Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2013 Jun;1(2):157-163. 10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.157.
Comparison of respiratory disease by human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pedjsyoon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2261864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.157
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is known to result in clinical manifestation similar to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children. But some recent studies showed different features. This study compared the clinical manifestation of respiratory disease between hMPV and RSV.
METHODS
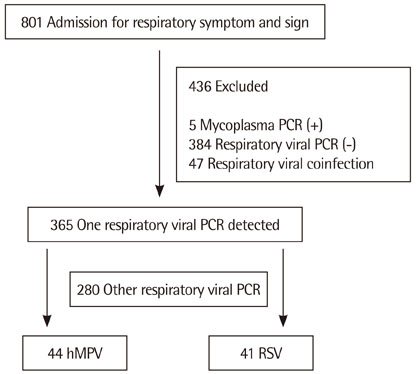
A total of 801 children who admitted to Seoul St. Mary's Hospital for respiratory infection from January to June, 2012 were enrolled. Respiratory viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using nasopharyngeal swab was performed in all children. We grouped hMPV positive children and RSV positive children and compared clinical features between them by retrospective chart review.
RESULTS
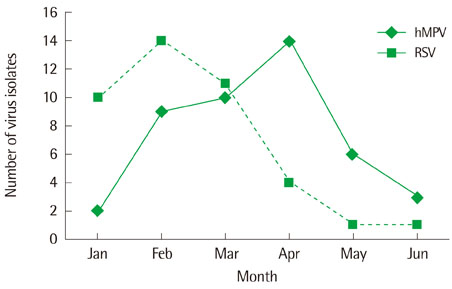
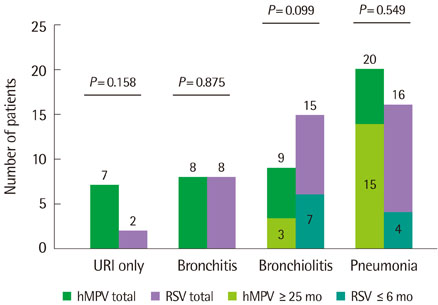
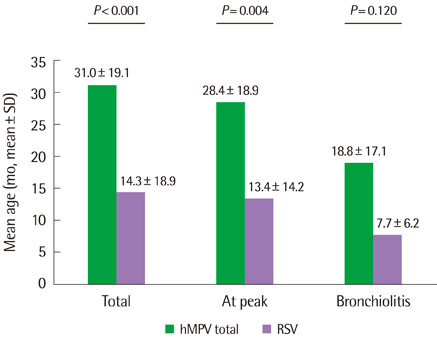
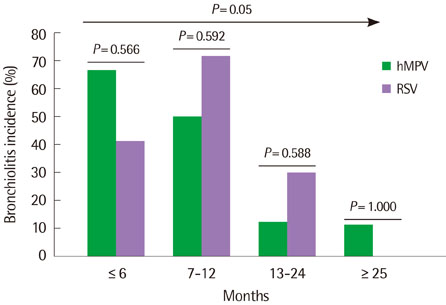
Among 801 children, 365 showed one virus PCR positive with 44 showing hMPV and 41 showing RSV. Respiratory diseases were upper respiratory infection, acute bronchitis, acute bronchiolitis and pneumonia. The peak season was March and April for hMPV and February and March for RSV. Fever incidence, fever duration and neutrophil percent of complete blood cell count were higher in hMPV group than RSV group (P<0.05). The mean age of hMPV group was higher than RSV group (P<0.05). But in acute bronchiolitis children, there was no mean age difference between two group. Acute bronchiolitis incidence declined with increased age for both group (P<0.05). The hMPV group showed relatively lower bronchiolitis and higher pneumonia incidence than RSV group, suggesting relation with age.
CONCLUSION
Respiratory infection by hMPV developed at late winter and spring, slightly later than RSV and at older age. The lower incidence of acute bronchiolitis for hMPV infection than RSV is maybe due to older age than RSV.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mathers CD, Lopez AD, Murray CJL. The burden of disease and mortality by condition: data, methods, and results for 2001. In : Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJL, editors. Global burden of disease and risk factors. Washington: World Bank;2006. p. 45–93.2. Papenburg J, Hamelin ME, Ouhoummane N, Carbonneau J, Ouakki M, Raymond F, et al. Comparison of risk factors for human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus disease severity in young children. J Infect Dis. 2012; 206:178–189.
Article3. Boyce TG, Mellen BG, Mitchel EF Jr, Wright PF, Griffin MR. Rates of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection among children in medicaid. J Pediatr. 2000; 137:865–870.
Article4. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, et al. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001; 7:719–724.
Article5. Freymouth F, Vabret A, Legrand L, Eterradossi N, Lafay-Delaire F, Brouard J, et al. Presence of the new human metapneumovirus in French children with bronchiolitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003; 22:92–94.
Article6. Marguet C, Lubrano M, Gueudin M, Le Roux P, Deschildre A, Forget C, et al. In very young infants severity of acute bronchiolitis depends on carried viruses. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e4596.
Article7. Kim YK, Kim JW, Wee YS, Yoo EG, Han MY. Clinical features of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus infection in hospitalized children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:12–19.8. Wolf DG, Greenberg D, Shemer-Avni Y, Givon-Lavi N, Bar-Ziv J, Dagan R. Association of human metapneumovirus with radiologically diagnosed community-acquired alveolar pneumonia in young children. J Pediatr. 2010; 156:115–120.
Article9. Hall CB, Weinberg GA, Iwane MK, Blumkin AK, Edwards KM, Staat MA, et al. The burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection in young children. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:588–598.
Article10. Papenburg J, Boivin G. The distinguishing features of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus. Rev Med Virol. 2010; 20:245–260.
Article11. Manoha C, Espinosa S, Aho SL, Huet F, Pothier P. Epidemiological and clinical features of hMPV, RSV and RVs infections in young children. J Clin Virol. 2007; 38:221–226.
Article12. Wolf DG, Greenberg D, Kalkstein D, Shemer-Avni Y, Givon-Lavi N, Saleh N, et al. Comparison of human metapneumovirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza A virus lower respiratory tract infections in hospitalized young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006; 25:320–324.
Article13. Jeong JH, Moon KH, Lee CW, Choi DY, Oh YG, Yoon HS, et al. Lower respiratory tract infection of positive antigen test for respiratory syncytial virus on children under 2 years of age. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:394–400.
Article14. Kim CK, Choi J, Callaway Z, Kim HB, Chung JY, Koh YY, et al. Clinical and epidemiological comparison of human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in seoul, Korea, 2003-2008. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:342–347.
Article15. Garcia-Garcia ML, Calvo C, Martin F, Perez-Brena P, Acosta B, Casas I. Human metapneumovirus infections in hospitalised infants in Spain. Arch Dis Child. 2006; 91:290–295.
Article16. Yeom HH, Park JS, Jeong DJ, Kim CJ, Kim YB, Lee DH, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:401–409.
Article17. Bastien N, Ward D, Van Caeseele P, Brandt K, Lee SH, McNabb G, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection in the Canadian population. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:4642–4646.
Article18. van den Hoogen BG, Osterhaus DM, Fouchier RA. Clinical impact and diagnosis of human metapneumovirus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23:1 Suppl. S25–S32.
Article19. Jartti T, van den Hoogen B, Garofalo RP, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Metapneumovirus and acute wheezing in children. Lancet. 2002; 360:1393–1394.
Article20. Williams JV, Harris PA, Tollefson SJ, Halburnt-Rush LL, Pingsterhaus JM, Edwards KM, et al. Human metapneumovirus and lower respiratory tract disease in otherwise healthy infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:443–450.
Article21. Hamelin ME, Abed Y, Boivin G. Human metapneumovirus: a new player among respiratory viruses. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 38:983–990.
Article22. Maggi F, Pifferi M, Vatteroni M, Fornai C, Tempestini E, Anzilotti S, et al. Human metapneumovirus associated with respiratory tract infections in a 3-year study of nasal swabs from infants in Italy. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:2987–2991.
Article23. Kahn JS. Epidemiology of human metapneumovirus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006; 19:546–557.
Article24. Vicente D, Montes M, Cilla G, Perez-Yarza EG, Perez-Trallero E. Differences in clinical severity between genotype A and genotype B human metapneumovirus infection in children. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:e111–e113.
Article25. Hamelin ME, Prince GA, Gomez AM, Kinkead R, Boivin G. Human metapneumovirus infection induces long-term pulmonary inflammation associated with airway obstruction and hyperresponsiveness in mice. J Infect Dis. 2006; 193:1634–1642.
Article26. Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Hamelin ME, Prince GA, Gagnon C, Bergeron Y, Bergeron MG, et al. Infection with human metapneumovirus predisposes mice to severe pneumococcal pneumonia. J Virol. 2009; 83:1341–1349.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Features of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Hospitalized Children
- A Case of Severe Human Metapneumovirus Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation in an Immunocompetent Adult
- Recovery of respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, influenza virus , and parainfluenza virus from nasopharyngeal aspirates from children with acute respiratory tract infections
- Detection of Respiratory Viruses and Atypical Bacterial Pathogens in Infants with Acute Respiratory Infections Using Multiplex PCR
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus