Adhesions
Frank Lee, David E. Jamison, Robert W. Hurley, Steven P. Cohen
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):3-15. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.3.
Reference
-
1. Andersson GB. Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 1999; 354:581–585. PMID: 10470716.
Article2. Jung SG. Epidural steroid injection in lumbosacral radiculopathy (due to herniated intervertebral disc) efficacy-randomized placebo controlled studies. J Korean Assoc Pain Med. 2007; 6:14–23.3. Hayashi N, Weinstein JN, Meller ST, Lee HM, Spratt KF, Gebhart GF. The effect of epidural injection of betamethasone or bupivacaine in a rat model of lumbar radiculopathy. Spine. 1998; 23:877–885. PMID: 9580954.
Article4. Murata Y, Onda A, Rydevik B, Takahashi K, Olmarker K. Distribution and appearance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the dorsal root ganglion exposed to experimental disc herniation in rats. Spine. 2004; 29:2235–2241. PMID: 15480134.5. Brisby H, Byröd G, Olmarker K, Miller VM, Aoki Y, Rydevik B. Nitric oxide as a mediator of nucleus pulposus-induced effects on spinal nerve roots. J Orthop Res. 2000; 18:815–820. PMID: 11117305.
Article6. McLain RF, Kapural L, Mekhail NA. Epidural steroid therapy for back and leg pain; mechanism of action and efficacy. Spine J. 2005; 5:191–201. PMID: 15749619.7. Lee KJ, Han SG, Yoon SH, Kim JS, Lee YS. Nerve root block with corticosteroids, hyaluronidase, and local anesthetic in the failed back surgery syndrome. J Korean Pain Soc. 1999; 12:191–194.8. Jo DH, Hong JH, Kim MH. The effect of transforaminal epidural block with hyaluronidase and triamcinolone. Korean J Pain. 2005; 18:176–180.
Article9. Carette S, Leclaire R, Marcoux S, Morin F, Blaise GA, St-Pierre A, Truchon R, Parent F, Levesque J, Bergeron V, et al. Epidural corticosteroid injections for sciatica due to herniated nucleus pulposus. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:1634–1640. PMID: 9171065.
Article10. Wilson-MacDonald J, Burt G, Griffin D, Glynn C. Epidural steroid injection for nerve root compression. A randomised, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:352–355. PMID: 15773645.11. Buchner M, Zeifang F, Brocai DR, Schiltenwolf M. Epidural corticosteroid injection in the conservative management of sciatica. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; 375:149–156. PMID: 10853164.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Hyaluronidase in Interlaminar Lumbar Epidural Injection for Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
- Delayed Allergic Reaction to Secondary Administrated Epidural Hyaluronidase
- The Effect of Transforaminal Epidural Block with Hyaluronidase and Triamcinolone
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- Unintentional lumbar facet joint injection guided by fluoroscopy during interlaminar epidural steroid injection: a retrospective analysis