J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Apr;49(4):661-668. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.661.
Effect of Nitric Oxide on the Migration and Fibroblast-mediated Contraction of Collagen Gels
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jwkim@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2211499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.4.661
Abstract
-
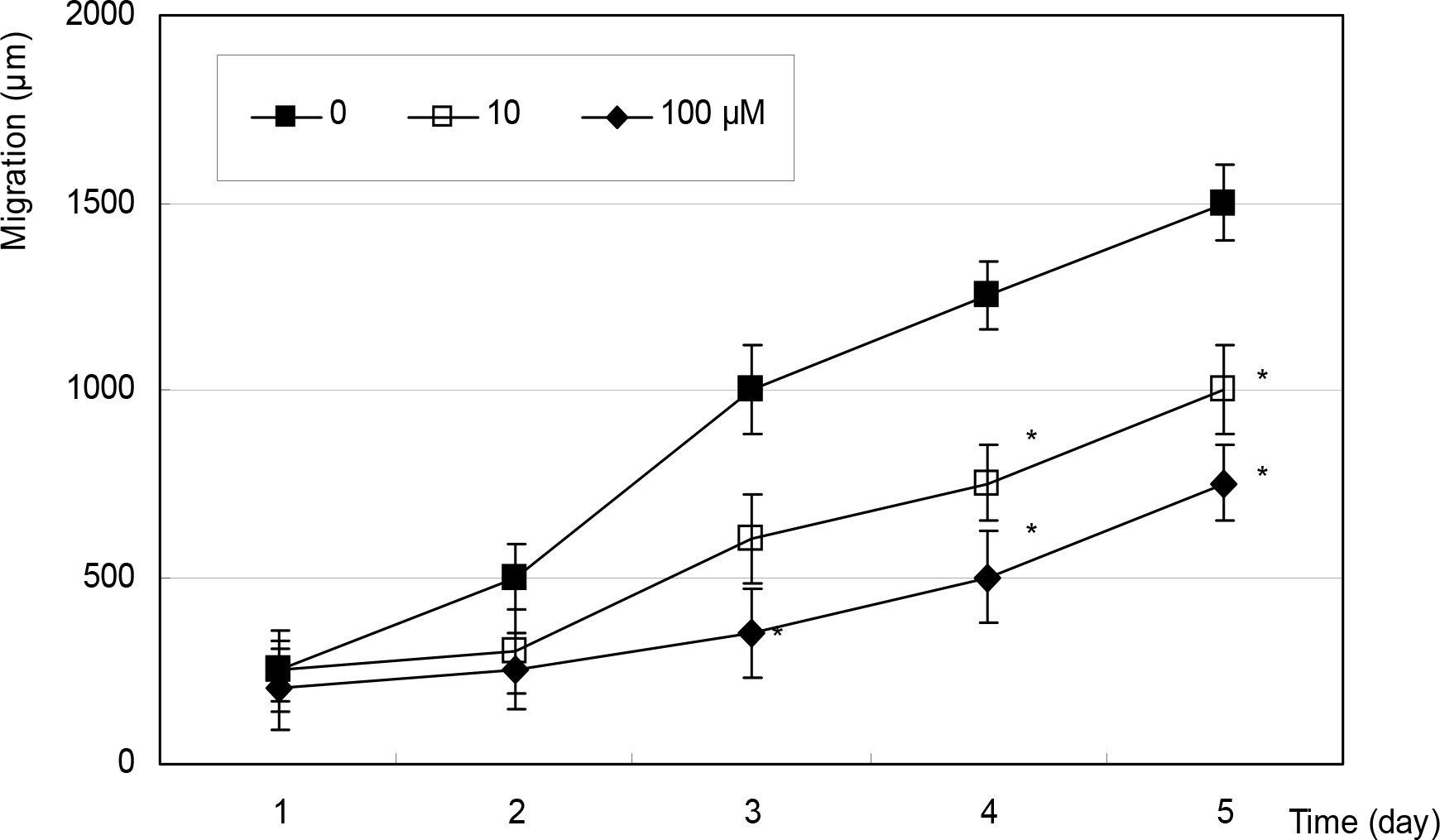
PURPOSE: To investigate the role of nitric oxide (NO) on the migration of cultured human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts (HTCF) and contraction of collagen gel.
METHODS
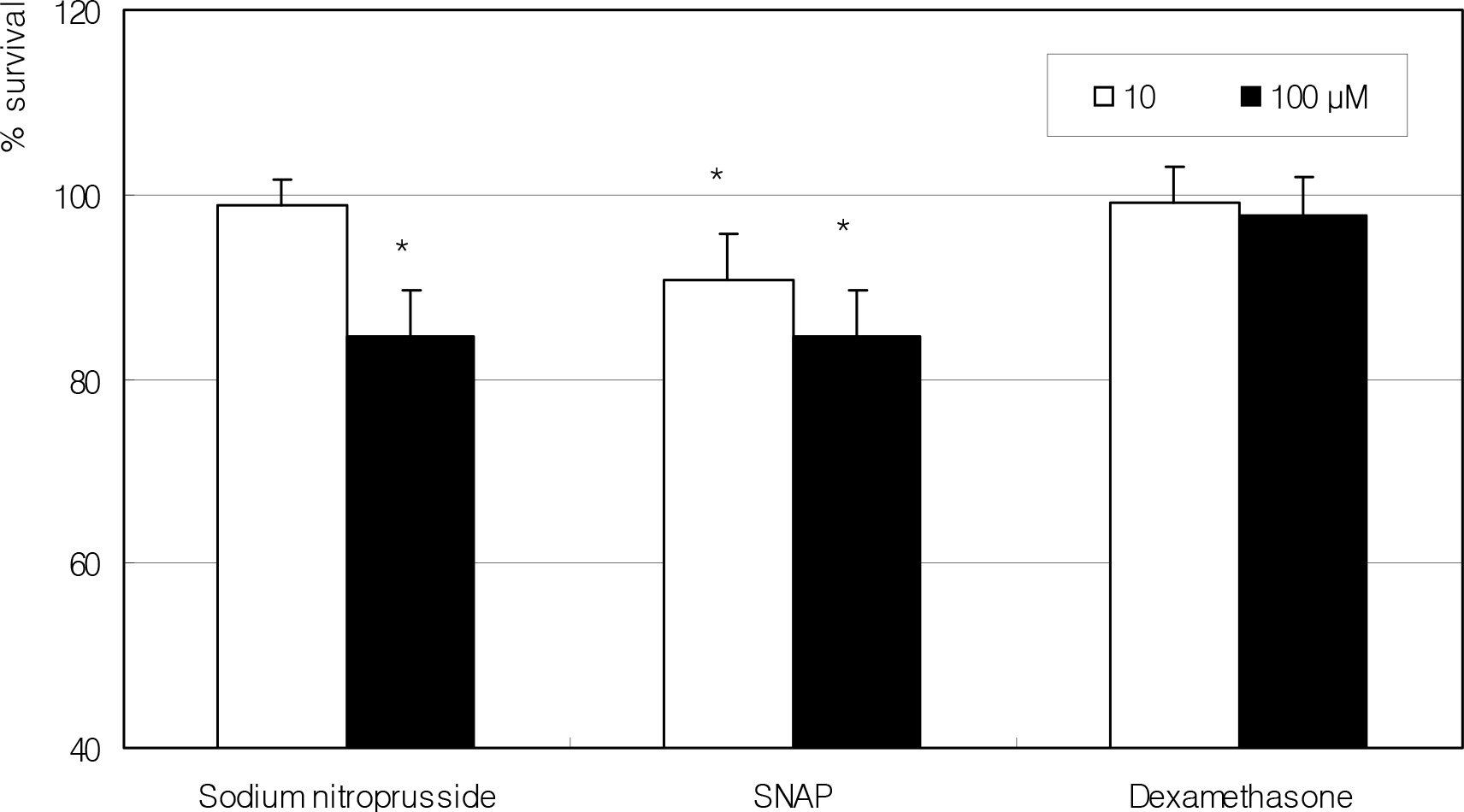
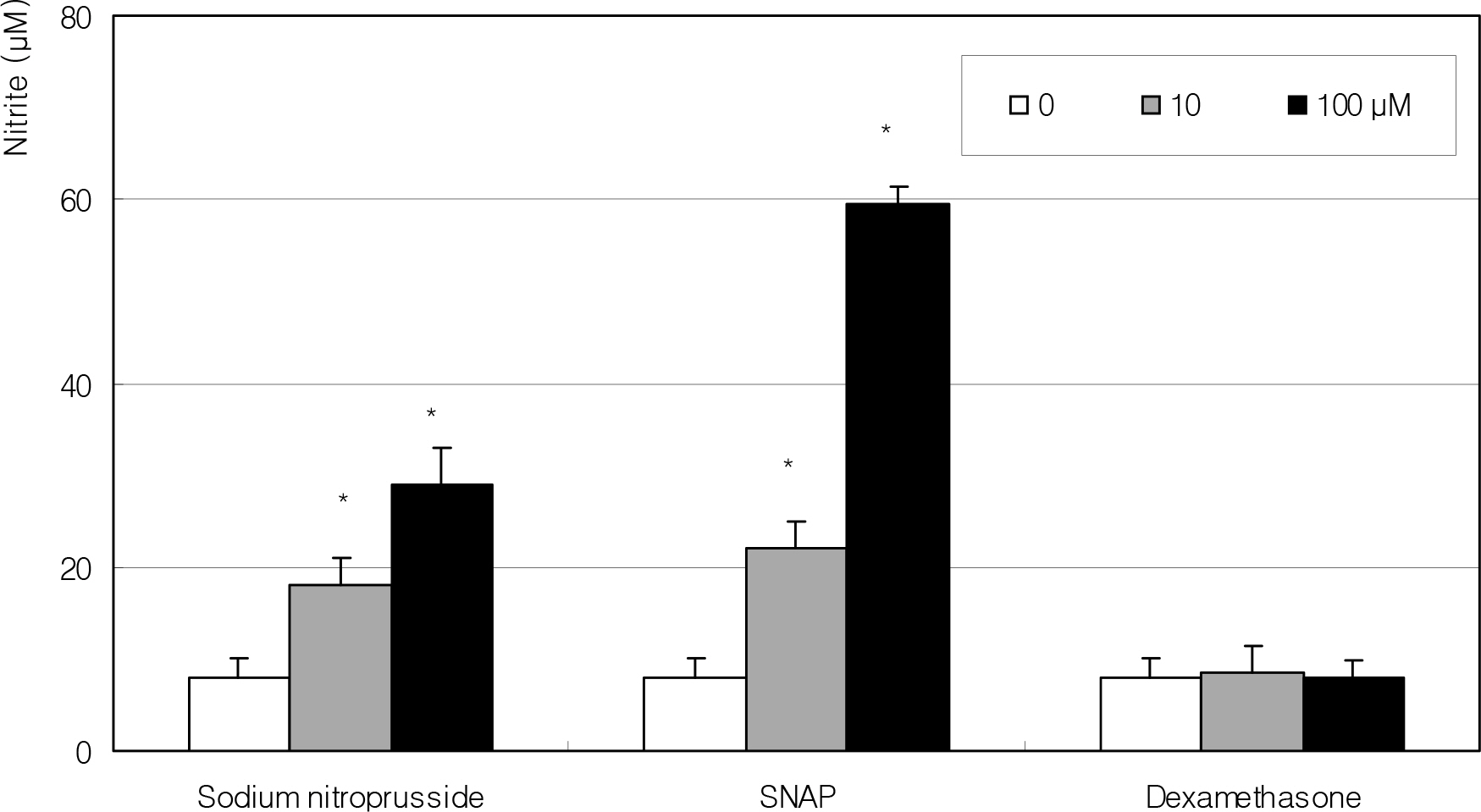
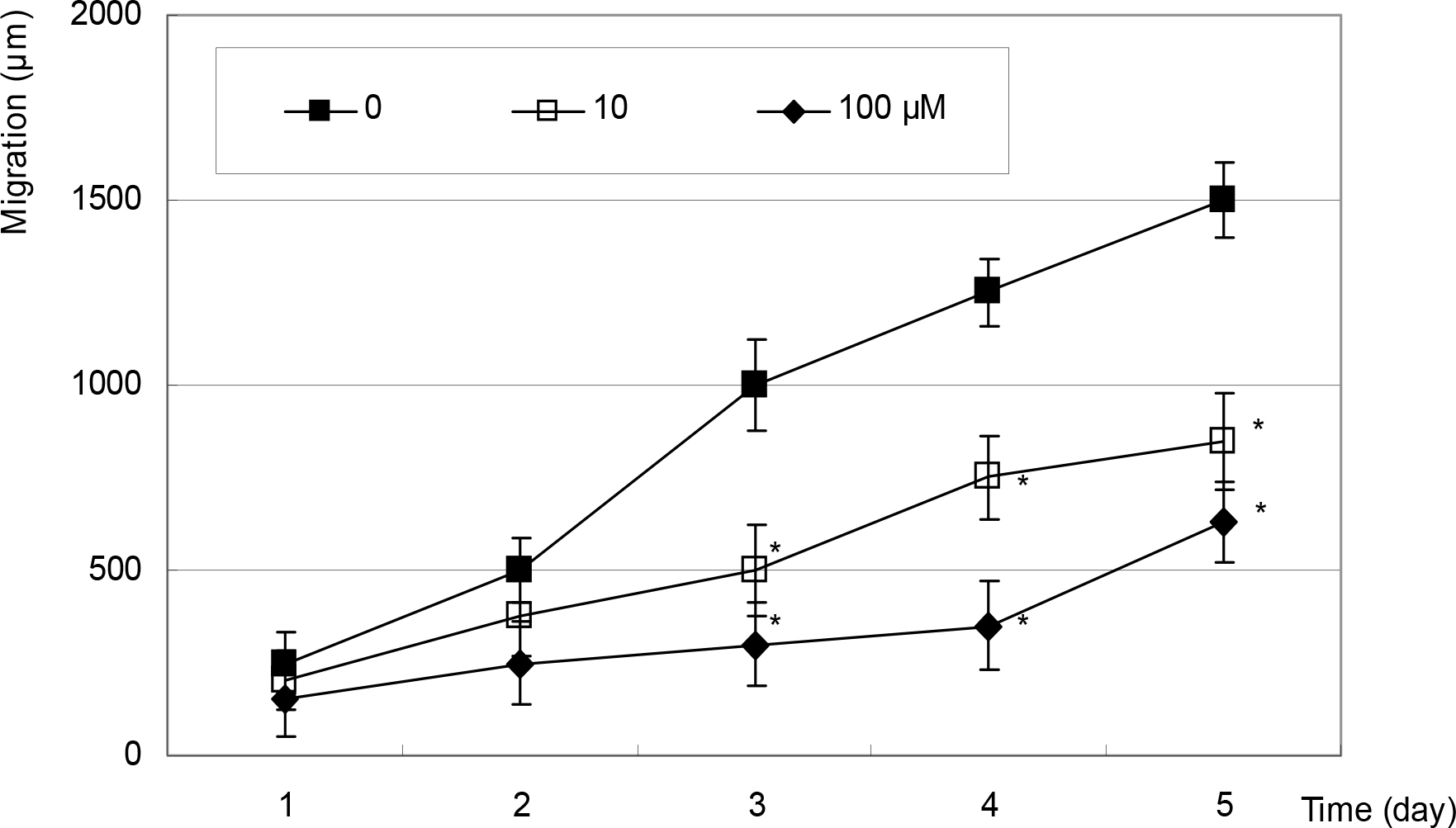
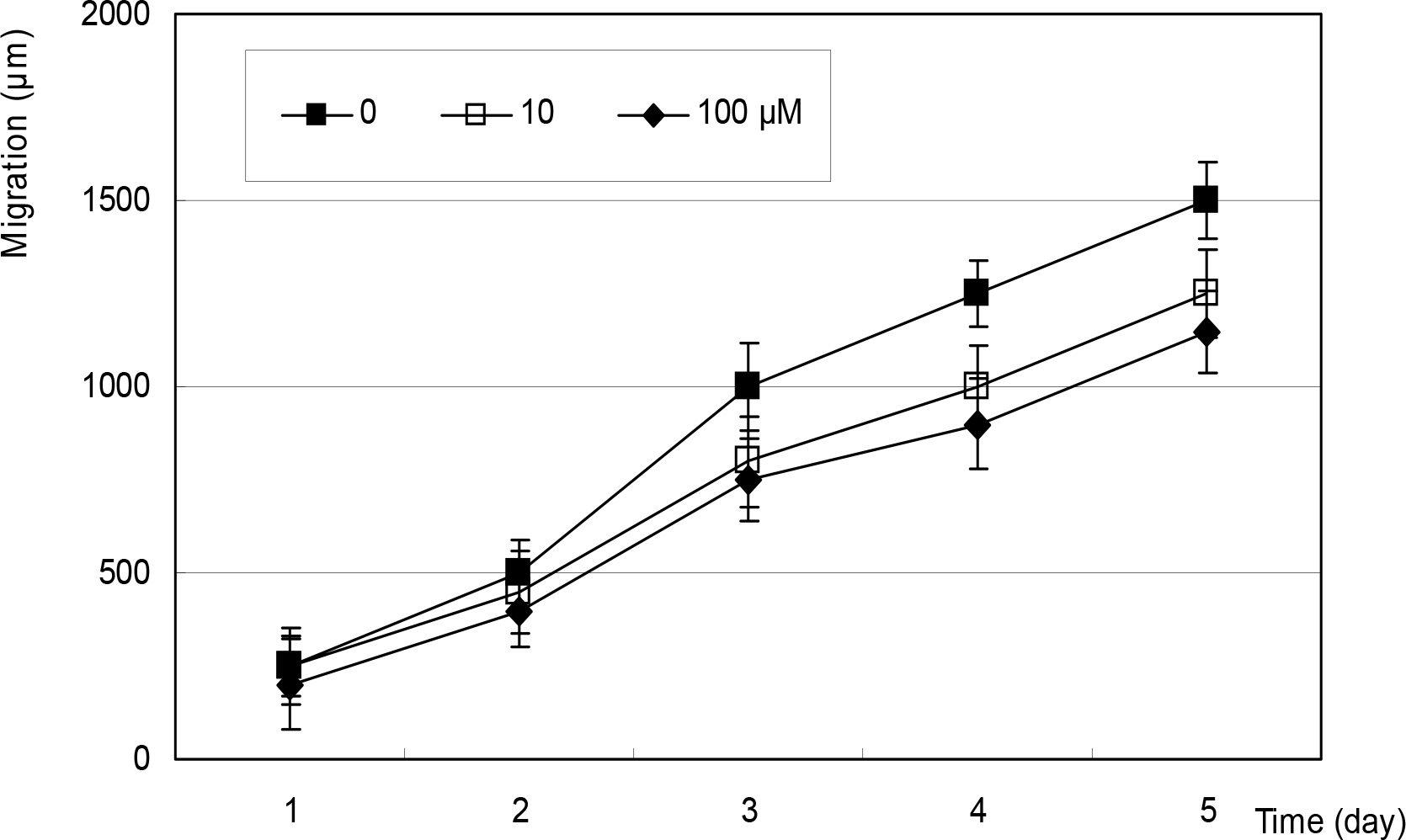
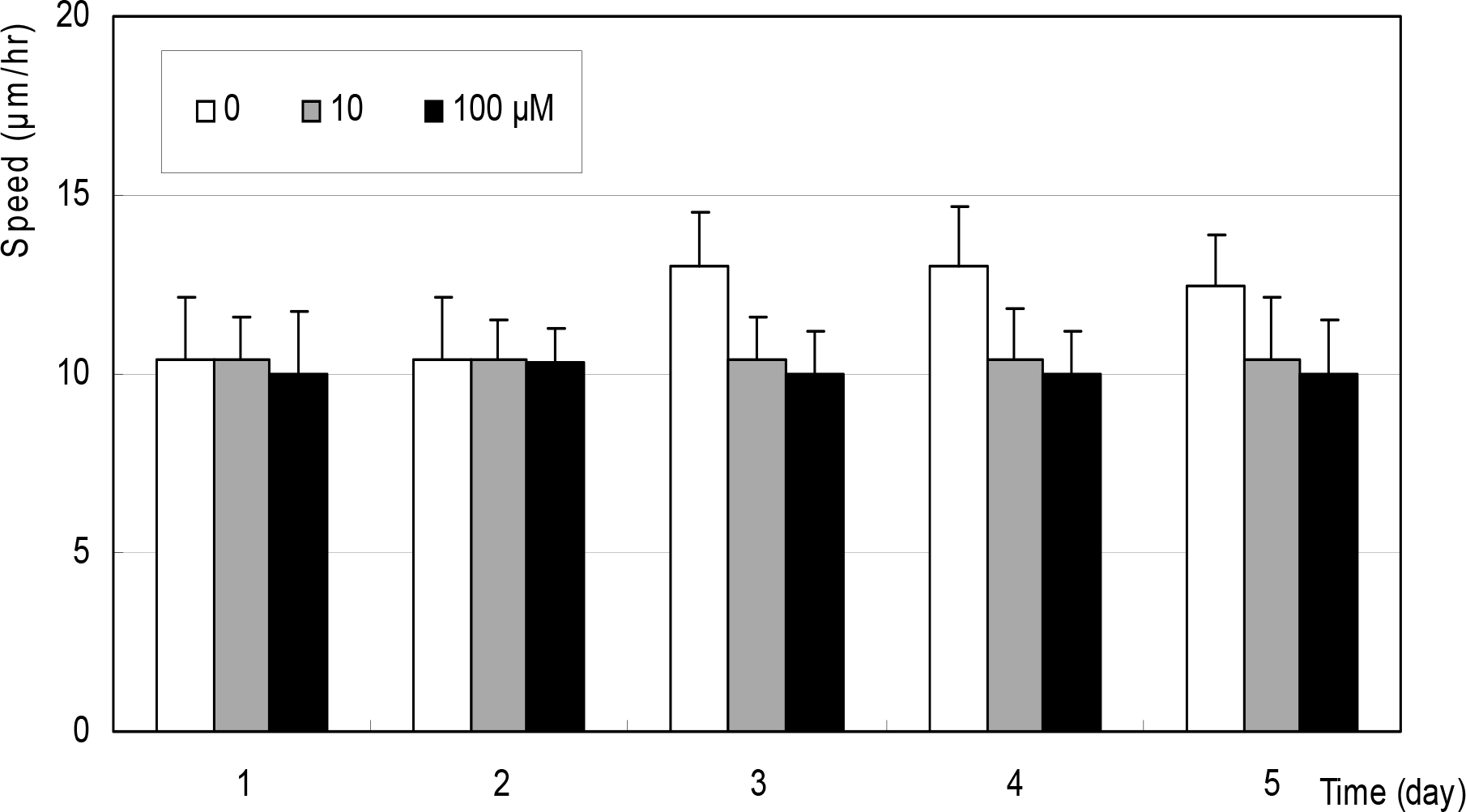
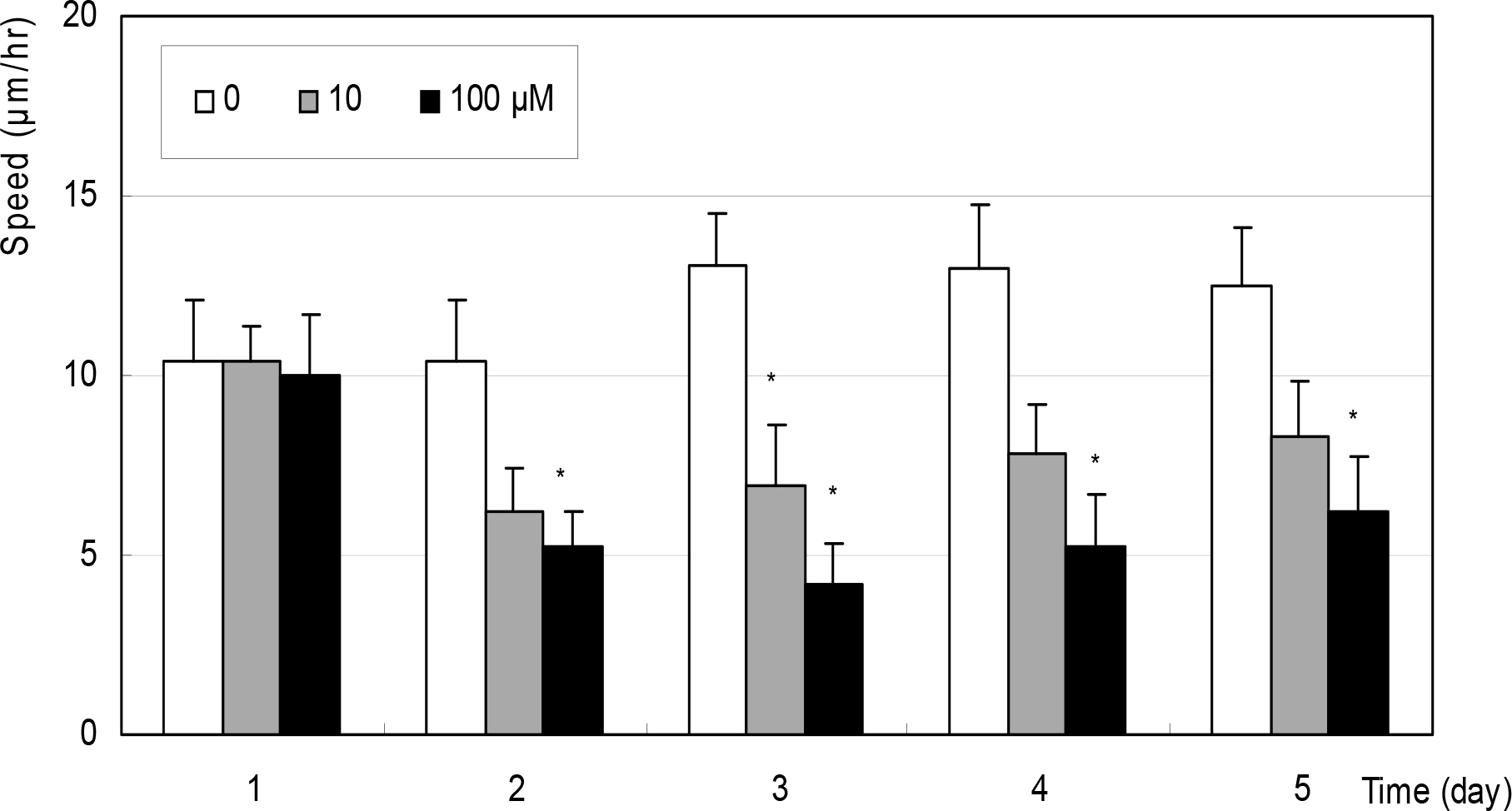
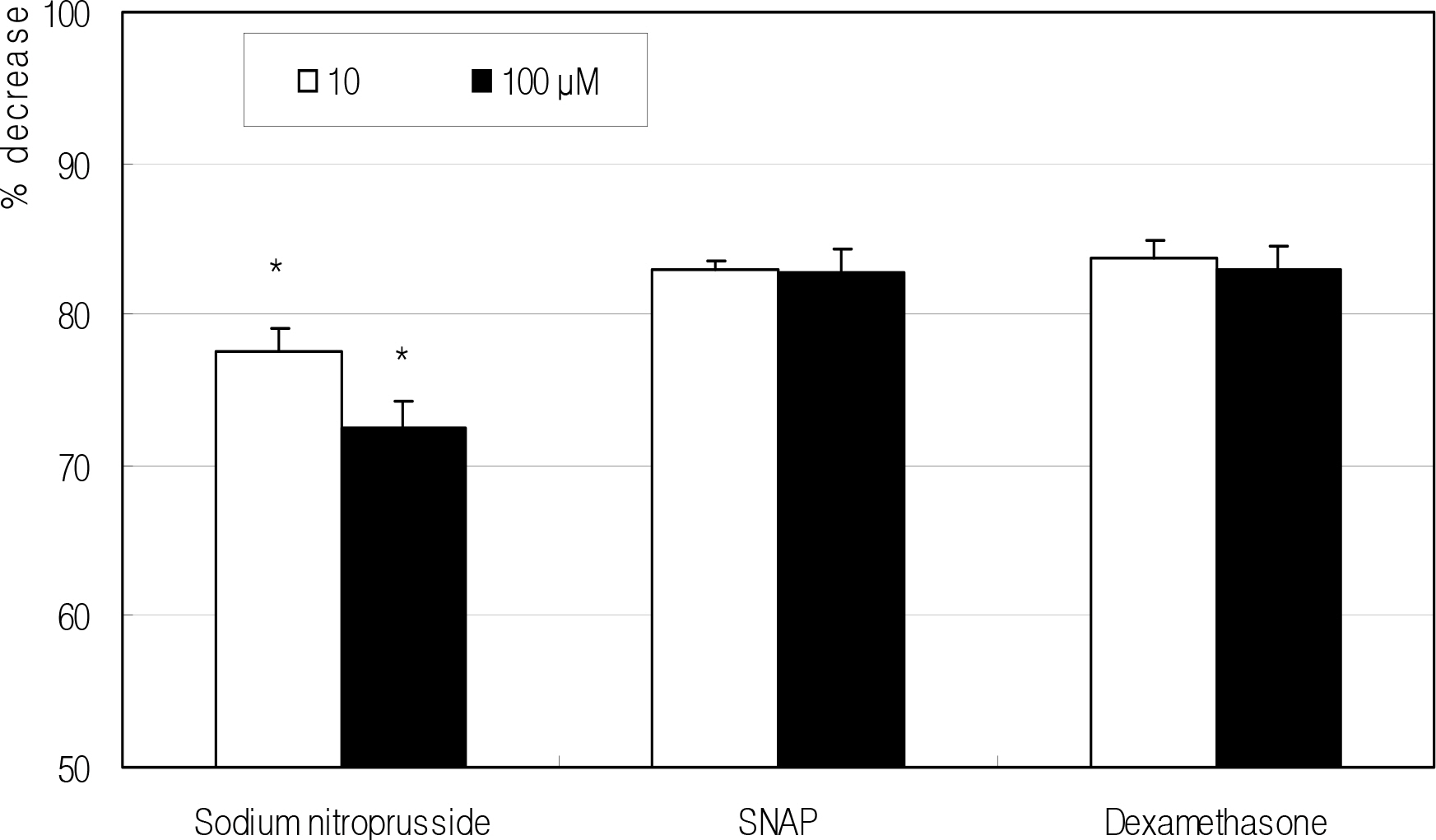
After artificial wounding, the primarily cultured HTCF were exposed to an NO donor such as sodium nitroprusside (SNP), S-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP), or dexamethasone at various concentrations. The cellular migration was measured up to five days. After embedding the cells in the collagen gels, the amount of contraction by the gels was also measured. Cellular survival and NO production were measured with MTT assay and Griess assay, respectively.
RESULTS
Cellular survival was decreased by both NO donors but not by dexamethasone. SNP inhibited migration of HTCF in a dose-dependent manner and enhanced contraction of collagen gels. However, SNAP had no effect on the cellular migration or gel contraction. Dexamethasone inhibited cellular migration but did not affect the contraction of collagen gels.
CONCLUSIONS
Among the NO donors, only SNP inhibited migration of HTCF and enhanced contraction of collagen gels in vitro. Thus, the effects between the two NO donors on fibroblast induced wound healing differ.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Addicks EM, Quigley HA, Green WR, Robin AL. Histologic characteristics of filtering blebs. Arch Ophthalmol. 1983; 101:795–8.2. Skuta GL, Parrish RK. Wound healing in glaucoma filtering surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 1987; 32:149–70.
Article3. Cordeiro MF. Beyond mitomycin: TGF-β and wound healing. Progr Retin Eye Res. 2002; 21:75–89.
Article4. Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991; 43:109–42.5. Bredt DS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994; 63:175–95.
Article6. Park GC, Kwon NS, Kim YM, Kim JC. The role of nitric oxide in ocular surface diseases. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2001; 15:59–66.
Article7. Haefliger IO, Dettmann E, Liu R, et al. Potential role of nitric oxide and endothelin in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol. 1999; 43:S51–8.
Article8. Nathanson JA, McKee M. Identification of an extensive system of nitric oxide‐ producing cells in the ciliary muscle and outflow pathway of the human eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995; 36:1765–73.9. Nathanson JA, McKee M. Alterations of ocular nitric oxide synthase in human glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995; 36:1774–84.10. Schaffer MR, Tantry U, Gross SS, et al. Nitric oxide regulates wound healing. J Surg Res. 1996; 63:237–40.11. Kiviluto T, Watanabe S, Hirose M, et al. Nitric oxide donors retard wound healing in cultured rabbit gastric epithelial cell monolayers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001; 281:G1151–7.12. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983; 65:55–63.
Article13. Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, et al. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15 N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982; 126:131–8.14. Liu XD, Skold CM, Umino T, et al. Sodium nitroprusside augments human lung fibroblast collagen gel contraction independently of NO‐ cGMP pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000; 278:L1032–8.15. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein‐ dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976; 72:248–54.16. Grierson I, Joseph J, Miller M, Day JE. Wound repair: The fibroblast and the inhibition of scar formation. Eye. 1988; 2:135–48.
Article17. Khaw PT, Occleston NL, Schultz G, et al. Activation and suppression of fibroblast function. Eye. 1994; 8:188–95.
Article18. Grant MD, Jones RC, Wilson SE, et al. Single dose cephalosporin prophylaxis in high‐ risk patients undergoing surgical treatment of the biliary tract. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992; 274:347–54.19. Kim YM, Bombeck CA, Billiar TR. Nitric oxide as a bifunctional regulator of apoptosis. Circ Res. 1999; 84:253–6.
Article20. Beckman JS, Koppenol WH. Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:1424–37.21. Clark RA. Regulation of fibroplasia in cutaneous wound repair. Am J Med Sci. 1993; 306:42–8.
Article22. Gabbiani GB, Hirschel GB, Ryan PR, et al. Granulation tissue as a contractile organ: a study of structure and function. J Exp Med. 1972; 135:719–33.23. Elsdale T, Bard J. Collagen substrata for studies on cell behavior. J Cell Biol. 1972; 54:626–37.
Article24. Bell E, Ivarsson B, Merrill C. Production of a tissue‐ like structure by contraction of collagen lattices by human fibroblasts of different proliferative potential in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979; 76:1274–8.25. Harris AK, Stopak D, Wild P. Fibroblast traction as a mechanism for collagen morphogenesis. Nature. 1981; 290:249–51.
Article26. Skold CM, Liu X, Zhu YK, et al. Glucocorticoids augment fibroblast mediated contraction of collagen gels by inhibition of endogenous PGE production. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1999; 111:249–58.27. Kim JW, Kim KH, Cho BJ. Effect of nitric oxide on the proliferation of cultured human Tenon capsule fibroblasts exposed to benzalkonium chloride. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 1908–13.28. Kanno M, Araie M, Koibuchi H, Masua K. Effects of topical nipradilol, a β blocking agent with α blocking and nitroglycerin‐ like activities, on intraocular pressure and aqueous dynamics in humans. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:293–9.29. Mizuno K, Koide T, Yoshimura M, et al. Neuroprotective effect and intraocular penetration of nipradilol, a β– blocker with nitric oxide donative action. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001; 42:688–94.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Nitric Oxide on the Trabecular Meshwork Cell-mediated Contraction of Collagen Gels
- Effect of Amniotic Membrane Extract on the Tenon's Capsule Fibroblasts
- The Effect of Anticancerous Drug in the Fiboblast-Mediated Collagen Matrix Contraction
- Effect of Nitric Oxide on Adhesion and Migration of Trabecular Meshwork Cells
- Role of Nitric Oxide in the Proliferative and Migratory Effect of Triamcinolone in RPE Cells