Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2012 Mar;4(2):110-111. 10.4168/aair.2012.4.2.110.
A Case of Korean Ginseng-Induced Anaphylaxis Confirmed by Open Oral Challenge and Basophil Activation Test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University, School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 3Korea National Sports University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2260369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.2.110
Abstract
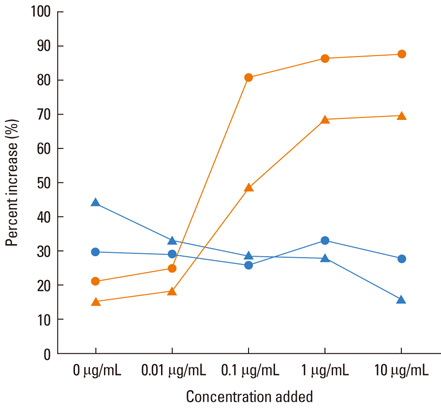
- Two case reports discussing Korean ginseng-induced allergic reactions have been published; both were inhalation-induced respiratory allergies in occupational settings. In this report we discuss the first case of anaphylaxis that developed after an oral intake of ginseng, confirmed by an open oral challenge, a skin prick test (SPT), and a basophil activation test (BAT). A 44-year-old man experienced rhinorrhea and nasal stiffness, followed by respiratory difficulty with wheeze and abdominal pain 10 minutes after oral intake of fresh ginseng. He had suffered from episodes of allergic rhinitis during the spring season for several years. Upon presentation, a physical examination, chest radiograph, and routine laboratory tests were unremarkable. Total serum IgE level was 41 IU/mL. The SPT results showed strong positive responses to alder, birch pollens, and ginseng extracts (1:500 w/v). The methacholine bronchial challenge test revealed a positive result at PC20 of 5.83 mg/mL. The open oral challenge was performed using 50 g of fresh ginseng and showed immediate onset of facial flushing, cough, respiratory difficulty with wheeze, and abdominal pain combined with a significant decrease in FEV1 levels (54% from the baseline). Serum-specific IgE and IgG4 antibodies were not detectable by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. BAT showed a remarkable increase in the expression of CD203c and CD63 with the addition of ginseng extract in a dose-dependent manner, while no changes were noted in the controls. In conclusion, oral intake of Korean ginseng could induce anaphylaxis, which is mediated by non-IgE-dependent direct activation of basophil/mast cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abdominal Pain
Adult
Alnus
Anaphylaxis
Antibodies
Basophils
Betula
Bronchial Provocation Tests
Cough
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Flow Cytometry
Flushing
Humans
Hypersensitivity
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin G
Methacholine Chloride
Panax
Physical Examination
Pollen
Rhinitis
Rhinitis, Allergic, Perennial
Seasons
Skin
Thorax
Antibodies
Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin G
Methacholine Chloride
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management
Gwang Cheon Jang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sun Hee Choi, Woo-Jung Song, Soo-Young Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yeong-Min Ye, Hyun-Jung Jin, Mi Yong Shin, Soo-Jin Lee, Hye One Kim, Jihyun Kim, Jae-Woo Jung, Hee-Bom Moon, Youngmin Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):181-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.181.Mixed plant extract-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis
Jin Wha Choi, Jeong Ok Lee, Jaehee Choi, Youngshin Han, Jihyun Kim, Kangmo Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):219-223. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.219.
Reference
-
1. Yun TK. Brief introduction of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Korean Med Sci. 2001. 16:Suppl. S3–S5.2. Lee JY, Lee YD, Bahn JW, Park HS. A case of occupational asthma and rhinitis caused by Sanyak and Korean ginseng dusts. Allergy. 2006. 61:392–393.3. Kim KM, Kwon HS, Jeon SG, Park CH, Sohn SW, Kim DI, Kim SS, Chang YS, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. Korean ginseng-induced occupational asthma and determination of IgE binding components. J Korean Med Sci. 2008. 23:232–235.4. Kim JH, An S, Kim JE, Choi GS, Ye YM, Park HS. Beef-induced anaphylaxis confirmed by the basophil activation test. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010. 2:206–208.5. Bühring HJ, Streble A, Valent P. The basophil-specific ectoenzyme E-NPP3 (CD203c) as a marker for cell activation and allergy diagnosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2004. 133:317–329.6. Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Hagendorens MM, Aerts NE, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ. Basophil activation test by flow cytometry: present and future applications in allergology. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2008. 74:201–210.