Efficacy of Probiotic Therapy on Atopic Dermatitis in Children: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Center, Department of Pediatrics, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bypyun@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2260682
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.3.208
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate a therapeutic efficacy of probiotics mixture (probiotics) in the treatment of children with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis (AD).
METHODS
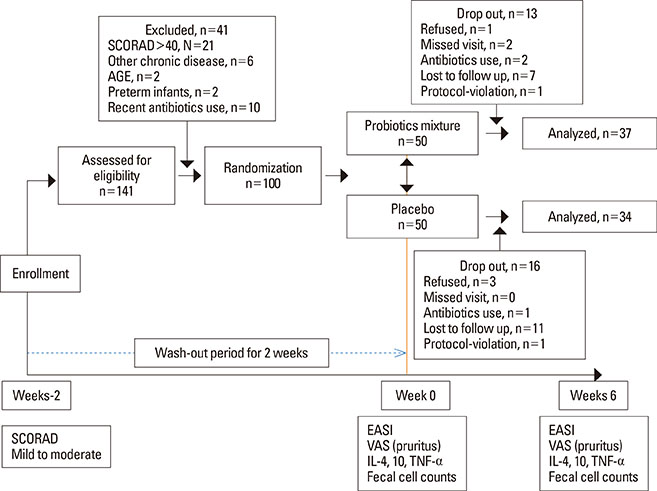
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel trial with a washout period of 2 weeks and an intervention period for 6 weeks, conducted from November 2010 to October 2011. One hundred children with mild to moderate AD (2-9 years old) were randomly allocated to the probiotics (Lactobacilluss casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bifidobacterium lactis) or placebo groups. The assessment of efficacy was based on the change in eczema area severity index (EASI), visual analogue scale for pruritus (VASP), fecal cell counts of each strains (log10[cell counts/g stool]), and serum cytokine levels (Interleukin-4 [IL-4]; IL-10; Tumor necrosis factor alpha, [TNF-alpha]) in weeks 0 and 6.
RESULTS
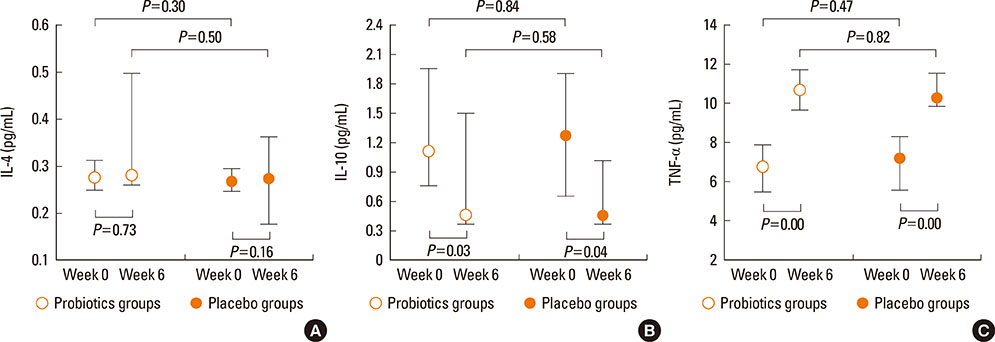
Demographics and baseline characteristics at the week 0 were not significantly different between the 2 groups. The significant increments in fecal-cell counts were observed in the probiotcs group at week 6 (P=0.00), while the cytokine levels between the 2 groups were not significantly different in week 6 (IL-4, P=0.50; IL-10, P=0.58; TNF-alpha, P=0.82). The probiotics significantly improved clinical severity after 6 weeks' intervention of probiotics; however, the placebo group also showed significant improvement (EASI; P=0.00, VASP; P=0.00).
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings showed that probiotics successfully colonized in the intestine after 6 weeks' intervention; nevertheless, we could not find an additional therapeutic or immunomodulatory effects on the treatment of AD. Further long-term studies will be necessary to clarify the therapeutic efficacy of probiotics.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
Bok Yang Pyun
J Korean Med Assoc. 2017;60(9):753-758. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2017.60.9.753.Personalized Immunomodulatory Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis: An Allergist's View
Dong-Ho Nahm
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(4):355-363. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.4.355.Lactobacillus plantarum-derived Extracellular Vesicles Protect Atopic Dermatitis Induced by Staphylococcus aureus-derived Extracellular Vesicles
Min-Hye Kim, Seng Jin Choi, Hyun-Il Choi, Jun-Pyo Choi, Han-Ki Park, Eun Kyoung Kim, Min-Jeong Kim, Byoung Seok Moon, Taek-ki Min, Mina Rho, Young-Joo Cho, Sanghwa Yang, Yoon-Keun Kim, You-Young Kim, Bok Yang Pyun
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(5):516-532. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.5.516.Probiotics as a Potential Immunomodulating Pharmabiotics in Allergic Diseases: Current Status and Future Prospects
Garima Sharma, Sin-Hyeog Im
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(6):575-590. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.6.575.
Reference
-
1. Williams H, Robertson C, Stewart A, Aït-Khaled N, Anabwani G, Anderson R, Asher I, Beasley R, Björkstén B, Burr M, Clayton T, Crane J, Ellwood P, Keil U, Lai C, Mallol J, Martinez F, Mitchell E, Montefort S, Pearce N, Shah J, Sibbald B, Strachan D, von Mutius E, Weiland SK. Worldwide variations in the prevalence of symptoms of atopic eczema in the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:125–138.2. Oh JW, Kim KE, Pyun BY, Lee HR, Choung JT, Hong SJ, Park KS, Lee SY, Song SW, Kim CH, Ahn KM, Nam SY, Shon MH, Kim WK, Lee MH, Kwon BC, Choi SY, Lee SY, Lee HB, Lee SI, Lee JS. Nationwide study for epidemiological change of atopic dermatitis in school aged children between 1995 and 2000 and kindergarten aged children in 2003 in Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2003; 13:227–237.3. Lluis A, Schaub B. Lesson from the farm environment. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 12:158–163.4. Martino DJ, Prescott SL. Silent mysteries: epigenetic paradigms could hold the key to conquering the epidemic of allergy and immune disease. Allergy. 2010; 65:7–15.5. Misery L. Therapeutic perspectives in atopic dermatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011; 41:267–271.6. Ghadimi D, Fölster-Holst R, de Vrese M, Winkler P, Heller KJ, Schrezenmeir J. Effects of probiotic bacteria and their genomic DNA on TH1/TH2-cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of healthy and allergic subjects. Immunobiology. 2008; 213:677–692.7. Rose MA, Stieglitz F, Köksal A, Schubert R, Schulze J, Zielen S. Efficacy of probiotic Lactobacillus GG on allergic sensitization and asthma in infants at risk. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:1398–1405.8. Oelschlaeger TA. Mechanisms of probiotic actions - A review. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010; 300:57–62.9. Chapman CM, Gibson GR, Rowland I. Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains? Eur J Nutr. 2011; 50:1–17.10. van der Aa LB, Heymans HS, van Aalderen WM, Sprikkelman AB. Probiotics and prebiotics in atopic dermatitis: review of the theoretical background and clinical evidence. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:e355–e367.11. Stanton C, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Van Sinderen D. Fermented functional foods based on probiotics and their biogenic metabolites. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005; 16:198–203.12. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh). 1980; (92):S44–S47.13. Consensus Report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Severity scoring of atopic dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Dermatology. 1993; 186:23–31.14. Saghaei M. Random allocation software for parallel group randomized trials. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2004; 4:26.15. Kalliomäki M, Antoine JM, Herz U, Rijkers GT, Wells JM, Mercenier A. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: prevention and management of allergic diseases by probiotics. J Nutr. 2010; 140:713S–721S.16. van Nimwegen FA, Penders J, Stobberingh EE, Postma DS, Koppelman GH, Kerkhof M, Reijmerink NE, Dompeling E, van den Brandt PA, Ferreira I, Mommers M, Thijs C. Mode and place of delivery, gastrointestinal microbiota, and their influence on asthma and atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:948–955.e1-e3.17. Gerasimov SV, Vasjuta VV, Myhovych OO, Bondarchuk LI. Probiotic supplement reduces atopic dermatitis in preschool children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010; 11:351–361.18. Woo SI, Kim JY, Lee YJ, Kim NS, Hahn YS. Effect of Lactobacillus sakei supplementation in children with atopic eczema-dermatitis syndrome. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 104:343–348.19. Kuitunen M, Kukkonen K, Juntunen-Backman K, Korpela R, Poussa T, Tuure T, Haahtela T, Savilahti E. Probiotics prevent IgE-associated allergy until age 5 years in cesarean-delivered children but not in the total cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:335–341.20. Kopp MV, Hennemuth I, Heinzmann A, Urbanek R. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of probiotics for primary prevention: no clinical effects of Lactobacillus GG supplementation. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:e850–e856.21. Vanderhoof JA. Probiotics in allergy management. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008; 47:Suppl 2. S38–S40.22. Candela M, Rampelli S, Turroni S, Severgnini M, Consolandi C, De Bellis G, Masetti R, Ricci G, Pession A, Brigidi P. Unbalance of intestinal microbiota in atopic children. BMC Microbiol. 2012; 12:95.23. Lee J, Seto D, Bielory L. Meta-analysis of clinical trials of probiotics for prevention and treatment of pediatric atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:116–121.e11.24. Won TJ, Kim B, Lim YT, Song DS, Park SY, Park ES, Lee DI, Hwang KW. Oral administration of Lactobacillus strains from Kimchi inhibits atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. J Appl Microbiol. 2011; 110:1195–1202.25. Albesharat R, Ehrmann MA, Korakli M, Yazaji S, Vogel RF. Phenotypic and genotypic analyses of lactic acid bacteria in local fermented food, breast milk and faeces of mothers and their babies. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2011; 34:148–155.26. Albano H, van Reenen CA, Todorov SD, Cruz D, Fraga L, Hogg T, Dicks LM, Teixeira P. Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from "Alheira", a traditional fermented sausage produced in Portugal. Meat Sci. 2009; 82:389–398.27. Dong H, Rowland I, Yaqoob P. Comparative effects of six probiotic strains on immune function in vitro. Br J Nutr. 2012; 108:459–470.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of cetirizine in dogs with chronic atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial
- Probiotic Supplementation for Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial
- A Double-Blind, Randomized, Crossover Study to Compare the Effectiveness of Montelukast on Atopic Dermatitis in Korean Children
- Effect of Probiotics on the Treatment of Children with Atopic Dermatitis
- Intramuscular Injection of Autologous Serum in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Preliminary Randomized Clinical Trial