J Rheum Dis.
2019 Oct;26(4):282-285. 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.282.
A Rare Case of Overlap Syndrome with Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Mediciney, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. min6403@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2459454
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.282
Abstract
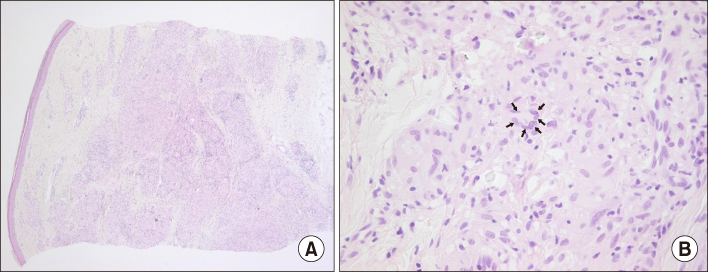
- Overlap syndrome is defined as a disease entity that satisfies the classification criteria of at least two connective tissue diseases occurring concurrently or separately in a single patient. Here, we report a rare case of a 59-year-old woman with diffuse systemic sclerosis with lung involvement-rheumatoid arthritis overlap syndrome accompanied by cutaneous sarcoidosis. Although there is no consensus for the optimal treatment of overlap syndrome to date, this case of co-existing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis with interstitial lung disease successfully responded to abatacept.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wanat KA, Rosenbach M. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med. 2015; 36:685–702.
Article2. Szücs G, Szekanecz Z, Zilahi E, Kapitány A, Baráth S, Szamosi S, et al. Systemic sclerosis-rheumatoid arthritis overlap syndrome: a unique combination of features suggests a distinct genetic, serological and clinical entity. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:989–993.3. Jinnin M, Ihn H, Yamane K, Asano Y, Yazawa N, Tamaki K. Clinical features of patients with systemic sclerosis accompanied by rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003; 21:91–94.4. Senda S, Igawa K, Nishioka M, Murota H, Katayama I. Systemic sclerosis with sarcoidosis: case report and review of the published work. J Dermatol. 2014; 41:421–423.5. Kato Y, Ohtsuka M, Yamamoto T. Cutaneous sarcoidosis concurrently involved in the sclerotic fingers of a patient with systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol. 2015; 42:331–333.
Article6. Vieira MA, Saraiva MI, Silva LK, Fraga RC, Kakizaki P, Valente NY. Development of exclusively cutaneous sarcoidosis in patient with rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with etanercept. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2016; 62:718–720.7. Pescitelli L, Emmi G, Tripo L, Lazzeri L, Urban ML, Silvesri E, et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis during rituximab treatment for microscopic polyangiitis: an uncommon adverse effect? Eur J Dermatol. 2017; 27:667–668.
Article8. Ando M, Miyazaki E, Hatano Y, Nishio S, Torigoe C, Yamasue M, et al. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis: a clinical analysis of nine patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2016; 35:2277–2281.9. Facco M, Cabrelle A, Teramo A, Olivieri V, Gnoato M, Teolato S, et al. Sarcoidosis is a Th1/Th17 multisystem disorder. Thorax. 2011; 66:144–150.
Article10. Ten Berge B, Paats MS, Bergen IM, van den Blink B, Hoogsteden HC, Lambrecht BN, et al. Increased IL-17A expression in granulomas and in circulating memory T cells in sarcoidosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012; 51:37–46.11. Liu M, Wu W, Sun X, Yang J, Xu J, Fu W, et al. New insights into CD4(+) T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016; 28:31–36.
Article12. Mathian A, Parizot C, Dorgham K, Trad S, Arnaud L, Larsen M, et al. Activated and resting regulatory T cell exhaustion concurs with high levels of interleukin-22 expression in systemic sclerosis lesions. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012; 71:1227–1234.13. Nakashima T, Jinnin M, Yamane K, Honda N, Kajihara I, Makino T, et al. Impaired IL-17 signaling pathway contributes to the increased collagen expression in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2012; 188:3573–3583.
Article14. Jani M, Hirani N, Matteson EL, Dixon WG. The safety of biologic therapies in RA-associated interstitial lung disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10:284–294.15. Ponsoye M, Frantz C, Ruzehaji N, Nicco C, Elhai M, Ruiz B, et al. Treatment with abatacept prevents experimental dermal fibrosis and induces regression of established inflammation-driven fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75:2142–2149.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Overlap Syndrome Consisting of Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Systemic Sclerosis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Polymyositis
- Successful Treatment of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis with Adalimumab in a Patient with Overlap Syndrome
- Sequential Development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Patient with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis