J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2012 Oct;50(4):285-291. 10.4047/jkap.2012.50.4.285.
A study of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and surface characteristics of the titanium discs coated with MS275/PLGA by an electrospray
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Seoul National University Dental Hospital, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. ksy0617@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Seoul Asan Medical Center, Ulsan University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2195470
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2012.50.4.285
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted to identify the surface characteristics of titanium discs coated with MS275/PLGA by electrospray and which is effective to mesenchymal stem cell proliferation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We used anodized surface coated with PLGA as a control group and anodized surface coated with MS275 0.5 microM, 1 microM, 1.5 microM as test groups. To examine that the coating particles are nanometer sized, FE-SEM was used and AFM was utilized to determine the difference of coating surface roughness. We checked the mesenchymal stem cell proliferation by using MTT assay on 1st, 4th, 7th days.
RESULTS
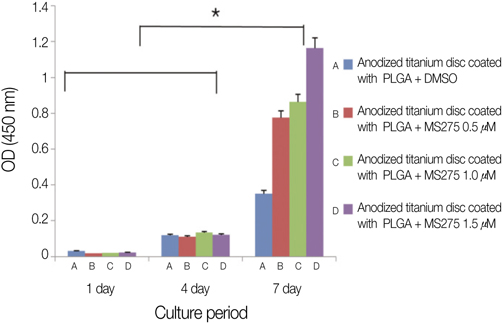
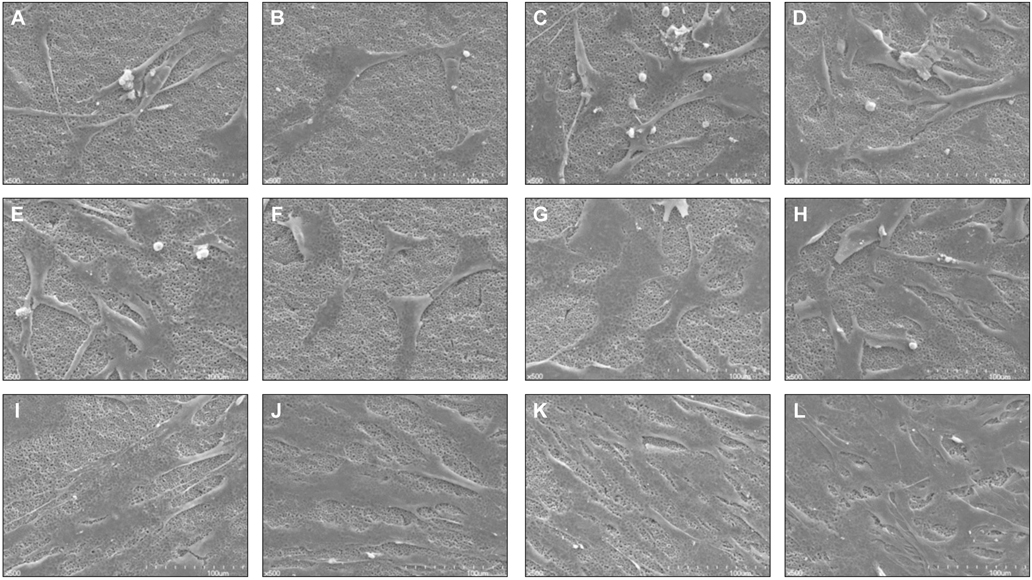
There was no significant difference between control groups and test groups in AFM results (P>.05). In MTT assay results, mesenchymal stem cell proliferation was increased with time, at 7th day, cell viability on discs coated with 1.5 microM MS275 was significantly higher than control group (P<.05). As SEM showed, the number of cells on all discs was increased and the morphology of cell attachment was also wider and closer with time.
CONCLUSION
Titanium surface coated with MS275/PLGA showed significantly higher cell proliferation and the more density of MS275 was dispersed on titanium discs, the faster cells grew.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Osseointegration of the titanium implant coated with rhTGF-β2/PLGA particles by electrospray: a preliminary microCT analyzing rabbit study
Woo-Sung Lee, Seong-Kyun Kim, Seong-Joo Heo, Jai-Young Koak, Joo-Hee Lee, Ji-Man Park, Yoon-Kyung Park
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2014;52(4):298-304. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2014.52.4.298.
Reference
-
1. Wong M, Eulenberger J, Schenk R, Hunziker E. Effect of surface topography on the osseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995. 29:1567–1575.
Article2. Hermann JS, Cochran DL, Nummikoski PV, Buser D. Crestal bone changes around titanium implants. A radiographic evaluation of unloaded nonsubmerged and submerged implants in the canine mandible. J Periodontol. 1997. 68:1117–1130.
Article3. Sul YT, Johansson CB, Petronis S, Krozer A, Jeong Y, Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Characteristics of the surface oxides on turned and electrochemically oxidized pure titanium implants up to dielectric breakdown: the oxide thickness, micropore configurations, surface roughness, crystal structure and chemical composition. Biomaterials. 2002. 23:491–501.
Article4. Xie J, Baumann MJ, McCabe LR. Osteoblasts respond to hydroxyapatite surfaces with immediate changes in gene expression. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004. 71:108–117.
Article5. Ivanoff CJ, Widmark G, Hallgren C, Sennerby L, Wennerberg A. Histologic evaluation of the bone integration of TiO2 blasted and turned titanium microimplants in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001. 12:128–134.
Article6. Orsini G, Assenza B, Scarano A, Piattelli M, Piattelli A. Surface analysis of machined versus sandblasted and acid-etched titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000. 15:779–784.7. Zhu X, Chen J, Scheideler L, Altebaeumer T, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Kern D. Cellular reactions of osteoblasts to micron- and submicronscale porous structures of titanium surfaces. Cells Tissues Organs. 2004. 178:13–22.
Article8. Huang HH, Ho CT, Lee TH, Lee TL, Liao KK, Chen FL. Effect of surface roughness of ground titanium on initial cell adhesion. Biomol Eng. 2004. 21:93–97.
Article9. Kim HN, Lee JH, Bae SC, Ryoo HM, Kim HH, Ha H, Lee ZH. Histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 stimulates bone formation in part by enhancing Dhx36-mediated TNAP transcription. J Bone Miner Res. 2011. 26:2161–2173.
Article10. Cho YJ, Heo SJ, Koak JY, Kim SK, Lee JH. Cellular responses on anodized titanium discs coated with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 incorporated Poly (D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2008. 46:620–627.
Article11. Lee SY. Effect of poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide)/bone morphogenic protein-2 coating of anodized titanium surface on osteoblast-like cells. 2010. Korea: Seoul University;MS Thesis.12. Freiberg S, Zhu XX. Polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Int J Pharm. 2004. 282:1–18.
Article13. Sims NA, Gooi JH. Bone remodeling: Multiple cellular interactions required for coupling of bone formation and resorption. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2008. 19:444–451.
Article14. Agrawal CM, Niederauer GG, Athanasiou KA. Fabrication and Characterization of PLA-PGA Orthopedic Implants. Tissue Eng. 1995. 1:241–252.
Article15. Hahn H, Palich W. Preliminary evaluation of porous metal surfaced titanium for orthopedic implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1970. 4:571–577.
Article16. Sammons RL, Lumbikanonda N, Gross M, Cantzler P. Comparison of osteoblast spreading on microstructured dental implant surfaces and cell behaviour in an explant model of osseointegration. A scanning electron microscopic study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:657–666.
Article17. Geesink RG, de Groot K, Klein CP. Bonding of bone to apatitecoated implants. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:17–22.
Article18. de Groot K, Geesink R, Klein CPAT, Serekian P. Plasma sprayed coatings of hydroxylapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 1987. 21:1375–1381.
Article19. Catledge SA, Vohra YK, Bellis SL, Sawyer AA. Mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and spreading on nanostructured biomaterials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004. 4:986–989.
Article20. Hans ML, Lowman AM. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery and targeting. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2002. 6:319–327.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An in vitro study of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation on titanium discs coated with rhTGF-β2/PLGA by electrospray
- Effect of RGD peptide coating of implant titanium surface on human mesenchymal stem cell response
- Cellular responses on anodized titanium discs coated with 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 incorporated Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles
- Analysis of attachment, proliferation and differentiation response of human mesenchymal stem cell to various implant surfaces coated with rhBMP-2
- Synergistic Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment and RGD Peptide Coating on Cell Proliferation over Titanium Surfaces