Korean J Hematol.
2005 Jun;40(2):120-123. 10.5045/kjh.2005.40.2.120.
A Case of Promyelocytic Leukemia with Basophil-like Granules
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hschi@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2252348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2005.40.2.120
Abstract
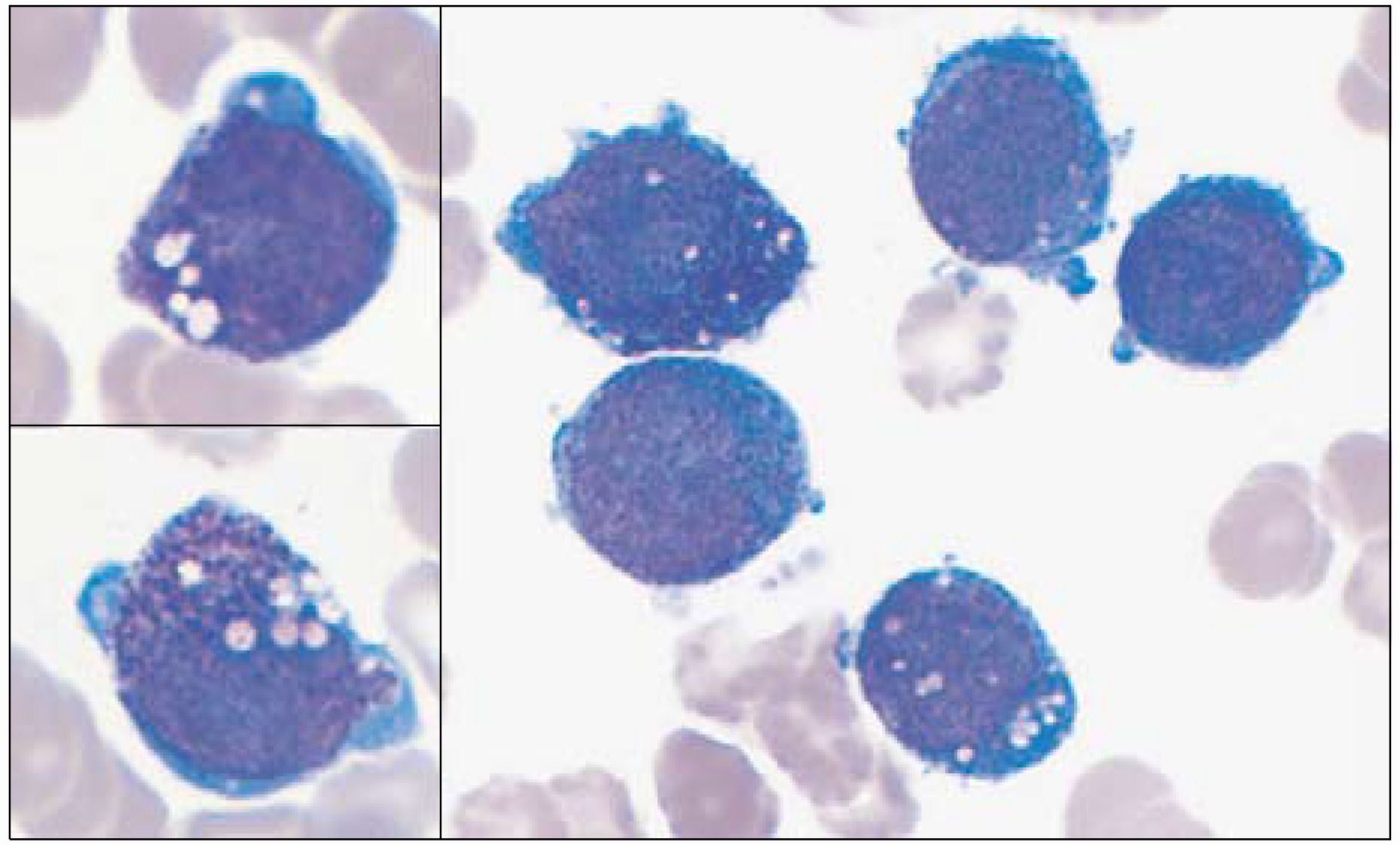
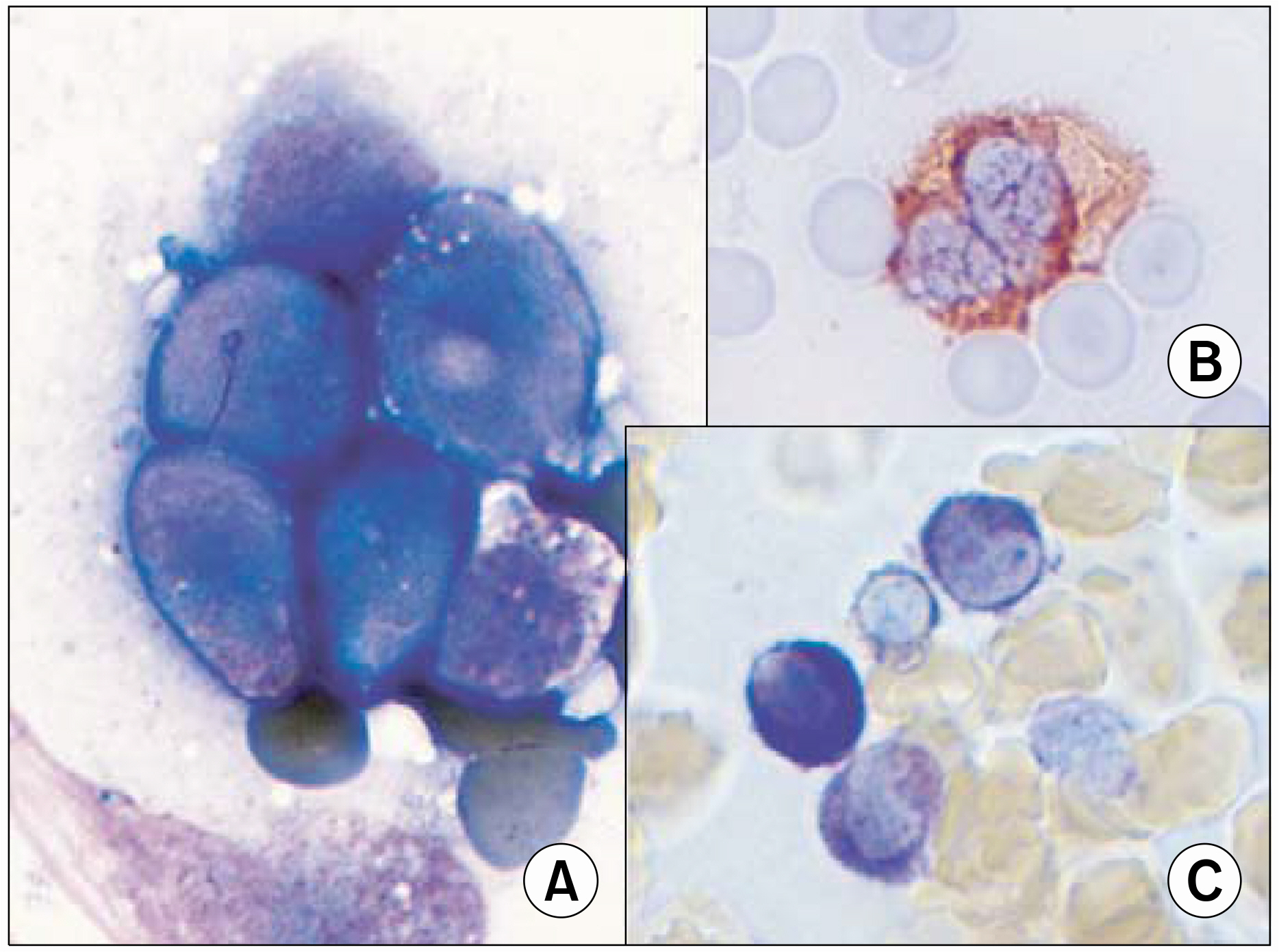
- According to the FAB (French-American-British) classification, two main cytological subtypes are recognized: the classical hypergranular and the microgranular variant. However, other morphological variants have been reported in the literature. Therefore, careful examination is needed to diagnose acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Herein, the case of an APL variant, with basophil-like granules, occurring in a 65 year-old woman admitted due to high fever is reported. The peripheral blood showed blasts and increased basophils. A bone marrow smear showed leukemic blasts, with irregular nuclei and coarse basophil-like granules, in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic vacuoles were also noted, but no Auer rod was found. The blasts showed positivity toward MPO, tryptase and toluidine blue staining. The immunophenotypes revealed a myeloid lineage, with aberrant expression of CD2 and CD7. The karyotype was t(15;17)(q22;q12) in 17 out of 20 metaphases. The RT-PCR was positive for long form PML/RARalpha transcripts. Four weeks after chemotherapy, her bone marrow status findings were in complete remission, with the karyotype converted to normal. Basophil-like granules in the blasts and promyelocytes became decreased during the course of all-transretinoic acid (ATRA) treatment. The chimeric transcript of PML/RARalpha converted to negative after consolidation chemotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Brunning RD, Matutes E, Flandrin G, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia with recurrent genetic abnormalities. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: IARC press. 2006. 84–6.2). Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, et al. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med. 1985; 103:620–5.3). Castoldi GL, Liso V, Specchia G, Tomasi P. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: morphological aspects. Leukemia. 1994; 8:1441–6.4). Neame PB, Soamboonsrup P, Leber B, et al. Morphology of acute promyelocytic leukemia with cytogenetic or molecular evidence for the diagnosis: characterization of additional microgranular variants. Am J Hematol. 1997; 56:131–42.
Article5). Liso V, Bennett J. Morphological and cytochemical characteristics of leukaemic promyelocytes. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2003; 16:349–55.
Article6). Sainty D, Liso V, Cantu-Rajnoldi A, et al. A new morphologic classification system for acute promyelocytic leukemia distinguishes cases with underlying PLZF/RARA gene rearrangements. Blood. 2000; 96:1287–96.7). Tallman MS, Andersen JW, Schiffer CA, et al. All-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia: longterm outcome and prognostic factor analysis from the North American Intergroup protocol. Blood. 2002; 100:4298–302.
Article8). Grimwade D, Biondi A, Mozziconacci MJ, et al. Characterization of acute promyelocytic leukemia cases lacking the classic t(15;17): results of the European Working Party. Groupe Francais de Cytogenetique Hematologique, Groupe de Francais d'Hematologie Cellulaire, UK Cancer Cytogenetics Group and BIOMED 1 European Community-Concerted Action Molecular Cytogenetic Diagnosis in Haematological Malignancies. Blood. 2000; 96:1297–308.9). McKenna RW, Parkin J, Bloomfield CD, Sundberg RD, Brunning RD. Acute promyelocytic leukaemia: a study of 39 cases with identification of a hyper-basophilic microgranular variant. Br J Haematol. 1982; 50:201–14.
Article10). Yu RQ, Huang W, Chen SJ, Jiang SD, Chen Z. A case of acute eosinophilic granulocytic leukemia with PML-RAR alpha fusion gene expression and response to all-trans retinoic acid. Leukemia. 1997; 11:609–11.
Article11). Tallman MS, Hakimian D, Snower D, Rubin CM, Rei-sel H, Variakojis D. Basophilic differentiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 1993; 7:521–6.12). Kaleem Z, Crawford E, Pathan MH, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of acute leukemias. Diagnostic utility and critical analysis of data. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003; 127:42–8.13). Gotoh H, Murakami S, Oku N, et al. Translocations t(15;17) and t(9;14)(q34;q22) in a case of acute promyelocytic leukemia with increased number of basophils. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988; 36:103–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Promyelocytic sarcoma of the sternum: a case report and review of the literature
- A case of microgranular acute promyelocytic leukemia
- A case of microgranular acute promyelocytic leukemia with positive reaction of nonspecific esterase
- A case of microgranular variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia with strong positive reaction in nonspecific esterase stain
- Overview of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia