J Rheum Dis.
2012 Apr;19(2):82-90. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.2.82.
COMP-Angiopoietin-1 Stimulates Synovial Proliferation but Suppresses Osteoclast by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Osteoblast Maturation in Collagen-Induced Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. goldgu@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Clinical Research Institute, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry, Medical School and Diabetes Research Center, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 4National Research Laboratory of Vascular Biology and Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2223105
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.2.82
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) is a potent angiogenic factor that can increase synovial angiogenesis and also enhance osteoblast maturation and bone formation. However, its role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has not been well documented. Thus, we investigated roles of Ang1 in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
METHODS
A recombinant adenovirus carrying the gene that encodes either cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (AdCOMP)-Ang1 (a modified form of Ang1) or LacZ (AdLacZ) was injected intravenously into CIA mice. Clinical, radiological, histopathological, and immunofluorescent analyses were performed. Serum levels of receptor activators of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) and expression of osteoblast maturation genes were analyzed.
RESULTS
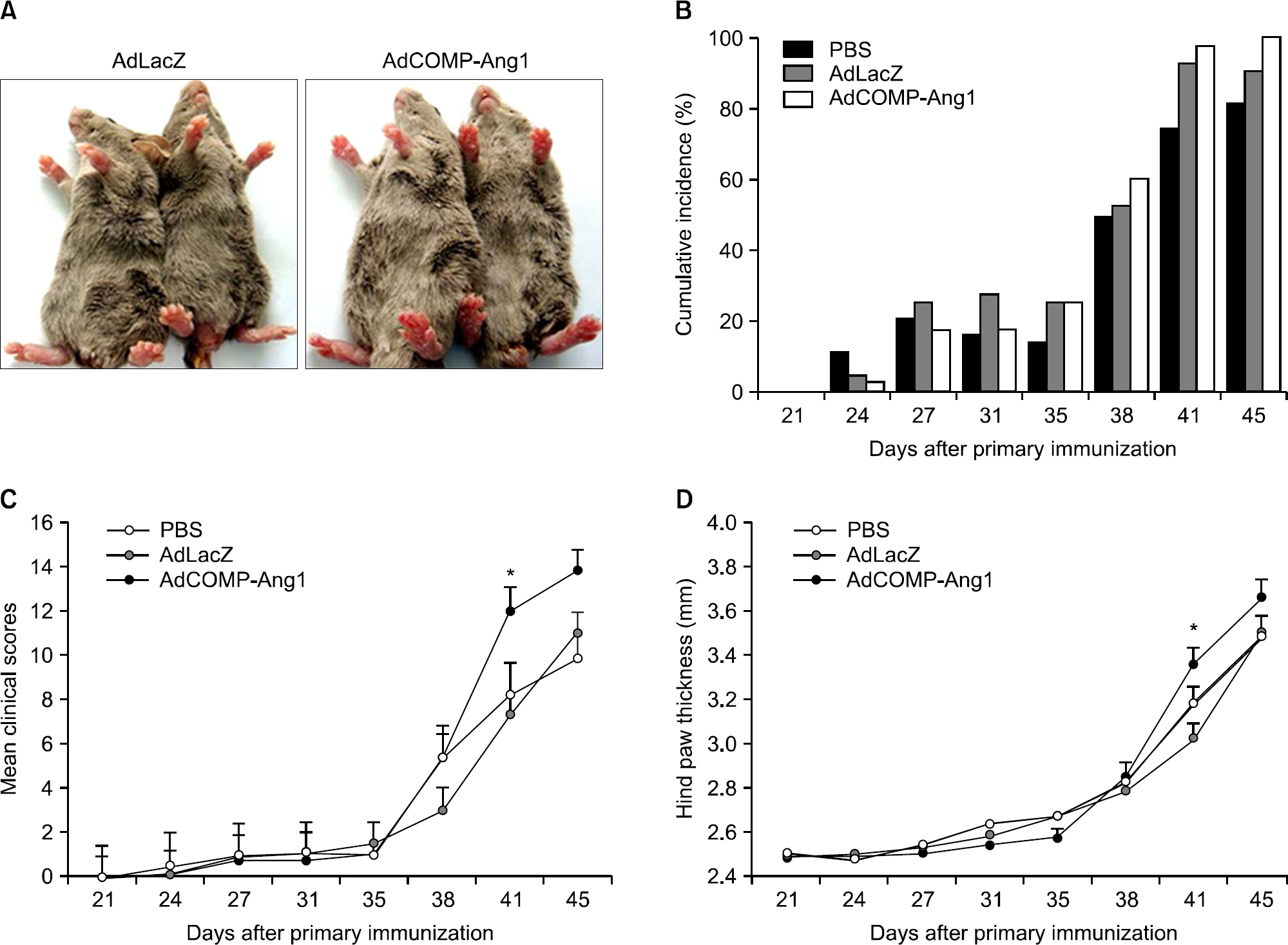
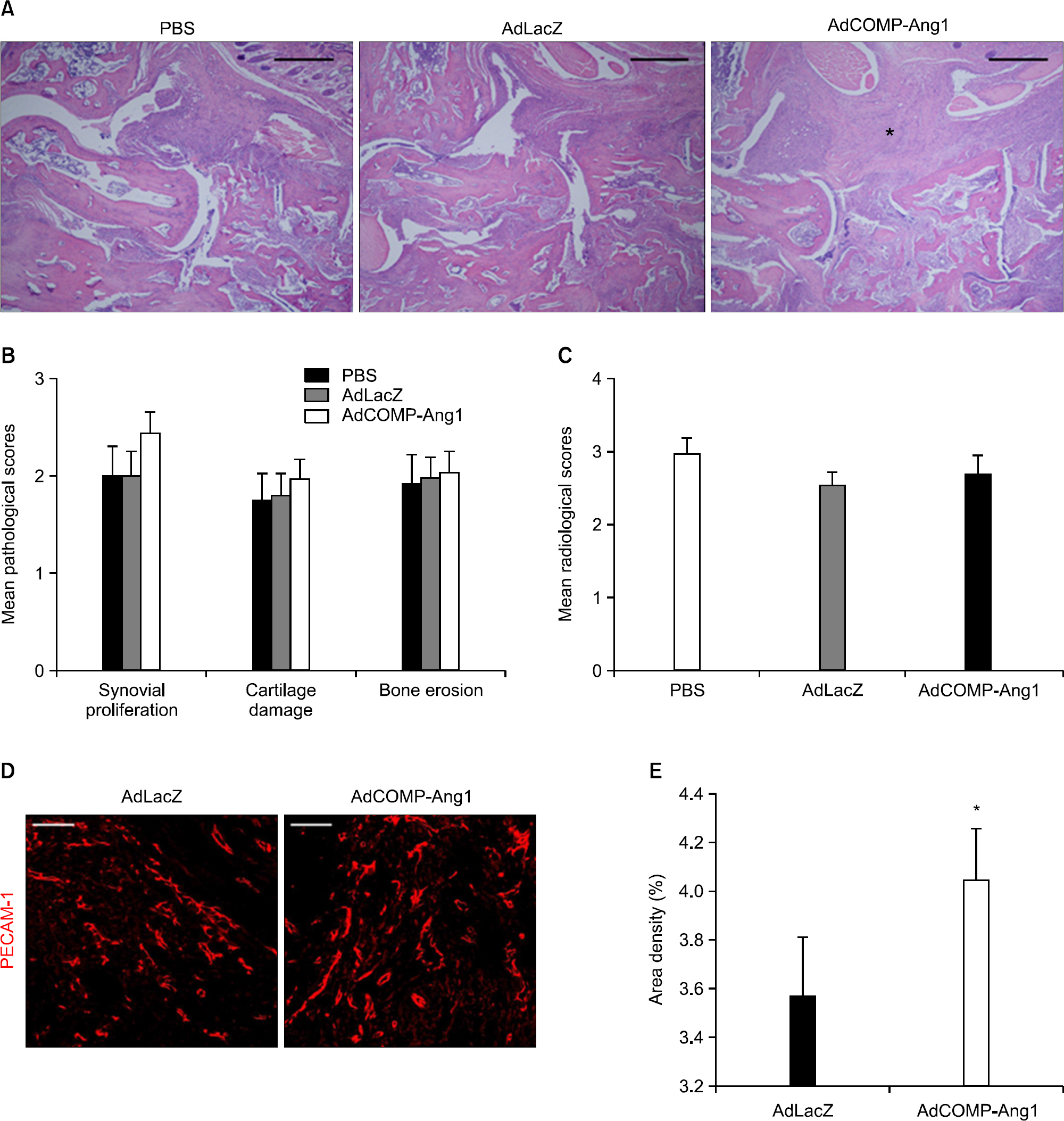
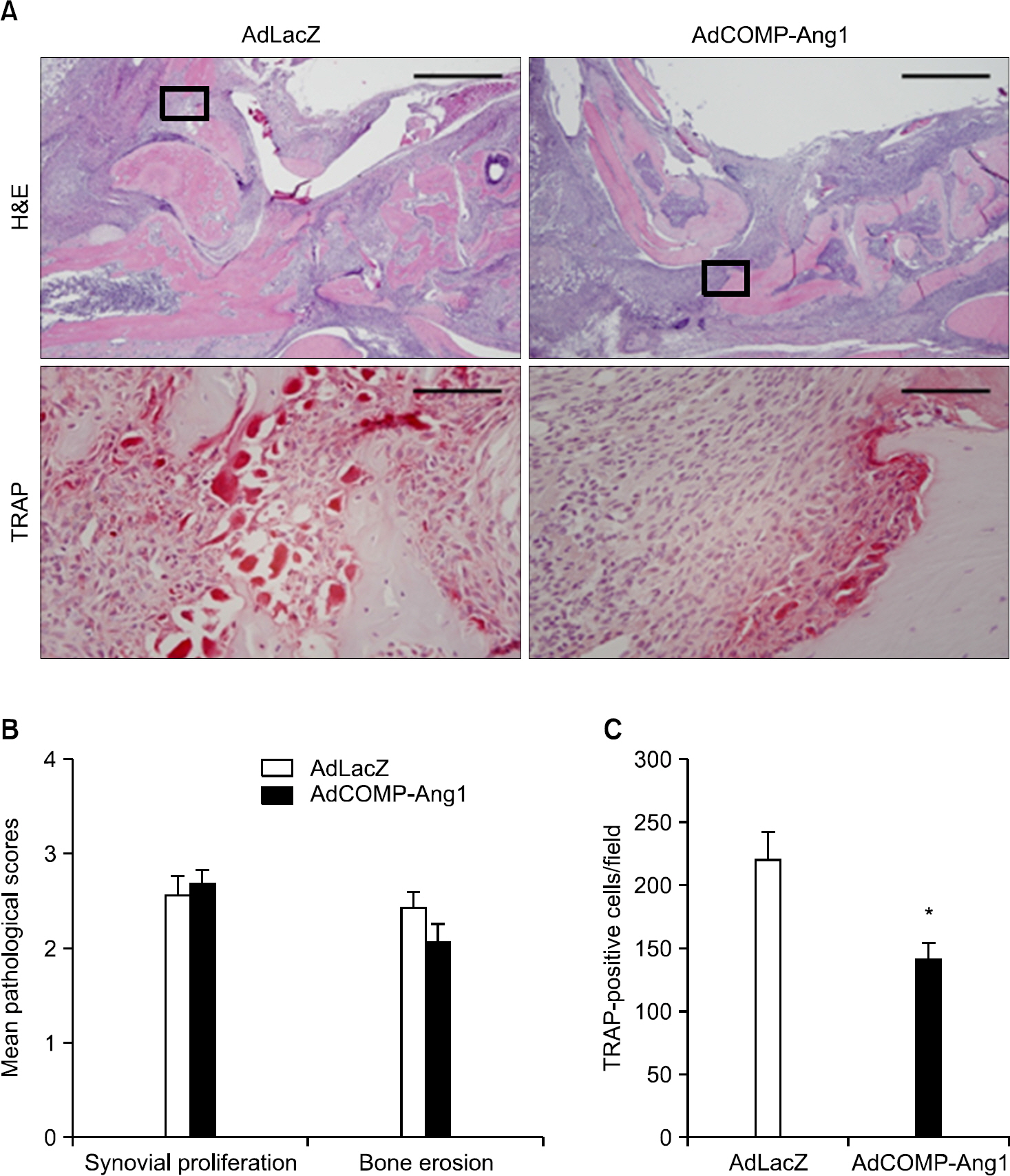
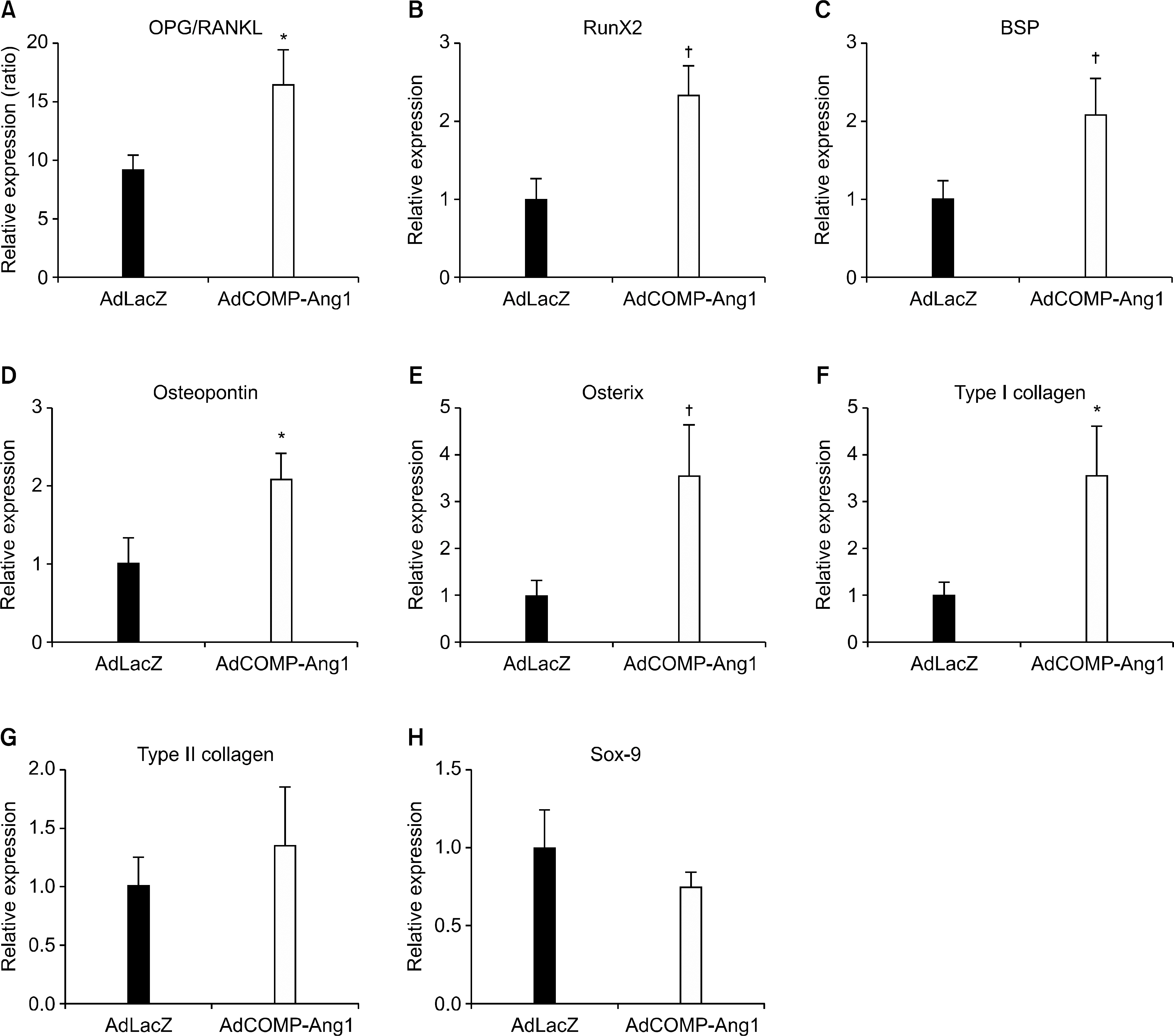
AdCOMP-Ang1-injected mice developed more severe inflammation than the AdLacZ-injected mice. However, there were no significant differences in cartilage damage and bone erosion. More PECAM-1-positive blood vessels were seen in the synovium of the AdCOMP-Ang1-injected mice than in those injected with AdLacZ. Interestingly, a lower number of TRAP-positive osteoclasts were observed in AdCOMP-Ang1-injected CIA mice than in the AdLacZ group when comparing sections obtained from joints showing similar synovial proliferation. The serum OPG/RANKL ratio and expression of osteoblast maturation genes, such as runt-related transcription factor 2, bone sialoprotein, type 1 collagen, osteopontin, and osterix, were significantly upregulated in the AdCOMP-Ang1 group.
CONCLUSION
COMP-Ang1 facilitates arthritis onset and increases synovial inflammation, but enhances osteoblast maturation, which in turn inhibits osteoclastogenesis by increasing the OPG/RANKL ratio in CIA. Our results suggest that careful investigation is necessary to delineate the possible therapeutic use of COMP-Ang1 as an adjunctive agent, in combination with anti-inflammatory therapies, for the prevention of bone destruction in RA.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoviridae
Angiogenesis Inducing Agents
Angiopoietin-1
Animals
Arthritis
Arthritis, Experimental
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Blood Vessels
Cartilage
Collagen Type I
Extracellular Matrix Proteins
Glycoproteins
Inflammation
Integrin-Binding Sialoprotein
Joints
Lifting
Mice
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Osteogenesis
Osteopontin
Osteoprotegerin
Synovial Membrane
Transcription Factors
Angiogenesis Inducing Agents
Angiopoietin-1
Collagen Type I
Extracellular Matrix Proteins
Glycoproteins
Integrin-Binding Sialoprotein
Osteopontin
Osteoprotegerin
Transcription Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Inhibitory Effects for Rheumatoid Arthritis of Dietary Supplementation with Resveratrol in Collagen-induced Arthritis
Yun-Hong Cheon, Hyun-Ok Kim, Young-Sun Suh, Jae Hyung Hur, Wonyong Jo, Hye-Song Lim, Young-Sool Hah, Mi Jeong Sung, Dae Young Kwon, Sang-Il Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2015;22(2):93-101. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.2.93.
Reference
-
References
1. Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003; 423:356–61.
Article2. Lainer-Carr D, Brahn E. Angiogenesis inhibition as a therapeutic approach for inflammatory synovitis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007; 3:434–42.
Article3. Szekanecz Z, Koch AE. Mechanisms of Disease: angiogenesis in inflammatory diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2007; 3:635–43.
Article4. Jones N, Iljin K, Dumont DJ, Alitalo K. Tie receptors: new modulators of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 2:257–67.
Article5. Augustin HG, Koh GY, Thurston G, Alitalo K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 10:165–77.
Article6. DeBusk LM, Chen Y, Nishishita T, Chen J, Thomas JW, Lin PC. Tie2 receptor tyrosine kinase, a major mediator of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:2461–71.7. Gravallese EM, Pettit AR, Lee R, Madore R, Manning C, Tsay A, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is expressed in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and is induced by tu-mour necrosis factor α. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003; 62:100–7.8. Chen Y, Donnelly E, Kobayashi H, Debusk LM, Lin PC. Gene therapy targeting the Tie2 function ameliorates col-lagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1585–94.
Article9. Romas E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ. Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-α in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2002; 30:340–6.10. Takayanagi H. Osteoimmunology and the effects of the immune system on bone. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5:667–76.
Article11. Choi Y, Arron JR, Townsend MJ. Promising bone-related therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009; 5:543–8.
Article12. Glass DA 2nd, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, et al. Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 2005; 8:751–64.
Article13. Walsh NC, Reinwald S, Manning CA, Condon KW, Iwata K, Burr DB, et al. Osteoblast function is compromised at sites of focal bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24:1572–85.
Article14. Pap T, Distler O. Linking angiogenesis to bone destruction in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:1346–8.
Article15. Suzuki T, Miyamoto T, Fujita N, Ninomiya K, Iwasaki R, Toyama Y, et al. Osteoblast-specific Angiopoietin 1 overexpression increases bone mass. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 362:1019–25.
Article16. Cho CH, Kammerer RA, Lee HJ, Steinmetz MO, Ryu YS, Lee SH, et al. COMP-Ang1: a designed angiopoie-tin-1 variant with nonleaky angiogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:5547–52.
Article17. Cho CH, Kim KE, Byun J, Jang HS, Kim DK, Baluk P, et al. Longterm and sustained COMP-Ang1 induces long-lasting vascular enlargement and enhanced blood flow. Circ Res. 2005; 97:86–94.
Article18. Thurston G, Suri C, Smith K, McClain J, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD, et al. Leakage-resistant blood vessels in mice transgenically overexpressing angiopoietin-1. Science. 1999; 286:2511–4.
Article19. Jeong BC, Kim HJ, Bae IH, Lee KN, Lee KY, Oh WM, et al. COMP-Ang1, a chimeric form of Angiopoietin 1, enhances BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Bone. 2010; 46:479–86.
Article20. Park BH, Jang KY, Kim KH, Song KH, Lee SY, Yoon SJ, et al. COMP-Angiopoietin-1 ameliorates surgery-induced ischemic necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Bone. 2009; 44:886–92.
Article21. Park BH, Yoon SJ, Jang KY, Kim MR, Lee HS, Kim KB, et al. COMP-angiopoietin-1 accelerates bone formation during distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 2010; 46:1442–8.
Article22. Hah YS, Lee YR, Jun JS, Lim HS, Kim HO, Jeong YG, et al. A20 suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:2313–21.
Article23. Lee S, Kim W, Kim DH, Moon SO, Jung YJ, Lee AS, et al. Protective effect of COMP-angiopoietin-1 on cyclosporine-induced renal injury in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008; 23:2784–94.
Article24. Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007; 6:273–86.
Article25. Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005; 438:932–6.
Article26. Eskens FA, Verweij J. The clinical toxicity profile of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) targeting angiogenesis inhibitors; a review. Eur J Cancer. 2006; 42:3127–39.
Article27. Hawighorst T, Skobe M, Streit M, Hong YK, Velasco P, Brown LF, et al. Activation of the tie2 receptor by angio-poietin-1 enhances tumor vessel maturation and impairs squamous cell carcinoma growth. Am J Pathol. 2002; 160:1381–92.
Article28. Machein MR, Knedla A, Knoth R, Wagner S, Neuschl E, Plate KH. Angiopoietin-1 promotes tumor angiogenesis in a rat glioma model. Am J Pathol. 2004; 165:1557–70.
Article29. Voskas D, Jones N, Van Slyke P, Sturk C, Chang W, Haninec A, et al. A cyclosporine-sensitive psoriasis-like disease produced in Tie2 transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 2005; 166:843–55.
Article30. Hashiramoto A, Sakai C, Yoshida K, Tsumiyama K, Miura Y, Shiozawa K, et al. Angiopoietin 1 directly induces destruction of the rheumatoid joint by cooperative, but independent, signaling via ERK/MAPK and phosphati-dylinositol 3-kinase/Akt. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:2170–9.
Article31. Komori T. Regulation of skeletal development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J Cell Biochem. 2005; 95:445–53.
Article32. Bais MV, Wigner N, Young M, Toholka R, Graves DT, Morgan EF, et al. BMP2 is essential for post natal osteogenesis but not for recruitment of osteogenic stem cells. Bone. 2009; 45:254–66.
Article33. Thomas GP, Baker SU, Eisman JA, Gardiner EM. Changing RANKL/OPG mRNA expression in differentiating murine primary osteoblasts. J Endocrinol. 2001; 170:451–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of Angiopoietin-1 in Kidney Disease
- COMP-Angiopoietin-1 Promotes Cavernous Angiogenesis in a Type 2 Diabetic Rat Model
- Expression of Osteoclastogenesis-related Genes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Macrophages
- Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Improvement of the Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap Viability Using Adenovirus-mediated VEGF and COMP-angiopoietin-1