J Rheum Dis.
2015 Dec;22(6):401-404. 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.401.
A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-related Interstitial Nephritis with Bicytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Hospital Pathology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. wan725@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2222817
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.401
Abstract
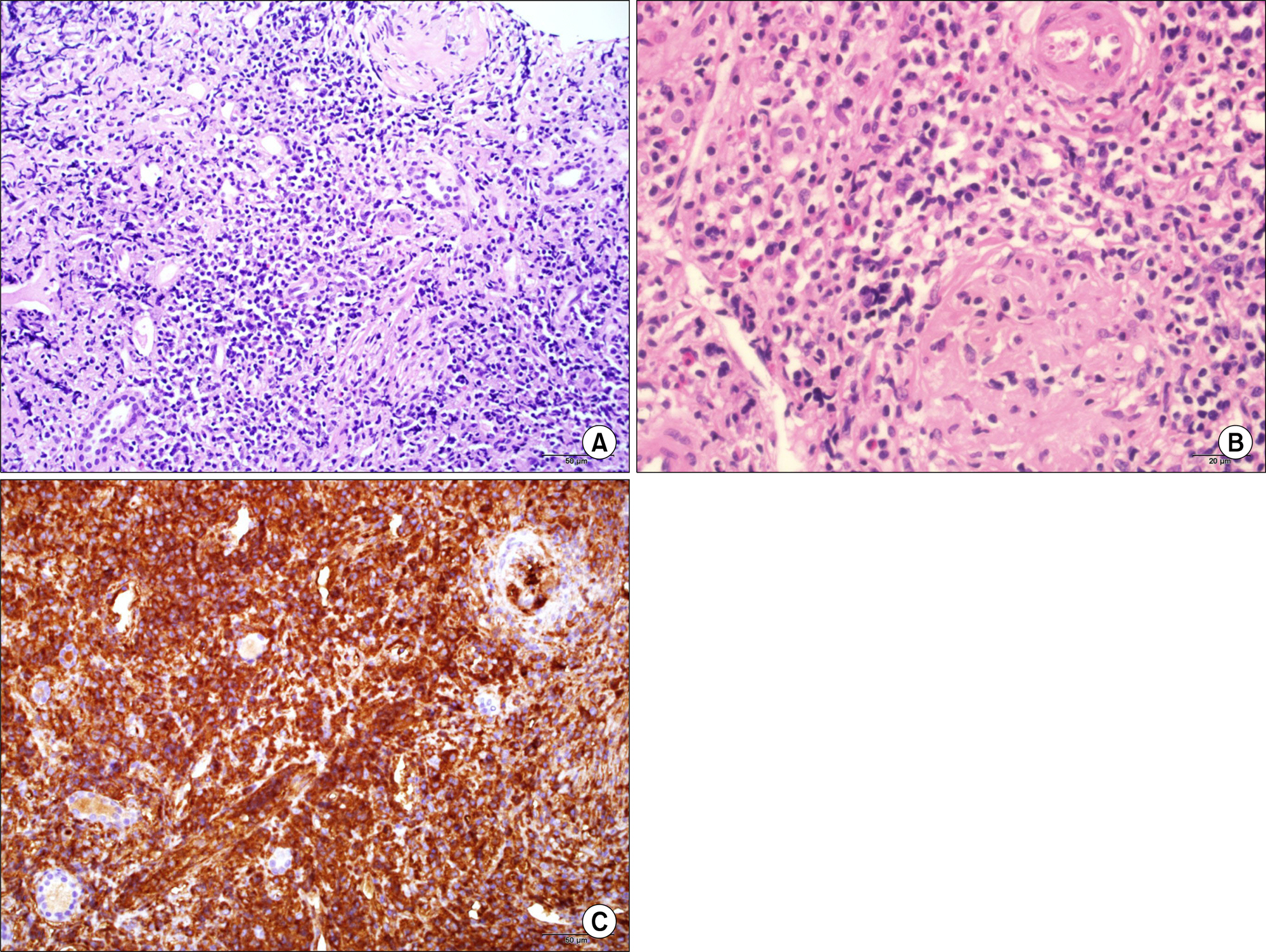
- Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic inflammatory disease found in many organs including biliary tract, salivary gland, kidney, and lung. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is the most common renal manifestation, but hematologic involvement of IgG4-RD is rare. Here, we report on a case of a 57-year-old male with IgG4-related interstitial nephritis with bicytopenia, which was initially thought to be systemic lupus erythematosus. He presented with proteinuria, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and low complement levels. Histological findings showed an increased number of IgG4-positive plasma cells (>200/high power field), and an elevated IgG4/IgG ratio (>90%). Serum levels of IgG and IgG4 were also increased. This case emphasized the importance of differential diagnosis of IgG4-RD and immune complex glomerulonephritis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anemia
Antigen-Antibody Complex
Biliary Tract
Complement System Proteins
Diagnosis, Differential
Glomerulonephritis
Humans
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins*
Kidney
Lung
Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic
Male
Middle Aged
Nephritis, Interstitial*
Plasma Cells
Proteinuria
Salivary Glands
Thrombocytopenia
Antigen-Antibody Complex
Complement System Proteins
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–51.
Article2. Nishi S, Imai N, Yoshida K, Ito Y, Saeki T. Clinicopathological findings of immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:810–9.
Article3. Saeki T, Kawano M. IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2014; 85:251–7.
Article4. Saeki T, Ito T, Youkou A, Ishiguro H, Sato N, Yamazaki H, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in IgG4-related disease with severe deficiency of ADAMTS-13 activity and IgG4 autoantibody against ADAMTS-13. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63:1209–12.
Article5. Nakamura A, Funatomi H, Katagiri A, Katayose K, Kitamura K, Seki T, et al. A case of autoimmune pancreatitis complicated with immune thrombocytopenia during maintenance therapy with prednisolone. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:1968–71.6. Monach PA. IgG4-related disease: 2013 update. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2013; 15:214–23.
Article7. Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP, Colvin RB, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 22:1343–52.
Article8. Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K, Kawano M, Yamada K, Takahira M, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1538–46.
Article9. Umehara H, Nakajima A, Nakamura T, Kawanami T, Tanaka M, Dong L, et al. IgG4-related disease and its pathogenesis-crosstalk between innate and acquired immunity. Int Immunol. 2014; 26:585–95.
Article10. Kihara M, Sugihara T, Hosoya T, Miyasaka N. Clinical significance of complement as a biomarker of disease activity in 4 cases of IgG4-related disease with retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013; 31:947–9.11. Soliotis F, Mavragani CP, Plastiras SC, Rontogianni D, Skopouli FN, Moutsopoulos HM. IgG4-related disease: a rheumatologist's perspective. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014; 32:724–7.12. Ali A, Al-Windawi S. Tubulointerstitial lupus nephritis. J Nephropathol. 2013; 2:75–80.
Article13. Sciascia S, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta M, Roccatello D. Renal involvement in antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014; 10:279–89.
Article14. Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014; 9:315–47.
Article15. Cornell LD. IgG4-related kidney disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:245–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis with Extrarenal Involvement
- IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis Accompanied by Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
- A Case of Carbamazepine-Induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis
- Interstitial Nephritis and IgA Nephropathy in a Patient with Acute Hepatitis A
- A Case of Recurrent Ischemic Stroke Associated with Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease