Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 Sep;2(4):310-313. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.4.310.
Serotonin syndrome associated with linezolid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. dr00nam@hanmail.net
- 2Dong-A University Hospital Regional Pharmacovigilance Center, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2262403
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.4.310
Abstract
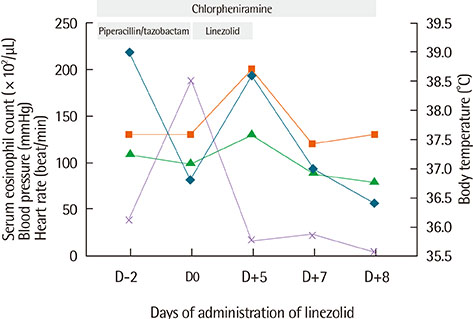
- Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a potentially life-threatening drug reaction characterized by mental status change, increased neuromuscular tone, and autonomic instability. Linezolid, an oxazolidinone antibacterial agent, is widely used in general hospitals; however, it interacts with some serotonin agonists and may cause SS. We report a case of SS caused by linezolid, without the concomitant use of serotonin agonist. A 72-year-old patient was admitted due to recurrent wound infection of his left ankle. He developed fever, skin rash, and renal function deterioration, and blood eosinophils and liver enzymes increased after administration of vancomycin. The antibiotic was changed to linezolid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Four days later, he developed agitation, fever, increased blood pressure, and tachycardia. There were no abnormal findings in laboratory and image tests, including brain and chest computed tomography suggesting the cause of his symptoms. He had not taken any serotonin agonists, including serotonin uptake inhibitors and monoamineoxidase-inhibiting antidepressants. When administration of linezolid was stopped, his symptoms improved within 24 hours and fully recovered within 2 days without additional treatments.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Ankle
Antidepressive Agents
Blood Pressure
Brain
Dihydroergotamine
Eosinophils
Exanthema
Fever
Hospitals, General
Humans
Liver
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin Syndrome*
Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors
Tachycardia
Thorax
Vancomycin
Wound Infection
Linezolid
Antidepressive Agents
Dihydroergotamine
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors
Vancomycin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gellynck E, Heyninck K, Andressen KW, Haegeman G, Levy FO, Vanhoenacker P, et al. The serotonin 5-HT7 receptors: two decades of research. Exp Brain Res. 2013; 230:555–568.
Article2. Birmes P, Coppin D, Schmitt L, Lauque D. Serotonin syndrome: a brief review. CMAJ. 2003; 168:1439–1442.3. Boyer EW, Shannon M. The serotonin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1112–1120.
Article4. Moellering RC. Linezolid: the first oxazolidinone antimicrobial. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 138:135–142.
Article5. Wigen CL, Goetz MB. Serotonin syndrome and linezolid. Clin Infect Dis. 2002; 34:1651–1652.
Article6. Quinn DK, Stern TA. Linezolid and serotonin syndrome. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2009; 11:353–356.
Article7. Birmingham MC, Rayner CR, Meagher AK, Flavin SM, Batts DH, Schentag JJ. Linezolid for the treatment of multidrug-resistant, gram-positive infections: experience from a compassionate-use program. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:159–168.
Article8. Wunderink RG, Rello J, Cammarata SK, Croos-Dabrera RV, Kollef MH. Linezolid vs vancomycin: analysis of two double-blind studies of patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus nosocomial pneumonia. Chest. 2003; 124:1789–1797.9. Lawrence KR, Adra M, Gillman PK. Serotonin toxicity associated with the use of linezolid: a review of postmarketing data. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1578–1583.
Article10. Alisky JM. Can chlorpheniramine cause serotonin syndrome? Singapore Med J. 2006; 47:1014.11. Savard S, Desmeules S, Riopel J, Agharazii M. Linezolid-associated acute interstitial nephritis and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009; 54:e17–e20.
Article12. Mills KC. Serotonin syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 1995; 52:1475–1482.13. Sternbach H. The serotonin syndrome. Am J Psychiatry. 1991; 148:705–713.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of postoperative serotonin syndrome following the administration of fentanyl, palonosetron, and meperidine: A case report
- Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Probable tramadol-induced atypical serotonin syndrome in a patient receiving selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and stopped at 10 days before surgery: A case report
- A Case of Serotonin Syndrome Induced by Fluoxetine and Duloxetine Independently in a Same Patient
- A Case of Lactic Acidosis Associated with Prolonged Linezolid Therapy