J Rheum Dis.
2013 Feb;20(1):30-39. 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.30.
Long-term Safety and Efficacy of Abatacept in Koreans with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Seoul St Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ysong@snu.ac.kr
- 6Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, New Jersey, USA.
- KMID: 2223046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2013.20.1.30
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The safety and efficacy of intravenous (IV) abatacept in patients with active RA unresponsive to methotrexate have been demonstrated in short-term (ST) studies in global populations and a ST, Phase III study in a Korean patient population. Abatacept's long-term safety and efficacy profile has been established in open-label global studies with treatment up to 5 years. The objective of this study was to determine the long-term safety and efficacy of abatacept in patients with RA from the ST Korean study.
METHODS
This was an open-label long-term extension (LTE) of a Phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in which Korean patients who had received IV abatacept or placebo in the ST trial (169 days) were given the option to receive open-label abatacept to Day 1485 with 84 days' follow-up (total 1,569 days, ~4 years).
RESULTS
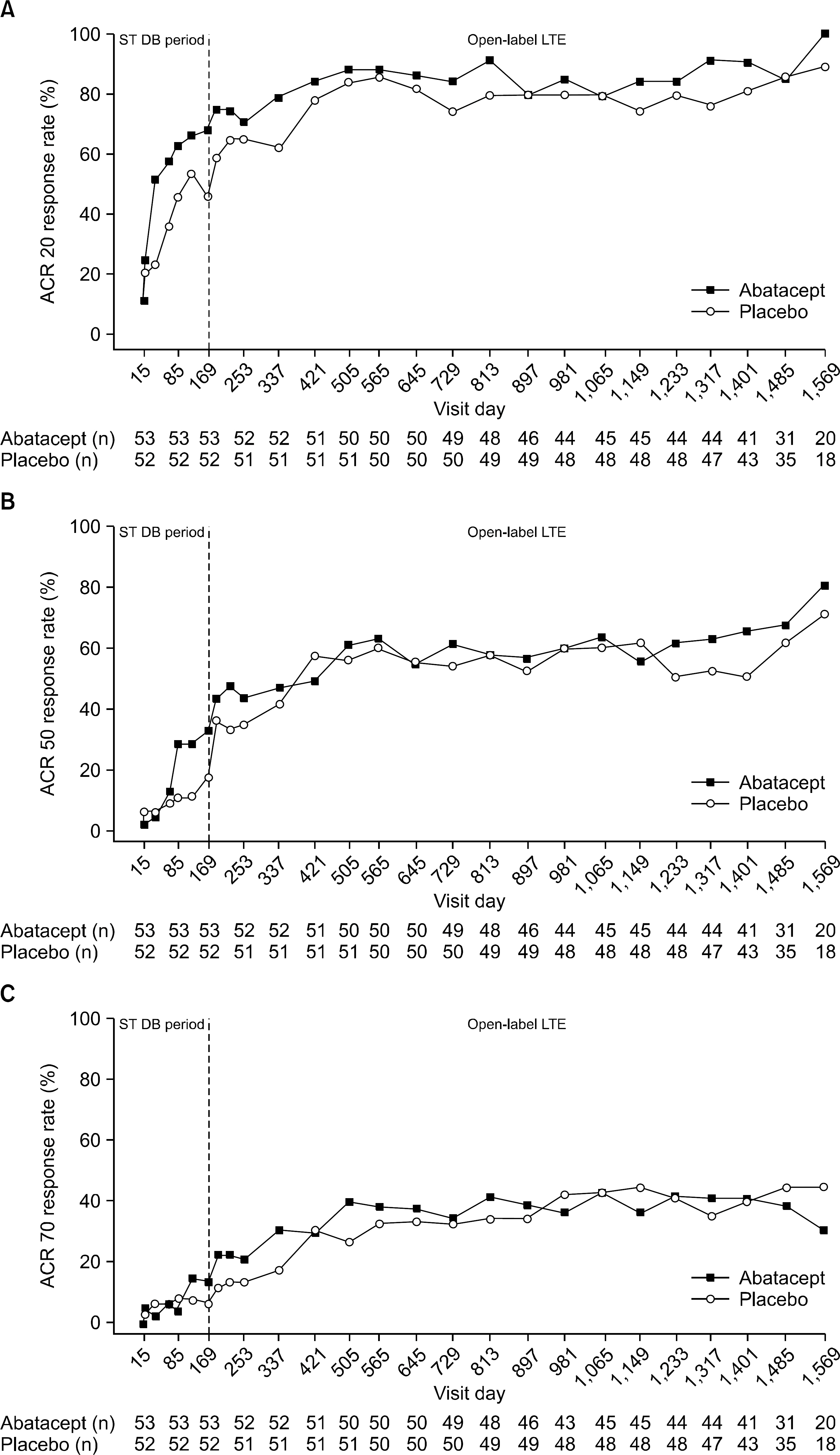
A total of 105 patients were enrolled in the LTE (86.7% female, median age 49.0 years). Abatacept was generally well tolerated. Adverse events were mostly mild or moderate and no new safety signals were identified. Improvement in disease activity (assessed by ACR response and DAS28 [CRP]), physical function (assessed by KHAQ-DI), and quality of life (assessed by SF-36 score) were maintained in patients initially treated with abatacept or observed in patients who had switched to abatacept after placebo in the ST study.
CONCLUSION
Long-term treatment with IV abatacept over 1485 days was generally well tolerated in Korean patients with RA. Additionally, the efficacy profile from the ST study was maintained over the LTE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Long Term Safety and Efficacy of Abatacept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Chang-Keun Lee
J Rheum Dis. 2013;20(2):71-73. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2013.20.2.71.
Reference
-
References
1. Bulpitt KJ. Biologic therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999; 1:157–63.
Article2. Moreland LW, Alten R, Van den Bosch F, Appelboom T, Leon M, Emery P, et al. Costimulatory blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot, dose-finding, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating CTLA-4Ig and LEA29Y eighty-five days after the first infusion. Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 46:1470–9.
Article3. Westhovens R, Robles M, Ximenes AC, Nayiager S, Wollenhaupt J, Durez P, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of abatacept in methotrexate-naive patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and poor prognostic factors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:1870–7.
Article4. Westhovens R, Kremer JM, Moreland LW, Emery P, Russell AS, Li T, et al. Safety and efficacy of the selective costimulation modulator abatacept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving background methotrexate: a 5-year extended phase IIB study. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:736–42.
Article5. Westhovens R, Kremer JM, Emery P, Russell AS, Li T, Aranda R, et al. Consistent safety and sustained improvement in disease activity and treatment response over 7 years of abatacept treatment in biologic-naïve patients with RA. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:577. (Abstract SAT0108).6. Shim SC, Park SH, Bae SC, Song YW, Macaraeg GM, Delvaux A, et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept in Korean patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: A phase III, multi-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled bridging study. 14th Congress of APLAR. 2010; Hong Kong. Abstract 12-2.4-0806.7. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:315–24.
Article8. Hochberg MC, Chang RW, Dwosh I, Lindsey S, Pincus T, Wolfe F. The American College of Rheumatology 1991 revised criteria for the classification of global functional status in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992; 35:498–502.
Article9. Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, et al. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:727–35.
Article10. Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:44–8.
Article11. Fransen J, van Riel PL. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009; 35:745–57.
Article12. Bae SC, Cook EF, Kim SY. Psychometric evaluation of a Korean Health Assessment Questionnaire for clinical research. J Rheumatol. 1998; 25:1975–9.13. Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, Baker PR, Groh J, Redelmeier DA. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient's perspective. J Rheumatol. 1993; 20:557–60.14. Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual frame-work and item selection. Med Care. 1992; 30:473–83.15. Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Schiff MH, Kalden JR, Emery P, Eberl G, et al. A simplified disease activity index for rheumatoid arthritis for use in clinical practice. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42:244–57.
Article16. Kremer JM, Westhovens R, Leon M, Di Giorgio E, Alten R, Steinfeld S, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by selective inhibition of T-cell activation with fusion protein CTLA4Ig. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:1907–15.
Article17. Kremer JM, Dougados M, Emery P, Durez P, Sibilia J, Shergy W, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with the selective costimulation modulator abatacept: twelve- month results of a phase iib, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:2263–71.18. Kremer JM, Genant HK, Moreland LW, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Results of a two-year followup study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who received a combination of abatacept and methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58:953–63.
Article19. Kremer JM, Genant HK, Moreland LW, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Effects of abatacept in patients with methotrexate-resistant active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 144:865–76.20. Kremer JM, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, Szechinski J, Westhovens R, et al. Longterm safety, efficacy and inhibition of radiographic progression with abatacept treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: 3-year results from the AIM trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:1826–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long Term Safety and Efficacy of Abatacept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Description of the Efficacy and Safety of Three New Biologics in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Rare Case of Overlap Syndrome with Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
- New drugs for Rheumatoid arthritis
- The Efficacy and Safety of Leflunomide in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis