Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 Mar;6(2):175-178. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.2.175.
Potential Masking of Airway Eosinophilic Inflammation by Combination Therapy in Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dcchoi@skku.edu
- 2Center for Health Promotion, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Bundang Jaeseng Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2260264
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.2.175
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Long-acting beta2 agonists (LABA) may mask ongoing bronchial inflammation, leaving asthmatic patients at greater risk of severe complications. The aim of this study was to compare the effect of combination therapy using low-dose inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) plus LABA on airway inflammation in asthma to the effect of medium-dose ICS alone.
METHODS
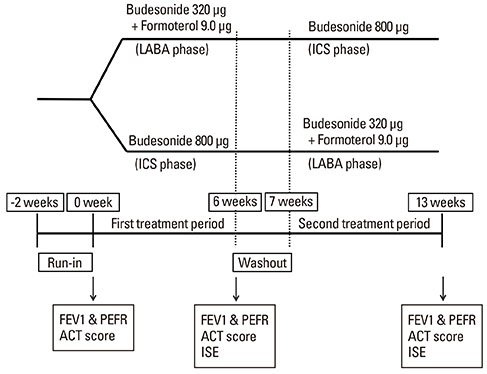
Twenty-four patients with asthma not controlled by low-dose (400 microg per day) budesonide alone were enrolled in this prospective crossover study. Patients were randomized into 2 treatment phases: one receiving medium-dose (800 microg per day) budesonide (ICS phase), and the other receiving a combination therapy of low-dose budesonide/formoterol (360 microg/9 microg per day) delivered by a single inhaler (LABA phase). Each treatment phase lasted for 6 week, after which patients were crossed over. Asthma symptoms, lung function, and airway inflammation were compared between the 2 phases.
RESULTS
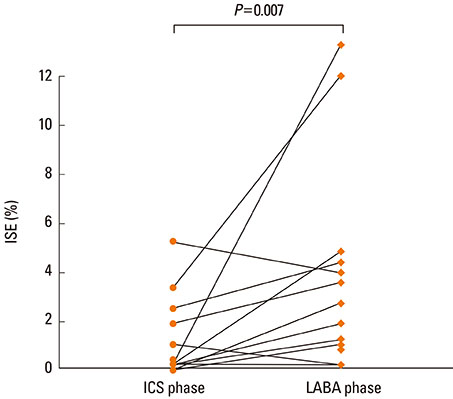
Twenty-three patients completed the study; adequate sputum samples were collected from 17 patients. Asthma symptoms and lung function remained similar between the 2 phases. However, the mean sputum eosinophil percentage was higher in the LABA phase than in the ICS phase (5.07+/-3.82% vs. 1.02+/-1.70%; P<0.01). Sputum eosinophilia (> or =3%) was more frequently observed in the LABA phase than in the ICS phase (six vs. two).
CONCLUSION
Addition of LABA may mask airway eosinophilic inflammation in asthmatic patients whose symptoms are not controlled with low-dose ICS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. United States: Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA);2010.2. Greenstone IR, Ni Chroinin MN, Masse V, Danish A, Magdalinos H, Zhang X, Ducharme FM. Combination of inhaled long-acting beta2-agonists and inhaled steroids versus higher dose of inhaled steroids in children and adults with persistent asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005; (4):CD005533.3. Kips JC, O'Connor BJ, Inman MD, Svensson K, Pauwels RA, O'Byrne PM. A long-term study of the antiinflammatory effect of low-dose budesonide plus formoterol versus high-dose budesonide in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:996–1001.4. Pauwels RA, Löfdahl CG, Postma DS, Tattersfield AE, O'Byrne P, Barnes PJ, Ullman A. Formoterol and Corticosteroids Establishing Therapy (FACET) International Study Group. Effect of inhaled formoterol and budesonide on exacerbations of asthma. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:1405–1411.5. Woolcock A, Lundback B, Ringdal N, Jacques LA. Comparison of addition of salmeterol to inhaled steroids with doubling of the dose of inhaled steroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 153:1481–1488.6. Gardiner PV, Ward C, Booth H, Allison A, Hendrick DJ, Walters EH. Effect of eight weeks of treatment with salmeterol on bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory indices in asthmatics. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994; 150:1006–1011.7. McIvor RA, Pizzichini E, Turner MO, Hussack P, Hargreave FE, Sears MR. Potential masking effects of salmeterol on airway inflammation in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 158:924–930.8. Aziz I, Wilson AM, Lipworth BJ. Effects of once-daily formoterol and budesonide given alone or in combination on surrogate inflammatory markers in asthmatic adults. Chest. 2000; 118:1049–1058.9. Salpeter SR, Ormiston TM, Salpeter EE. Meta-analysis: respiratory tolerance to regular beta2-agonist use in patients with asthma. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 140:802–813.10. Cates CJ, Cates MJ. Regular treatment with salmeterol for chronic asthma: serious adverse events. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; (3):CD006363.11. Thomas M, von Ziegenweidt J, Lee AJ, Price D. High-dose inhaled corticosteroids versus add-on long-acting beta-agonists in asthma: an observational study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:116–121.e10.12. Kwon HS, Lee SH, Yang MS, Lee SM, Kim SH, Kim DI, Sohn SW, Park CH, Park HW, Kim SS, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY, Chang YS. Correlation between the Korean version of Asthma Control Test and health-related quality of life in adult asthmatics. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:621–627.13. Kwon NH, Oh MJ, Min TH, Lee BJ, Choi DC. Causes and clinical features of subacute cough. Chest. 2006; 129:1142–1147.14. Sims EJ, Price D, Haughney J, Ryan D, Thomas M. Current control and future risk in asthma management. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:217–225.15. Crimi E, Spanevello A, Neri M, Ind PW, Rossi GA, Brusasco V. Dissociation between airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 157:4–9.16. O'Byrne PM. Therapeutic strategies to reduce asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:257–263.17. Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 360:1715–1721.18. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: new safety requirements for long-acting inhaled asthma medications called Long-Acting Beta-Agonists (LABAs). Silver Spring (MD): U.S. Food and Drug Administration;cited 2012 Feb 18. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/postmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPatientsandProviders/ucm200776.htm.19. Salpeter SR, Buckley NS, Ormiston TM, Salpeter EE. Meta-analysis: effect of long-acting beta-agonists on severe asthma exacerbations and asthma-related deaths. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 144:904–912.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eosinophilic Bronchitis, Eosinophilia Associated Genetic Variants, and Notch Signaling in Asthma
- Evolution of Asthma Concept and Effect of Current Asthma Management Guidelines
- Relation between Eosinophils in Induced Sputum and Severity of Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Viral Infections and the Inception and Exacerbation of Asthma
- Inhaled Corticosteroids in Asthma