J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2009 Jun;16(2):133-143. 10.4078/jkra.2009.16.2.133.
The Effect of Inflammatory Cytokines on the Differentiation of Th17 Cells in Human Peripheral Blood
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Rheumatism Research Center, Catholic Research Institute of Medical Science, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. rheuma@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2202129
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2009.16.2.133
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
IL-17-producing T cells (Th17 cells) have been identified as a distinct lineage of CD4+ T helper cells in mice. Since this discovery, many efforts have been made to investigate the characteristics and the role of human Th17 cells and the factors involved in their differentiation. This study was undertaken to assess the effects of cytokines and stimulatory conditions on the differentiation of human CD4+ T cells into Th17 cells.
METHODS
Peripheral blood CD4+ T cells were isolated from healthy humans and then these cells were cultured with using various stimulatory conditions. The Th17 cells and regulatory T (Treg) cells were detected by flow cytometry (FACs). The related gene expressions of cytokines, transcription factors and chemokine receptors were determined by ELISA and RT-PCR.
RESULTS
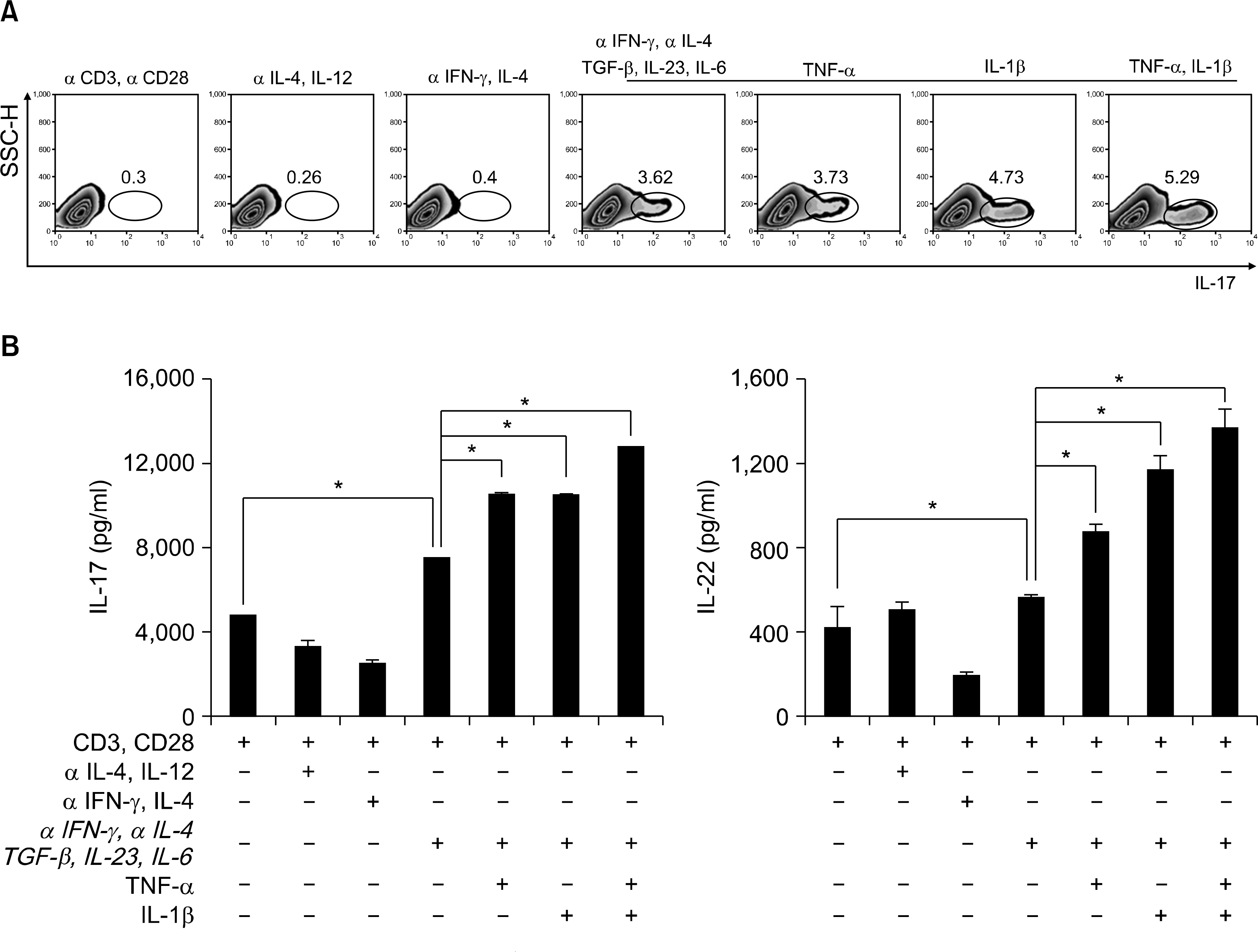
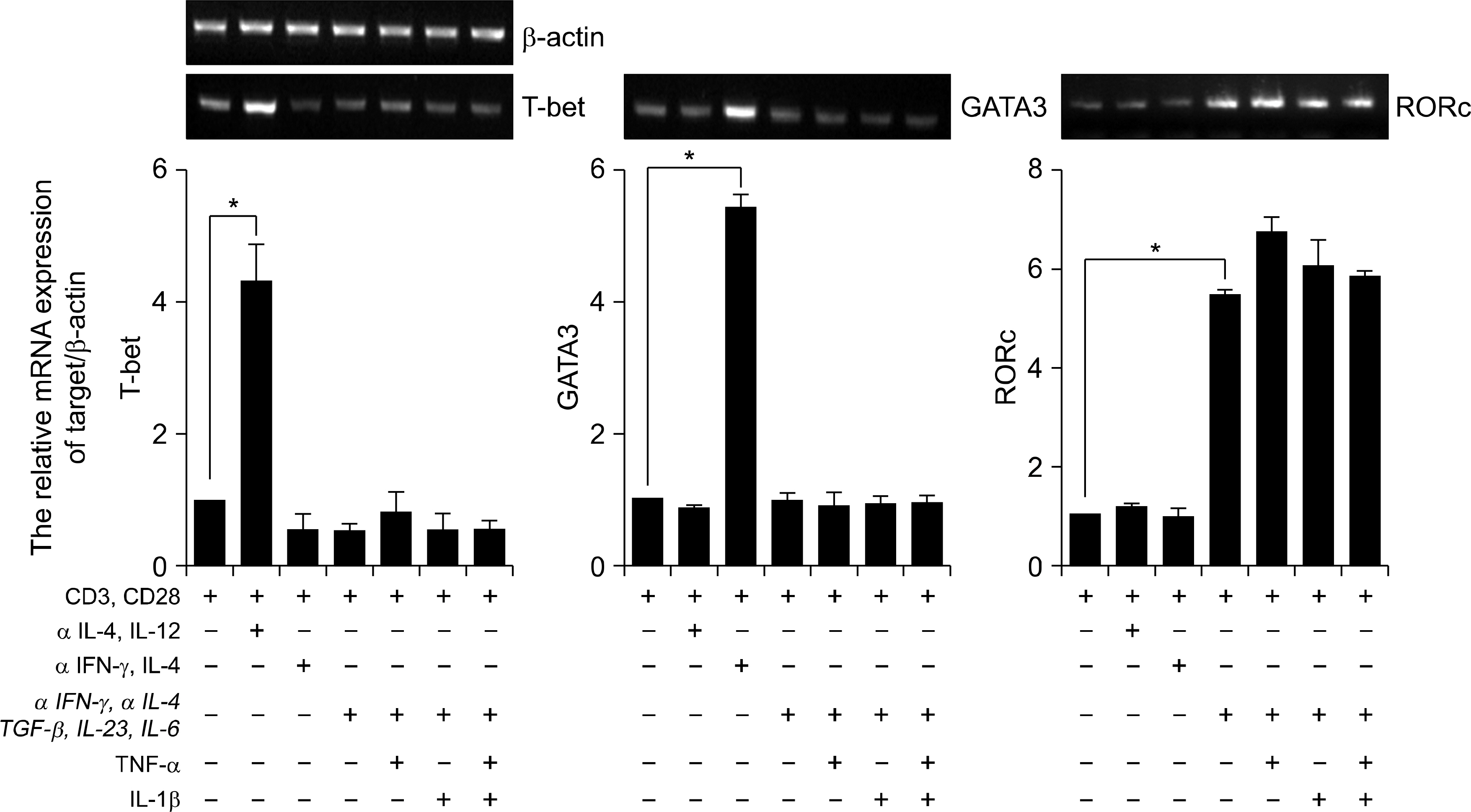
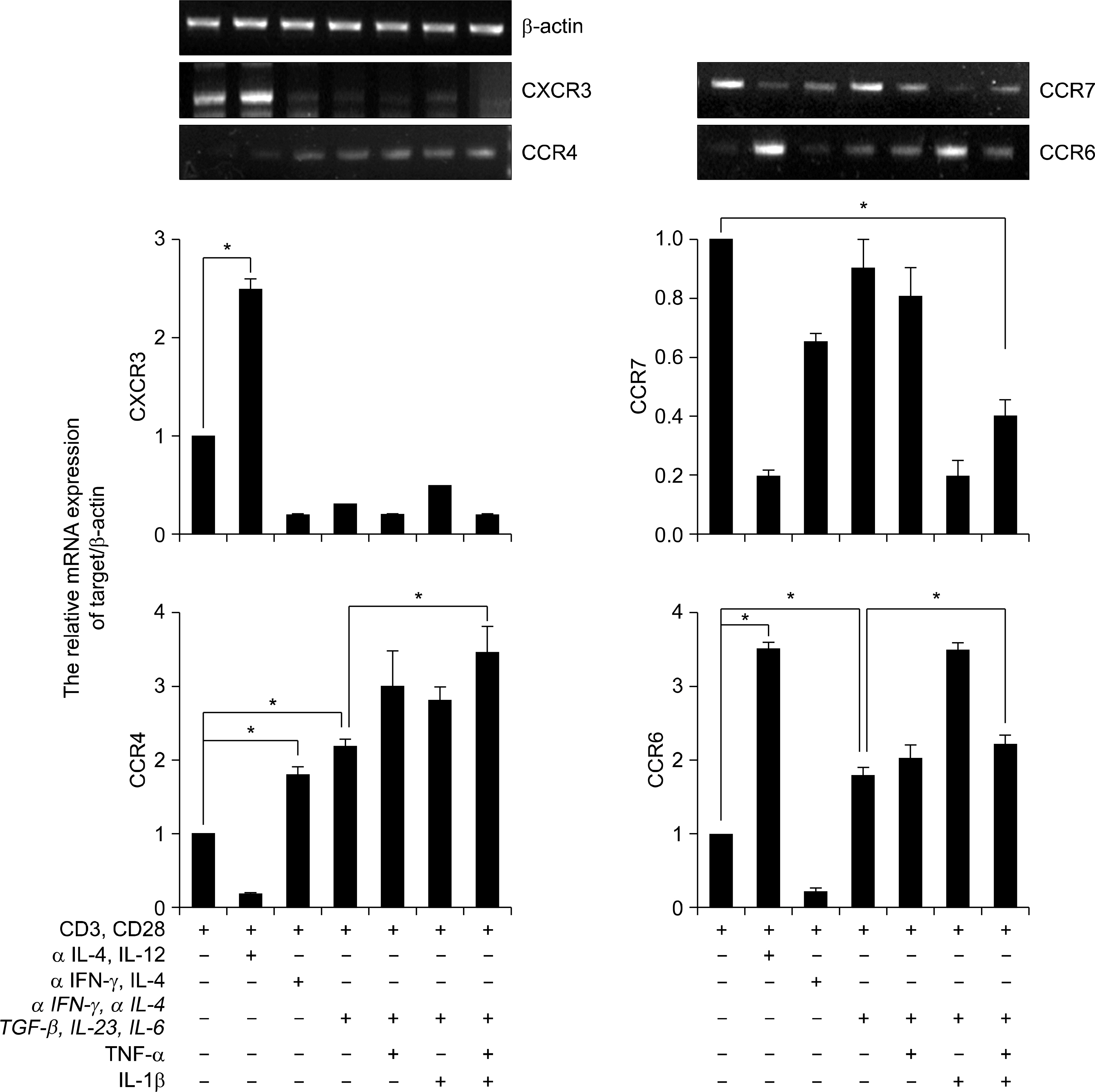
In the presence of inflammatory cytokines, TNFa and IL-1b, the human CD4+ T cells rapidly produced IL-17 in response to anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation, whereas, with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation alone, the CD4+ T cells expressed low levels of IL-17. TNFa and IL-1b were also important inducers of IL-22 production. IL-6 and IL-23 up-regulated the RORgammat, CCR4 and CCR6 expressions in the human CD4+ T cells. In response to TGF-b and IL-2, the human CD4+ T cells were rapidly induced to express FoxP3, IL-10 and CCR7, as compared with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation alone.
CONCLUSION
The effect of inflammatory cytokines on the differentiation of human Th17 cells may help us to understand their pathogenic role. Moreover, the differential expression of chemokine receptors and transcription factors of the subsets of CD4+ T cells with the different features of Th17 and Treg, may raise new issues concerning the pathogenesis of autoimmune inflammatory diseases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Cytokines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Flow Cytometry
Gene Expression
Humans
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-23
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Mice
Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1, Group F, Member 3
Receptors, Chemokine
T-Lymphocytes
T-Lymphocytes, Helper-Inducer
T-Lymphocytes, Regulatory
Th17 Cells
Transcription Factors
Cytokines
Interleukin-10
Interleukin-17
Interleukin-2
Interleukin-23
Interleukin-6
Interleukins
Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1, Group F, Member 3
Receptors, Chemokine
Transcription Factors
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989; 7:145–73.
Article2. Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003; 14:1030–1.3. Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006; 126:1121–33.4. Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Weaver CT. Expanding the effector CD4 T-cell repertoire: the Th17 lineage. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006; 18:349–56.
Article5. Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007; 25:821–52.
Article6. Wei L, Laurence A, Elias KM, O'Shea JJ. IL-21 is produced by Th17 cells and drives IL-17 production in a STAT3-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:34605–10.
Article7. McGeachy MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, Tato CM, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, et al. TGF-beta and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain T(H)-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:1281–3.8. Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP, Karim R, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M, et al. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med. 2006; 203:2271–9.
Article9. Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, et al. T(H)-17 differentiation: of mice and men. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:903–5.
Article10. Elisabetta V, Nicolas St, Raphael Zr, Sofia IB, Philippe H, Emmanuel B, et al. A critical function for ransforming growth factor-b, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human Th-17 responses. Nat Immunol. 2008; 9:650–7.11. Eva AR, Laura R, Jens G, David J, Marco G, Antonio L, et al. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:639–46.
Article12. Estelle B, Mohamed O, Vijay KK. Th-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:345–50.
Article13. Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not ransforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:903–5.14. Wilson NJ, Boniface K, Chan JR, McKenzie BS, Blumenschein WM, Mattson JD, et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:950–7.
Article15. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25-naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta nduction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. 2003; 15:1875–86.16. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakihama T, Itoh M, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995; 1:1151–64.17. Shevach EM, Piccirillo CA, Thornton AM, McHugh RS. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and rans-plantation tolerance. Immunol Rev. 2001; 182:18–32.18. Matsui T, Akahoshi T, Namai R, Hashimoto A, Kurihara Y, Rana M, et al. Selective recruitment of CCR6-expressing cells by increased production of MIP-3 alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001; 125:155–61.19. Ruth JH, Shahrara S, Park CC, Morel JC, Kumar P, Qin S, et al. Role of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha and its ligand CCR6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Invest. 2003; 83:579–88.20. Brennan FM, Feldmann M. Cytokines in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996; 8:872–7.
Article21. Miossec P. Interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis: if T cells were to contribute to inflammation and destruction through synergy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:594–601.
Article22. Nakae S, Komiyama Y, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwase M, Homma I, et al. Antigen-specific T cell sensitization is impaired in IL-17-deficient mice, causing suppression of allergic cellular and humoral responses. Immunity. 2002; 17:375–87.
Article23. Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collageninduced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003; 171:6173–7.
Article24. Elias KM, Laurence A, Davidson TS, Stephens G, Kanno Y, Shevach EM, et al. Retinoic acid inhibits Th17 polarization and enhances FoxP3 expression through a Stat-3/Stat-5 independent signaling pathway. Blood. 2008; 111:1013–20.
Article25. Anne B, Sylvia H, Magdalena H, Christine R, Christine S, Philipp Y, et al. The development of inflammatory Th-17 cells requires interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:958–66.
Article26. Mangan PR, Harrington LE, Quinn DB, Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature. 2006; 441:231–4.27. Chung Y, Yang X, Chang SH, Ma L, Tian Q, Dong C. Expression and regulation of IL-22 in the IL-17-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes. Cell Res. 2006; 16:902–7.
Article28. Macias I, Garcia-Perez S, Ruiz-Tudela M, Medina F, Chozas N, Giron-Gonzalez JA. Modification of pro-and antiinflammatory cytokines and vascular-related molecules by tumor necrosis factor-a blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:2102–8.29. Aarvak T, Chabaud M, Miossec P, Natvig JB. IL-17 is produced by some proinflammatory Th1/Th0 cells but not by Th2 cells. J Immunol. 1999; 162:1246–51.30. Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006; 441:235–8.
Article31. Afzali B, Lombardi G, Lechler RI, Lord GM. Department of Nephrology and Transplantation, The role of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg) human organ transplantation and autoimmune disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007; 148:32–46.32. Shevach EM. CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol Review. 2002; 2:389–400.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis mediated by Th17 cells: cytokines, microbiota, and therapies
- Genetic controls of Th17 cell differentiation and plasticity
- Ciglitazone, a Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Ligand, Inhibits Proliferation and Differentiation of Th17 Cells
- Catalpol Inhibits Tregs-to-Th17 Cell Transdifferentiation by Up-Regulating Let-7g-5p to Reduce STAT3 Protein Levels
- Effect of Spa Spring Water on Cytokine Expression in Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells and on Differentiation of CD4+ T Cells