J Rheum Dis.
2012 Jun;19(3):118-124. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.118.
Small Molecule Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leb7616@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2223092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.118
Abstract
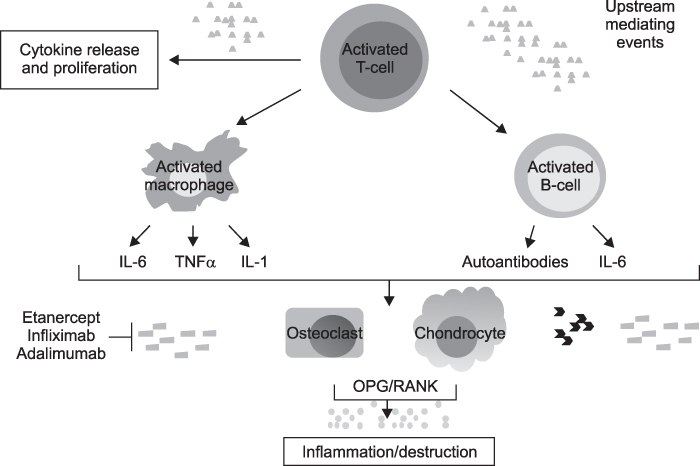
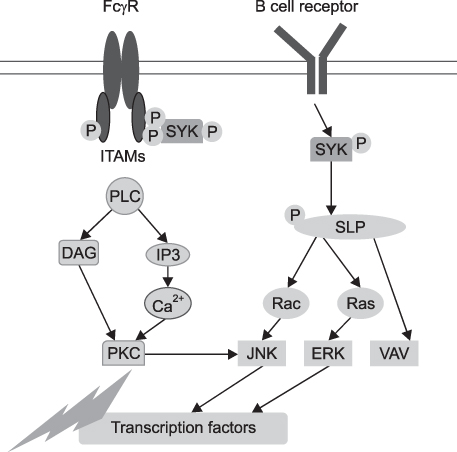
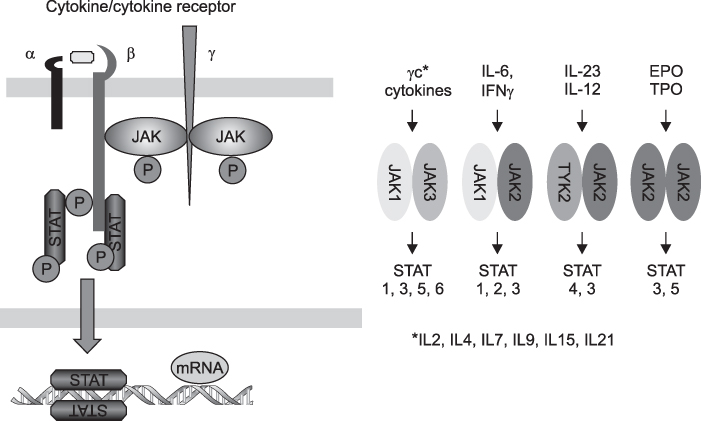
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease predominantly affecting diarthroidal joints. Following the successful application of biologic agents, several small molecule inhibitors are currently under clinical trials. Small molecule inhibitors have several strengths compared with biologics. First, they can target several inflammatory cytokines together by blocking common signal transduction pathways. Second, they can be taken orally. Third, the price can be made flexible. Among the several small molecule inhibitors in the development process, fostamatinib and tofacitinib are the closest to the clinics at the moment. Fostamatinib, which is a Syk inhibitor, showed superior efficacy over placebo with tolerable safety signals. Diarrhea, hypertension and infection are representative adverse events. Tofacitinib, which is JAK inhibitor, is now finishing phase 3 clinical trials. It showed clinical efficacy comparable to Adalimumab and similar adverse effect profiles to the biologics, which include opportunistic infections. For laboratory abnormalities, leukopenia, anemia, increase of LDL and serum Cr were reported, which, however, were stabilized with prolonged use. Other classes of small molecule inhibitors did not show impressive efficacy as these small molecule inhibitors. In conclusion, small molecule inhibitors are promising novel therapeutic agents for the treatment of RA. They will be able to change the treatment paradigm of RA if they can show long-term safety.
MeSH Terms
-
Anemia
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Biological Agents
Cytokines
Diarrhea
Hypertension
Joints
Leukopenia
Opportunistic Infections
Oxazines
Piperidines
Pyridines
Pyrimidines
Pyrroles
Signal Transduction
Antibodies, Monoclonal, Humanized
Biological Agents
Cytokines
Oxazines
Piperidines
Pyridines
Pyrimidines
Pyrroles
Adalimumab
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pharmacologic treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Soo-Kyung Cho, Sang-Cheol Bae
J Korean Med Assoc. 2017;60(2):156-163. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2017.60.2.156.
Reference
-
1. Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001. 358:903–911.2. Moreland LW, Schiff MH, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Bulpitt KJ, et al. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999. 130:478–486.3. Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1594–1602.4. Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Moreland LW, Weisman MH, Birbara CA, et al. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal anti-body, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:35–45.5. Kay J, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B, Nash P, Durez P, Hall S, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:964–975.6. Keystone E, Heijde D, Mason D Jr, Landewé R, Vollenhoven RV, Combe B, et al. Certolizumab pegol plus methotrexate is significantly more effective than placebo plus methotrexate in active rheumatoid arthritis: findings of a fifty-two-week, phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:3319–3329.7. Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, Pavelka K, Bröll J, Balint G, et al. CHARISMA Study Group. Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 54:2817–2829.8. Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2572–2581.9. Genovese MC, Covarrubias A, Leon G, Mysler E, Keiserman M, Valente R, et al. Subcutaneous abatacept versus intravenous abatacept: a phase IIIb noninferiority study in patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:2854–2864.10. Tak PP, Kalden JR. Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. 13:Suppl 1. S5.11. Weinblatt ME, Kavanaugh A, Burgos-Vargas R, Dikranian AH, Medrano-Ramirez G, Morales-Torres JL, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a Syk kinase inhibitor: a twelve-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. 58:3309–3318.12. Weinblatt ME, Kavanaugh A, Genovese MC, Musser TK, Grossbard EB, Magilavy DB. An oral spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2010. 363:1303–1312.13. Genovese MC, Kavanaugh A, Weinblatt ME, Peterfy C, DiCarlo J, White ML, et al. An oral Syk kinase inhibitor in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a three-month randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis that did not respond to biologic agents. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:337–345.14. Bajpai M, Chopra P, Dastidar SG, Ray A. Spleen tyrosine kinase: a novel target for therapeutic intervention of rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. 17:641–659.15. Weinblatt ME, Kavanaugh A, Genovese MC, Jones DA, Musser TK, Grossbard EB, et al. Effects of the Oral SYKInhibitor, fostamatinib (R788), on health-related quality of life in a phase II study of active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:S158.16. Riese RJ, Krishnaswami S, Kremer J. Inhibition of JAK kinases in patients withrheumatoid arthritis: scientific rationale and clinical outcomes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2010. 24:513–526.17. Fleischmann R, Cutolo M, Genovese MC, Lee EB, Kanik KS, Sadis S, et al. Phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) or adalimumab monotherapy versus placebo in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to disease- modifying antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. 64:617–629.18. Kremer JM, Cohen S, Wilkinson BE, Connell CA, French JL, Gomez-Reino J, et al. A phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) versus placebo in combination with background methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. 64:970–981.19. Fleishmann R, Kremer J, Cush J, et al. Phase 3 study of Oral JAK inhibitor Tasocitinib (CP-690-550) Monotherapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. 62:LB8.20. Kremer J, Li ZG, Hall S, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral JAK inhibitor, in combination with traditional DMARDs: phase 3 study in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to DMARDs (abstract). Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. 70:170.21. van der Heijde D, Tanaka Y, Fleischmann R, Keystone EC, Kremer JM, Zerbini CAF, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in combination with methotrexate reduced the progression of structural damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 24-month phase 3 study. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 2592.22. Van Vollenhoven R, Fleischmann R, Cohen S, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral Janus Kinase inhibitor, or adalimumab versus placebo in patients with rheumatoid arthritis on background methotrexate: a phase 3 study. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 408.23. Burmester G, Blanco R, Charles-Schoeman C, Wollenhaupt J, Zerbini C, Benda B, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in combination with methotrexate, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor-inhibitor: a 6-month phase 3 study. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 718.24. Wollenhaupt J, Silverfield JC, Lee EB, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: open-label, long-term extension studies up to 36 months. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 407.25. Cohen S, Radominski S, Asavartanabodee P, et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550), an oral Janus kinase inhibitor: analysis of infections and all-cause mortality across phase 3 and long-term extension studies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 409.26. Fleischmann R. Novel small-molecular therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012. 24:335–341.27. Genovese MC, Cohen SB, Wofsy D, Weinblatt ME, Firestein GS, Brahn E, et al. A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of the efficacy of oral SCIO-469, a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2011. 38:846–854.28. Damjanov N, Kauffman RS, Spencer-Green GT. Efficacy, pharmacodynamics, and safety of VX-702, a novel p38 MAPK inhibitor, in rheumatoid arthritis: results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. 60:1232–1241.29. Fleischmann R, Poiley J, Stoilov R, et al. The oral S1P lyase inhibitor LX3305 (LX2931) demonstrates favorable safety and potential clinical benefit at 12 weeks in a phase 2 proof-of-concept trial in pateints with active rheumatoid arthritis on stable methotrexate therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 63:10 Suppl. Abstract 2593.30. Tak PP, Balanescu A, Tseluyko V, Bojin S, Drescher E, Dairaghi D, et al. Chemokine receptor CCR1 antagonist CCX354-C treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: CARAT-2, a randomised, placebo controlled clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Increased Fungal Infections while using Emerging Therapies (Biologics and Small-molecule Inhibitors) for Treating Skin Diseases: A Review
- Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis
- Advantages and disadvantages of targeted therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- The Roles of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule I in T Cell Adhesion Tosynovial Cell in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis