Korean Circ J.
2008 Apr;38(4):212-219. 10.4070/kcj.2008.38.4.212.
Effect of High Dose External Irradiation on the Matrix Metalloprotease-2 Expression in a Rat Carotid Artery Injury Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. whitesh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2225822
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2008.38.4.212
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Remodeling of the injured arterial wall is dependent on the action of several extracellular proteases, including matrix metalloprotease-2 (MMP-2), and this protein is associated with the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. The effect of a high dose of external irradiation (20 Gy) on the MMP-2 expression in neointimal hyperplasia is not known.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
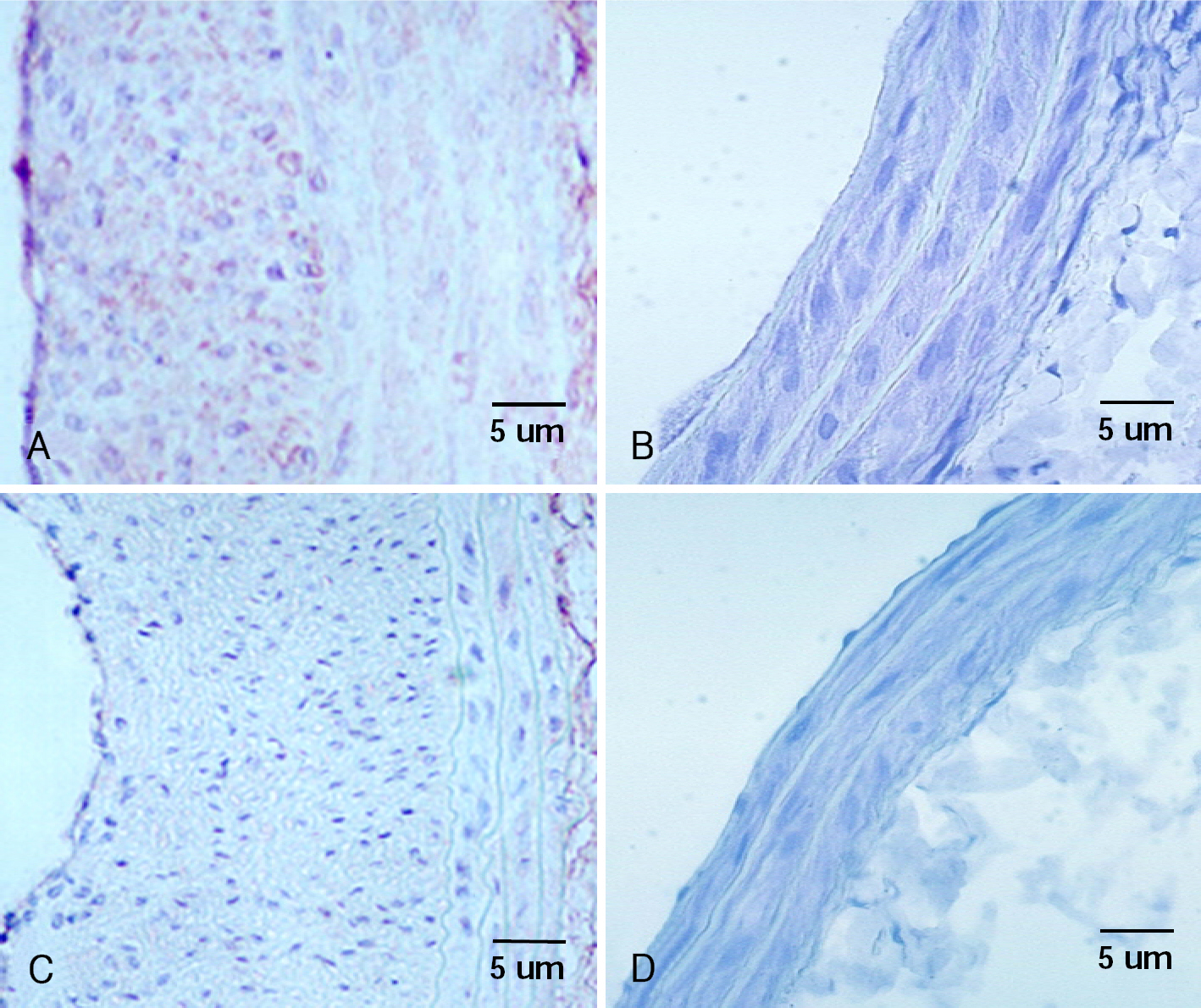
Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to balloon injury to the common carotid artery. At 24 hours after injury, 20 Gy external irradiation was done for the irradiated group (n=25) and this was not done for the control group (n=25). The percent area stenosis, the maximal intimal thickness, the intima/media area ratio on H-E staining and the MMP-2 positivity on the immunohistochemical staining were measured. Western blotting and a gelatin zymogram for determining the MMP-2 protein expression were also performed after the injury.
RESULTS
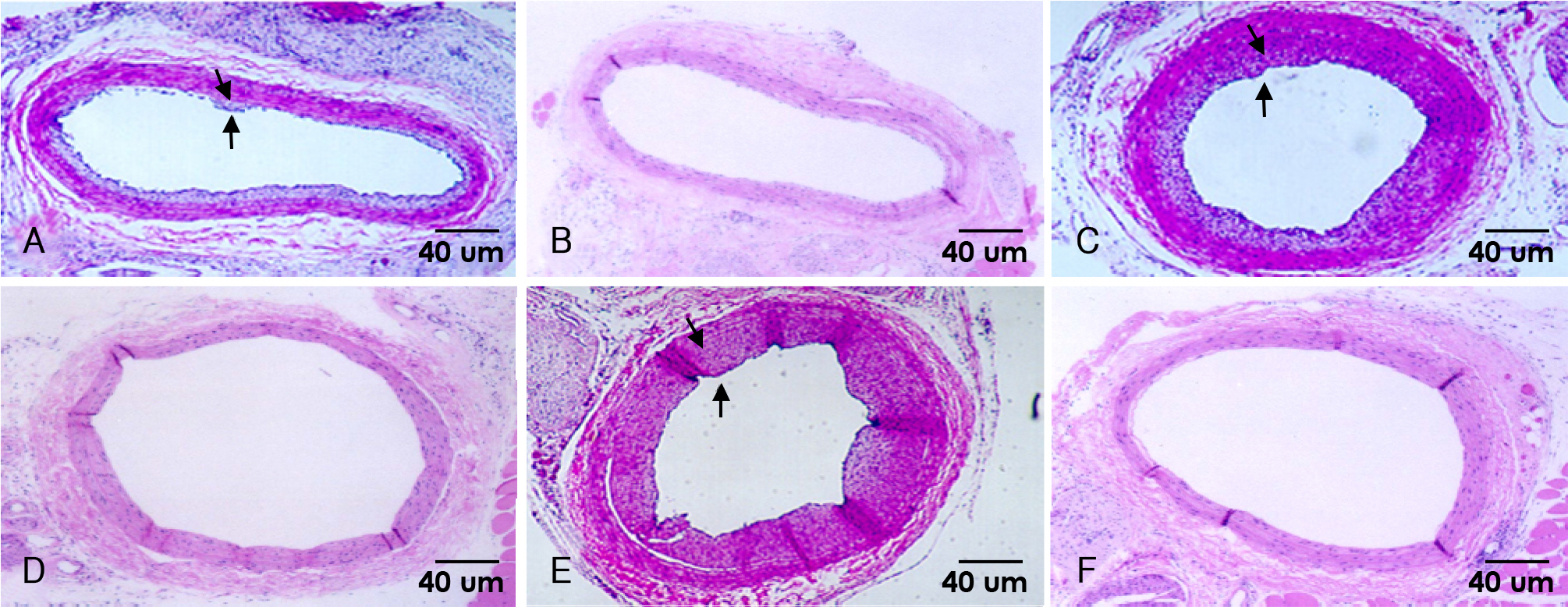
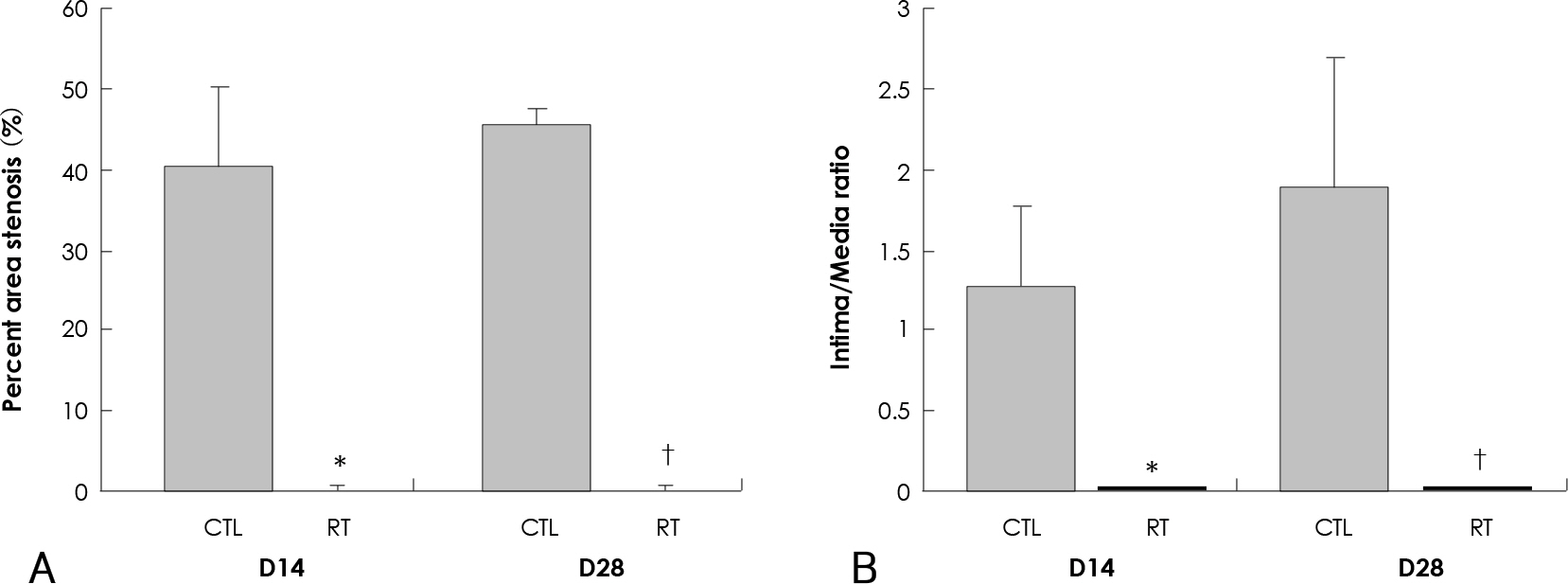
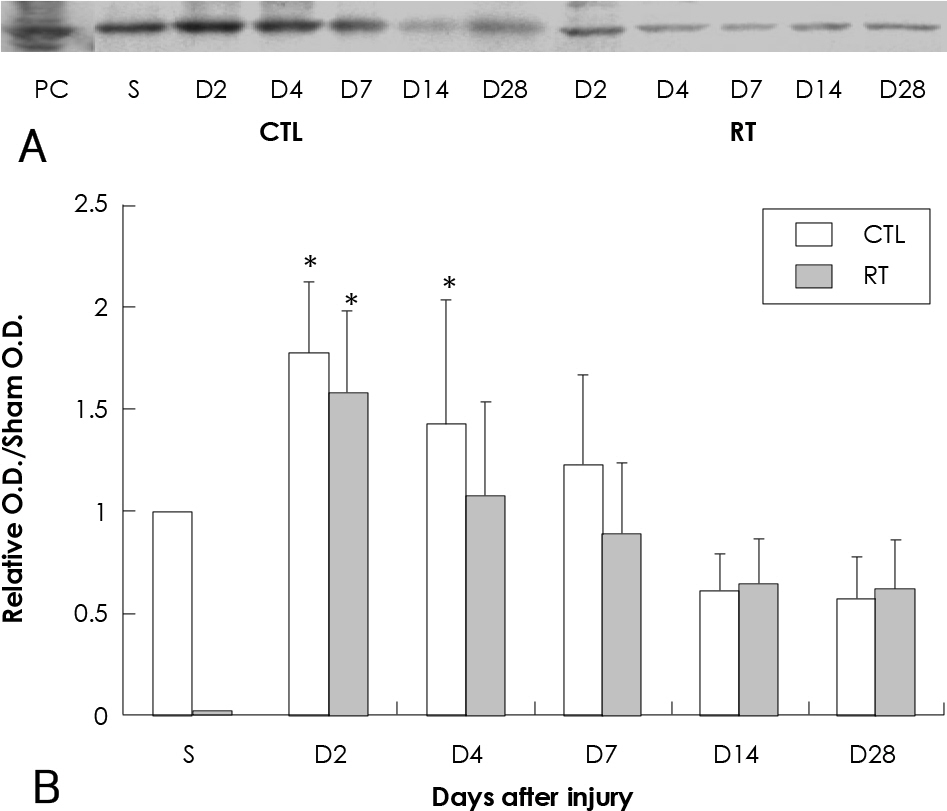
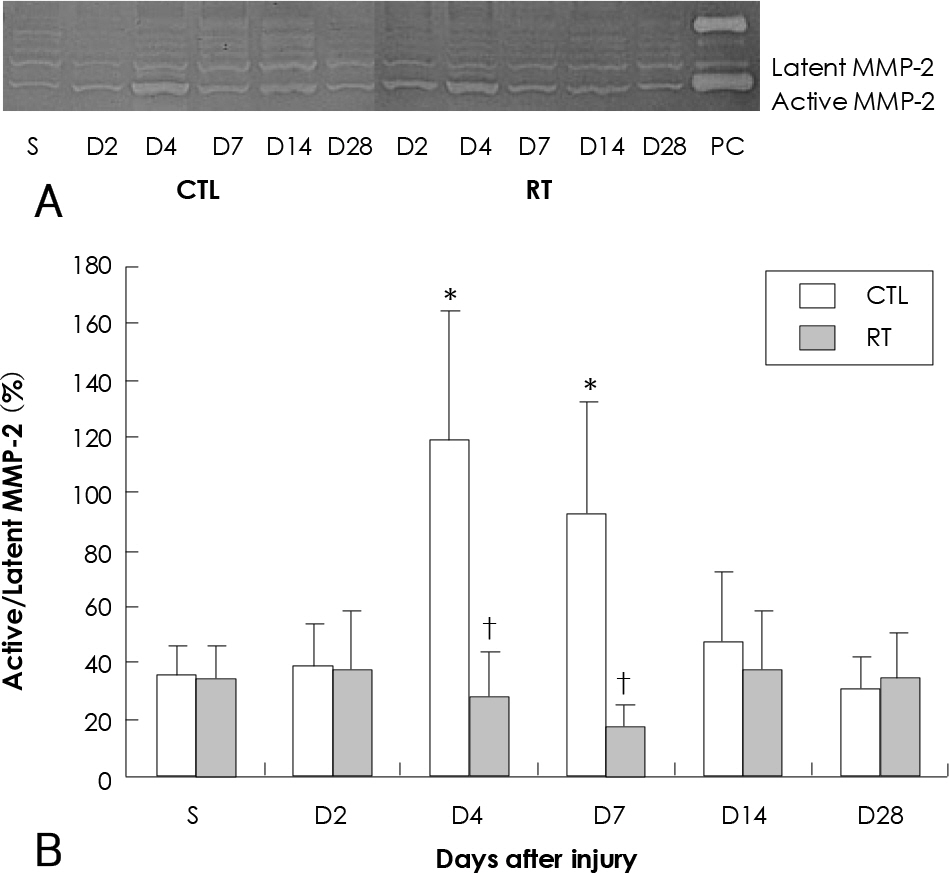
The parameters of neointimal hyperplasia such as the percent area stenosis, the maximal intimal thickness and the intima/media area ratio were 40.2+/-12.1%, 0.30+/-0.12 mm and 1.27+/-0.32, respectively, at 14 days after injury, and these parameters were maintained as a hyperplastic state at 28 days after injury in the control group. There was undetectable neointimal hyperplasia in the irradiated group compared with the control group (p<0.01). Western blotting demonstrated an increase in the MMP-2 protein level beginning 2 to 4 days after injury in the control group, but there was only a transient increase in the MMP-2 level at day 2 after injury in the irradiated group. The gelatin zymogram and immunohistochemical staining also showed the expression of MMP-2 in the control group, but not in the irradiated group.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest the suppressed expression of MMP-2 is associated with reduced neointimal hyperplasia in the balloon injury-rat model.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Serruys PW, de Jaegere P, Kiemeneij F, et al. A comparison of balloon-expandable-stent implantation with balloon angioplasty in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:489–95.
Article2. Bhargava B, Karthikeyan G, Abizaid AS, Mehran R. New approaches to preventing restenosis. BMJ. 2003; 327:274–9.
Article3. Fingerle J, Johnson R, Clowes AW, Majesky MW, Reidy MA. Role of platelets in smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration after vascular injury in rat carotid artery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989; 86:8412–6.
Article4. Clowes AW, Reidy MA, Clowes MM. Mechanisms of stenosis after arterial injury. Lab Invest. 1983; 49:208–15.5. Dollery CM, McEwan JR, Henny AM. Matrix metalloproteinases and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 1995; 77:863–8.
Article6. Pauly RR, Passaniti A, Bilato C, et al. Migration of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells through a basement membrane barrier requires type IV collagenase activity and is inhibited by cellular differentiation. Circ Res. 1994; 75:41–54.
Article7. vom Dahl J, Dietz U, Haager PK, et al. Rotational atherectomy does not reduce recurrent in-stent restenosis: results of the angioplasty versus rotational atherectomy for treatment of diffuse in-stent restenosis trial (ARTIST). Circulation. 2002; 105:583–8.8. Alfonso F, Zueco J, Cequier A, et al. A randomized comparison of repeat stenting with balloon angioplasty in patients with in-stent restenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 42:796–805.9. Albiero R, Nishida T, Karvouni E, et al. Cutting balloon angioplasty for the treatment of in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2000; 50:452–9.
Article10. Waksman R, Raizner AE, Yeung AC, Lansky AJ, Vandertie L. Use of localised intracoronary beta-radiation in treatment of in-stent restenosis. Lancet. 2002; 359:551–7.11. Leon MB, Teirstein PS, Moses JW, et al. Localized intracoronary gamma-radiation therapy to inhibit the recurrence of restenosis after stenting. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:250–6.
Article12. Bae JW, Kang HJ, Kim KI, et al. Long-term effect of repeated brachytherapy in intracoronary brachytherapy failed lesions. Korean Circ J. 2004; 34:937–44.
Article13. Shimotakahara S, Mayberg MR. Gamma irradiation inhibits neointimal hyperplasia in rats after arterial injury. Stroke. 1994; 25:424–8.
Article14. Verin V, Popowski Y, Urban P, et al. Intra-arterial beta irradiation prevents neointimal hyperplasia in a hypercholesterolemic rabbit restenosis model. Circulation. 1995; 92:2284–90.
Article15. Wiedermann JG, Marboe C, Amols H, Schwartz A, Weinberger J. Intracoronary irradiation markedly reduces neointimal proliferation after balloon angioplasty in swine: persistent benefit at 6-month follow-up. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995; 25:1451–6.
Article16. Verin V, Popowski Y, de Bruyne B, et al. Endoluminal beta-radiation therapy for the prevention of coronary restenosis after balloon angioplasty. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:243–9.
Article17. Zeymer U, Fishbein MC, Forrester JS, Cercek B. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemisty in rat aorta after balloon denudation. Am J Pathol. 1992; 141:685–90.18. Stone GW, Ellis SG, O'Shaughnessy CD, et al. Paclitaxel-eluting stents vs vascular brachytherapy for in-stent restenosis within bare-metal stents. JAMA. 2006; 295:1253–63.
Article19. Holmes DR Jr, Teirstein P, Satler L, et al. Sirolimus-eluting stents vs vascular brachytherapy for in-stent restenosis within bare-metal stents. JAMA. 2006; 295:1264–73.
Article20. Liu MW, Roubin GS, King SB 3rd. Restenosis after coronary angioplasty: potential biologic determinants and role of intimal hyperplasia. Circulation. 1989; 79:1374–87.21. Hong YJ, Jeong MH. New methods of vascular brachytherapy for coronary stent restenosis. Korean Circ J. 2003; 33:967–76.
Article22. Pfisterer M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Buser PT, et al. Late clinical events after clopidogrel discontinuation may limit the benefit of drug-eluting stents: an observational study of drug-eluting versus bare-metal stents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:2584–91.23. Park DW, Park SW, Park KH, et al. Frequency of and risk factors for stent thrombosis after drug-eluting stent implantation during longterm follow up. Am J Cardiol. 2006; 98:352–6.24. Powers BE, Thames HD, Gillette EL. Long-term adverse effects of radiation inhibiton of restenosis: radiation injury to the aorta and branch arteries in a canine model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 45:753–9.25. Weinberger J, Amols H, Ennis RD, Schwartz A, Wiedermann JG, Marboe CM. Intracoronary irradiation: dose response for the prevention of restenosis in swine. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 36:767–75.
Article26. Zempo N, Kenagy RD, Au YP, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases of vascular wall cells are increased in balloon-injured rat carotid artery. J Vasc Surg. 1994; 20:209–17.
Article27. Ge J, Shen C, Liang C, Chen L, Qian J, Chen H. Elevated matrix metalloproteinase expression after stent implantation is associated with restenosis. Int J Cardiol. 2006; 112:85–90.
Article28. Kim YJ, Beak SH, Jin SW, et al. Effect of low dose external radiation on MMP-2 expression in rat carotid artery injury model. Korean Circ J. 2002; 32:1091–9.29. Jenkins GM, Crow MT, Bilato C, et al. Increased expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase and preferential localization of matrix metalloprotenase-2 to the neointima of balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Circulation. 1998; 97:82–90.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Low Dose External Irradiation on MMP-2 Expression in Rat Carotid Artery Injury Model
- The Effect of External Beam Radiation on Neointimal Formation in the Rat Carotid Injury Model
- The Inhibition of Neointimal Hyperplasia by Combination of External Radiation and Paclitaxel in A Rat Carotid Injury Model
- An Anatomical Variant : Low-Lying Bifurcation of the Common Carotid Artery, and Its Surgical Implications in Anterior Cervical Discectomy
- Congenital External Carotid-Internal Carotid Artery Anastomosis