J Korean Med Assoc.
2008 Aug;51(8):757-763. 10.5124/jkma.2008.51.8.757.
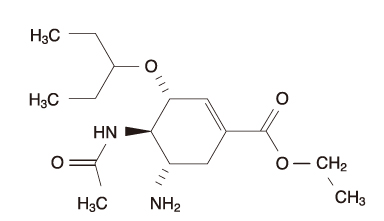
Clinical Use of Tamiflu (Oseltamivir)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Korea. thanks1126@paran.com
- KMID: 2185935
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2008.51.8.757
Abstract
- Oseltamivir (Tamiflu, the trade name) is a neuraminidase inhibitor used for the treatment and prevention of influenza virus infection as well as those of avian influenza infection. The mechanism of action is inhibition of neuraminidase for blocking the release of newly formed virus particles from the infected respiratory epithelial cells and preventing the further spread of the virus. Development of resistance is rare. The adult dose is 75mg (p.o.) b.i.d. for 5 days for treatment of influenza. The adverse drug reactions of oseltamivir are very rare but in children and adolescents careful monitoring is needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean Medical Association. Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Material for Media. Avian Influenza (AI) Recommendations for People May 8, 2008.2. The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases. Infectious Diseases. 2007. Seoul: Koonja Publishing.3. Moscona A. Medical management of Influenza infection. Annu Rev Med. 2008. 59:397–413.
Article4. Beigel JH, Farrar J, Han AM, Hayden FG, Hyer R, de Jong MD, Lochindarat S, Nguyen TK, Nguyen TH, Tran TH, Nicoll A, Touch S, Yuen KY. Writing Committee of the World Health Organization (WHO). Consultation on Human Influenza A/H5. Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1374–1385.5. Writing committee of the second world health organization consultation on clinical aspects of human infection with avian influenza A(H5N1) virus. Update of avian influenza A (H5N1) virus infection in humans. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:261–273.6. Woo JH. Pneumonia and Clinical Understanding Ulsan UUP. 1998.7. World Health Organization. Influenza pandemic preparedness plan. The role of WHO and guidelines for national and regional planning. 1999. 04. Geneva: Switzerland.8. Cheong HJ. Avian Influenza. J Korean Med Assoc. 2005. 48:1195–1205.
Article9. De Clercq E. Antiviral agents active against influenza A viruses. Nature reviews. 2006. 5:1015–1025.
Article10. Moscona A. Neuraminidase Inhibitors for Influenza. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1363–1373.
Article11. Monto AS, McKimm-Breschkin JL, Macken C, Hampson AW, Hay A, Klimov A, Tashiro M, Webster RG, Aymard M, Hayden FG, Zambon M. Detection of influenza viruses resistant to neuraminidase inhibitors in global surveillance during the first 3 years of their use. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. 50:2395–2402.
Article12. Sheu TG, Deyde VM, Okomo-Adhiambo M, Garten R, Xu X, Bright R, Butler E, Wallis TR, Klimov AI, Gubareva LV. Surveillance for neuraminidase inhibitor resistance among human influenza A and B viruses circulating worldwide in 2004-2008. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. 06. 14. (Epub ahead of print).13. Hayden FG, Atmar RL, Schilling M, Johnson C, Poretz D, Paar D, Huson L, Ward P, Mills RG. Use of the selective oral neuraminidase inhibitor oseltamivir to prevent influenza. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1336–1343.
Article14. Couch RB. Prevention and treatment of influenza. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1787.
Article15. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention and control of influenza. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007. 56:(RR-6).16. Whitley RJ. The role of oseltamivir in the treatment and prevention of influenza in children. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2007. 3:755–767.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Psychiatric Symptoms in a Patient with Influenza A (H1N1) Treated with Oseltamivir (Tamiflu): A Case Report
- A Case of Bilateral Vestibular Hypofunction Following Oseltamivir Medication
- Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) Induced Depressive Episode in a Female Adolescent
- Delayed Onset of Manic Symptoms in a Patient with Influenza A (H1N1) after administration of Oseltamivir (Tamiflu): A Case Report
- Role of the ABCB1 Drug Transporter Polymorphisms in the Pharmacokinetics of Oseltamivir in Humans: a Preliminary Report