J Breast Cancer.
2011 Mar;14(1):20-27. 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.1.20.
Role of Estrogen Receptor-alpha in the Regulation of Claudin-6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Key Laboratory of Pathobiology, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun, China. shuangxicmu@163.com
- KMID: 2175638
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2011.14.1.20
Abstract
- PURPOSE
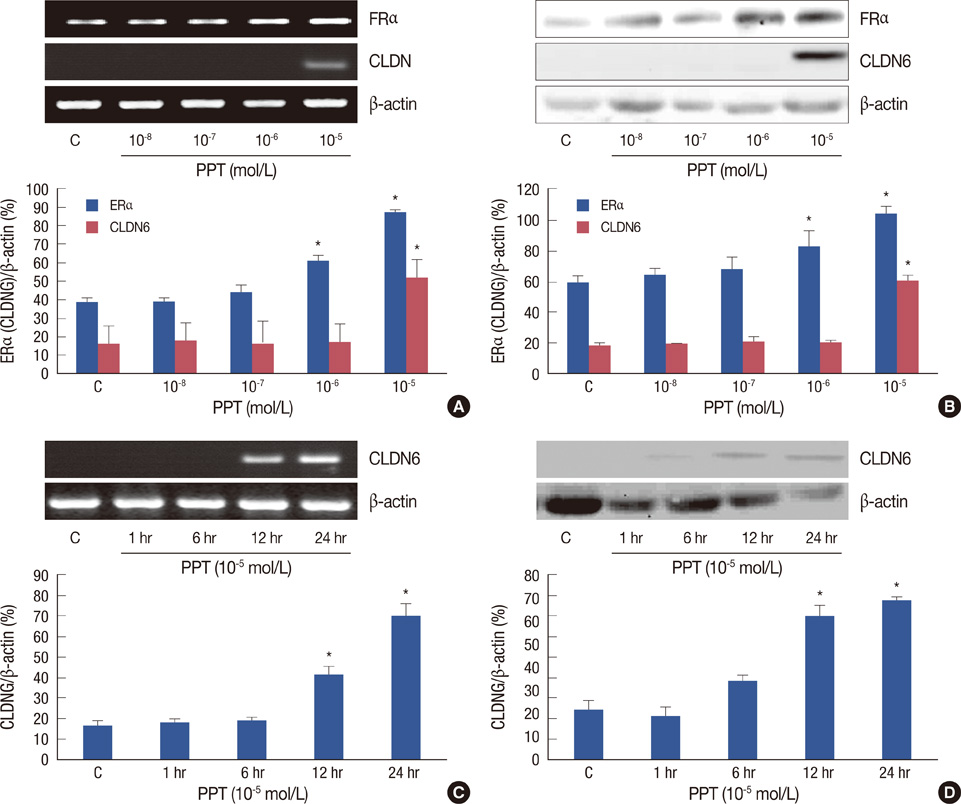
In our previous studies we showed that upregulating claudin-6 (CLDN6) expression may contribute to preventing breast cancer, and that 17beta-estradiol induces a concentration- and time-related effect on CLDN6 mRNA and protein expression in MCF-7 cells. However, the mechanisms of 17beta-estradiol regulation of CLDN6 are still unclear. We determined the role of estrogen receptors in the regulation of CLDN6 expression in human breast cancer tissues and a cell line.
METHODS
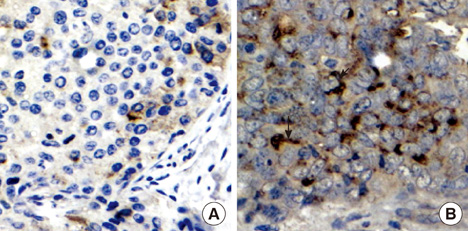
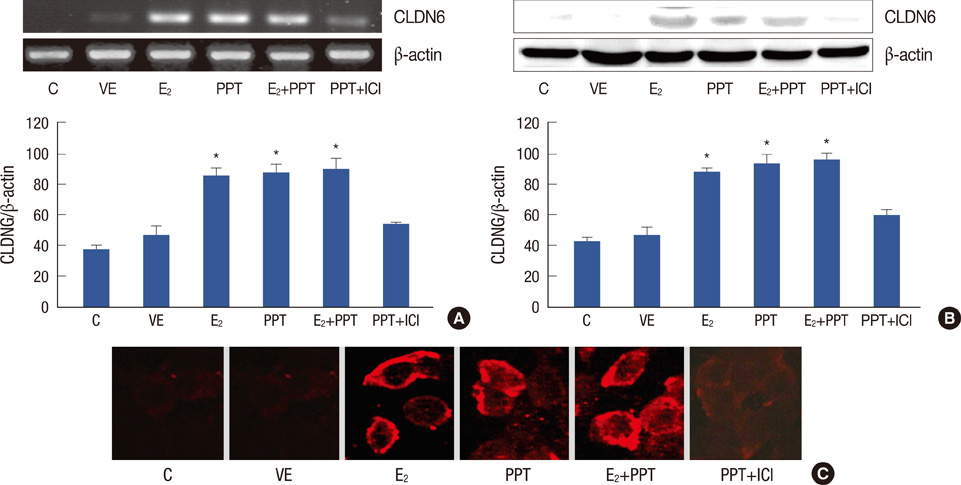
CLDN6, estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) expression in breast cancer tissues were examined using immunohistochemistry. The human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7, which expresses ERalpha but not ERbeta was used. CLDN6 and ERalpha expression were measured by reverse transcriptase-PCR, Western blotting and immunofluorescent staining. Treatments with propyl pyrazole triol (PPT) and ICI 182, 780 (ICI) were performed.
RESULTS
The results revealed that CLDN6 expression was related to ERalpha in breast cancer tissues (p=0.033). PPT, an ERalpha-selective ligand, upregulated CLDN6 expression at 10-5 mol/L after 24 hours. The effect of PPT on regulating CLDN6 expression in MCF-7 cells was blocked by ICI.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that Eralpha reulates CLDN6 expression in breast cancer tissues and that 17beta-estradiol induces CLDN6 expression through an ERalpha pathway in MCF-7 cells.
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Breast
Breast Neoplasms
Cell Line
Claudins
Estrogen Receptor alpha
Estrogen Receptor beta
Estrogens
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
MCF-7 Cells
Pyrazoles
Receptors, Estrogen
RNA, Messenger
Tight Junctions
Claudins
Estrogen Receptor alpha
Estrogen Receptor beta
Estrogens
Pyrazoles
RNA, Messenger
Receptors, Estrogen
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Invited Commentary: Role of Estrogen Receptor-α in Regulating Claudin-6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
Hyun Jo Youn, Sung Hoo Jung
J Breast Cancer. 2011;14(1):76-77. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2011.14.1.76.
Reference
-
1. Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001. 2:285–293.
Article2. Matter K, Balda MS. Signalling to and from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. 4:225–236.
Article3. McCarthy KM, Skare IB, Stankewich MC, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Rogers RA, et al. Occludin is a functional component of the tight junction. J Cell Sci. 1996. 109(Pt 9):2287–2298.
Article4. Lui WY, Lee WM, Cheng CY. Transforming growth factor-beta3 perturbs the inter-Sertoli tight junction permeability barrier in vitro possibly mediated via its effects on occludin, zonula occludens-1, and claudin-1. Endocrinology. 2001. 142:1865–1877.
Article5. Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S. Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. 96:511–516.
Article6. Kramer F, White K, Kubbies M, Swisshelm K, Weber BH. Genomic organization of claudin-1 and its assessment in hereditary and sporadic breast cancer. Hum Genet. 2000. 107:249–256.
Article7. Resnick MB, Konkin T, Routhier J, Sabo E, Pricolo VE. Claudin-1 is a strong prognostic indicator in stage II colonic cancer: a tissue microarray study. Mod Pathol. 2005. 18:511–518.
Article8. Oliveira SS, Morgado-Diaz JA. Claudins: multifunctional players in epithelial tight junctions and their role in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. 64:17–28.
Article9. Cheung ST, Leung KL, Ip YC, Chen X, Fong DY, Ng IO, et al. Claudin-10 expression level is associated with recurrence of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. 11(2 Pt 1):551–556.10. Offner S, Hekele A, Teichmann U, Weinberger S, Gross S, Kufer P, et al. Epithelial tight junction proteins as potential antibody targets for pancarcinoma therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005. 54:431–445.
Article11. Troy TC, Rahbar R, Arabzadeh A, Cheung RM, Turksen K. Delayed epidermal permeability barrier formation and hair follicle aberrations in Inv-Cldn6 mice. Mech Dev. 2005. 122:805–819.
Article12. Quan C, Lu SJ. Identification of genes preferentially expressed in mammary epithelial cells of Copenhagen rat using subtractive hybridization and microarrays. Carcinogenesis. 2003. 24:1593–1599.
Article13. Wu Q, Liu Y, Ren Y, Xu X, Yu L, Li Y, et al. Tight junction protein, claudin-6, downregulates the malignant phenotype of breast carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2010. 19:186–194.
Article14. Osanai M, Murata M, Chiba H, Kojima T, Sawada N. Epigenetic silencing of claudin-6 promotes anchorage-independent growth of breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2007. 98:1557–1562.
Article15. Liu YF, Wu Q, Xu XM, Ren Y, Yu LN, Quan CS, et al. Effects of 17 beta-estradiol on proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cell by regulating expression of claudin-6. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010. 39:44–47.16. Blanchard AA, Skliris GP, Watson PH, Murphy LC, Penner C, Tomes L, et al. Claudins 1, 3, and 4 protein expression in ER negative breast cancer correlates with markers of the basal phenotype. Virchows Arch. 2009. 454:647–656.
Article17. Ye L, Martin TA, Parr C, Harrison GM, Mansel RE, Jiang WG. Biphasic effects of 17-beta-estradiol on expression of occludin and transendothelial resistance and paracellular permeability in human vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2003. 196:362–369.
Article18. Angelow S, Ahlstrom R, Yu AS. Biology of claudins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. 295:F867–F876.
Article19. Blanco D, Vicent S, Elizegi E, Pino I, Fraga MF, Esteller M, et al. Altered expression of adhesion molecules and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in silica-induced rat lung carcinogenesis. Lab Invest. 2004. 84:999–1012.
Article20. Krause G, Winkler L, Mueller SL, Haseloff RF, Piontek J, Blasig IE. Structure and function of claudins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. 1778:631–645.
Article21. Colegio OR, VanItallie C, Rahner C, Anderson JM. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003. 284:C1346–C1354.
Article22. Hong YH, Hishikawa D, Miyahara H, Nishimura Y, Tsuzuki H, Gotoh C, et al. Up-regulation of the claudin-6 gene in adipogenesis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2005. 69:2117–2121.
Article23. Moriwaki K, Tsukita S, Furuse M. Tight junctions containing claudin 4 and 6 are essential for blastocyst formation in preimplantation mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 2007. 312:509–522.
Article24. Anderson WJ, Zhou Q, Alcalde V, Kaneko OF, Blank LJ, Sherwood RI, et al. Genetic targeting of the endoderm with claudin-6CreER. Dev Dyn. 2008. 237:504–512.
Article25. Tsunoda S, Smith E, De Young NJ, Wang X, Tian ZQ, Liu JF, et al. Methylation of CLDN6, FBN2, RBP1, RBP4, TFPI2, and TMEFF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2009. 21:1067–1073.
Article26. Putti TC, El-Rehim DM, Rakha EA, Paish CE, Lee AH, Pinder SE, et al. Estrogen receptor-negative breast carcinomas: a review of morphology and immunophenotypical analysis. Mod Pathol. 2005. 18:26–35.
Article27. Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, Tujague M, Thomsen J, Andersson G, et al. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev. 2001. 81:1535–1565.
Article28. Losel R, Wehling M. Nongenomic actions of steroid hormones. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. 4:46–56.
Article29. Gottlicher M, Heck S, Herrlich P. Transcriptional cross-talk, the second mode of steroid hormone receptor action. J Mol Med. 1998. 76:480–489.
Article30. O'Lone R, Frith MC, Karlsson EK, Hansen U. Genomic targets of nuclear estrogen receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. 18:1859–1875.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invited Commentary: Role of Estrogen Receptor-alpha in Regulating Claudin-6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells
- Expression of Claudin-1 and -4 in Benign Lesions and Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
- Up-regulation of P13K/Akt Signaling by 17 beta-estradiol through Activation of Estrogen Receptor-alpha in Breast Cancer Cells
- Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Human Breast Carcinoma: Relevance to Tumor Angiogenesis and Expression of Estrogen Receptor
- Significance of the Decreased Expressions of Claudin-1 and ZO-1 Protein as Prognostic Factors in Breast Cancer