Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2015 Sep;19(3):146-152. 10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.146.
Associated Brain Parenchymal Abnormalities in Developmental Venous Anomalies: Evaluation with Susceptibility-weighted MR Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. choids@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2175605
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.146
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the associated brain parenchymal abnormalities of developmental venous anomalies (DVA) with susceptibility-weighted image (SWI).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2012 and June 2013, 2356 patients underwent brain MR examinations with contrast enhancement. We retrospectively reviewed their MR examinations and data were collected as per the following criteria: incidence, locations, and associated parenchymal signal abnormalities of DVAs on T2-weighted image, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR), and SWI. Contrast enhanced T1-weighted image was used to diagnose DVA.
RESULTS
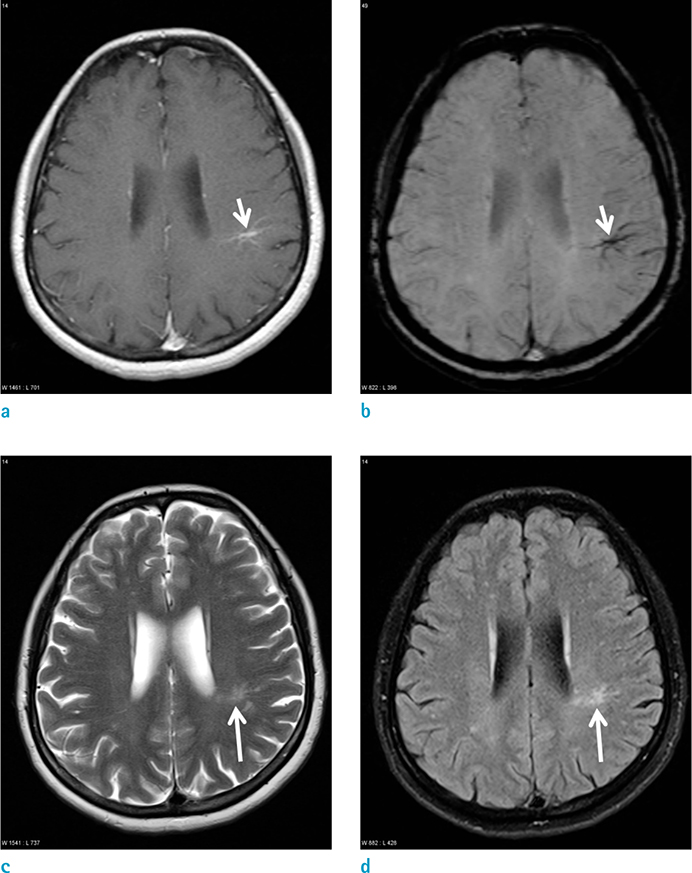
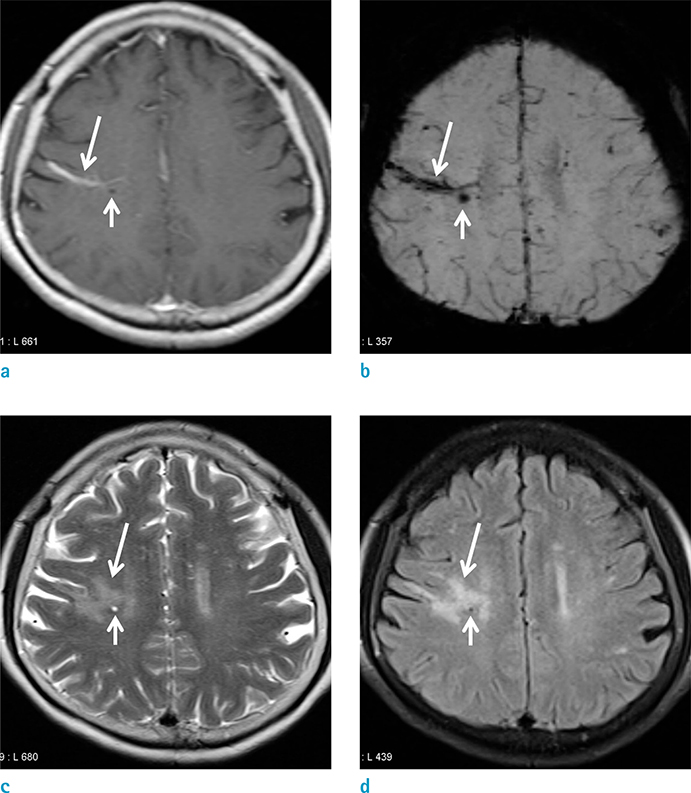
Of the 2356 patients examined, 57 DVAs were detected in 57 patients (2.4%); 47 (82.4%) were in either lobe of the supratentorial brain, 9 (15.7%) were in the cerebellum, and 1 (1.7%) was in the pons. Of the 57 DVAs identified, 20 (35.1%) had associated parenchymal abnormalities in the drainage area. Among the 20 DVAs which had associated parenchymal abnormalities, 13 showed hemorrhagic foci on SWI, and 7 demonstrated only increased parenchymal signal abnormalities on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. In 5 of the 13 patients (38.5%) who had hemorrhagic foci, the hemorrhagic lesions were demonstrated only on SWI.
CONCLUSION
The overall incidence of DVAs was 2.4%. Parenchymal abnormalities were associated with DVAs in 35.1% of the cases. On SWI, hemorrhage was detected in 22.8% of DVAs. Thus, we conclude that SWI might give a potential for understanding of the pathophysiology of parenchymal abnormalities in DVAs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruiz DS, Yilmaz H, Gailloud P. Cerebral developmental venous anomalies: current concepts. Ann Neurol. 2009; 66:271–283.2. San Millan Ruiz D, Gailloud P. Cerebral developmental venous anomalies. Childs Nerv Syst. 2010; 26:1395–1406.3. Sarwar M, McCormick WF. Intracerebral venous angioma. Case report and review. Arch Neurol. 1978; 35:323–325.4. Garner TB, Del Curling O Jr, Kelly DL Jr, Laster DW. The natural history of intracranial venous angiomas. J Neurosurg. 1991; 75:715–722.5. Santucci GM, Leach JL, Ying J, Leach SD, Tomsick TA. Brain parenchymal signal abnormalities associated with developmental venous anomalies: detailed MR imaging assessment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1317–1323.6. San Millan Ruiz D, Delavelle J, Yilmaz H, et al. Parenchymal abnormalities associated with developmental venous anomalies. Neuroradiology. 2007; 49:987–995.7. Wilms G, Bleus E, Demaerel P, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of developmental venous anomalies and cavernous angiomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15:1247–1254. discussion 1255-12578. Huber G, Henkes H, Hermes M, Felber S, Terstegge K, Piepgras U. Regional association of developmental venous anomalies with angiographically occult vascular malformations. Eur Radiol. 1996; 6:30–37.9. Abe T, Singer RJ, Marks MP, Norbash AM, Crowley RS, Steinberg GK. Coexistence of occult vascular malformations and developmental venous anomalies in the central nervous system: MR evaluation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 19:51–57.10. Uchino A, Hasuo K, Matsumoto S, et al. Cerebral venous angiomas associated with hemorrhagic lesions. Their MRI manifestations. Clin Imaging. 1996; 20:157–163.11. Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haacke EM, et al. Clinical applications of neuroimaging with susceptibility-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005; 22:439–450.12. Tong KA, Ashwal S, Obenaus A, Nickerson JP, Kido D, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:9–17.13. Tsui YK, Tsai FY, Hasso AN, Greensite F, Nguyen BV. Susceptibility-weighted imaging for differential diagnosis of cerebral vascular pathology: a pictorial review. J Neurol Sci. 2009; 287:7–16.14. Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YC. Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:19–30.15. de Souza JM, Domingues RC, Cruz LC Jr, Domingues FS, Iasbeck T, Gasparetto EL. Susceptibility-weighted imaging for the evaluation of patients with familial cerebral cavernous malformations: a comparison with t2-weighted fast spin-echo and gradient-echo sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:154–158.16. Takasugi M, Fujii S, Shinohara Y, Kaminou T, Watanabe T, Ogawa T. Parenchymal hypointense foci associated with developmental venous anomalies: evaluation by phase-sensitive MR Imaging at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 34:1940–1944.17. Jung HN, Kim ST, Cha J, et al. Diffusion and perfusion MRI findings of the signal-intensity abnormalities of brain associated with developmental venous anomaly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:1539–1542.18. Saito Y, Kobayashi N. Cerebral venous angiomas: clinical evaluation and possible etiology. Radiology. 1981; 139:87–94.19. Senegor M, Dohrmann GJ, Wollmann RL. Venous angiomas of the posterior fossa should be considered as anomalous venous drainage. Surg Neurol. 1983; 19:26–32.20. Thomas B, Somasundaram S, Thamburaj K, et al. Clinical applications of susceptibility weighted MR imaging of the brain - a pictorial review. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:105–116.21. Haacke EM, Xu Y, Cheng YC, Reichenbach JR. Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn Reson Med. 2004; 52:612–618.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between Abnormal Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images Around Developmental Venous Anomalies and Magnetic Susceptibility of Their Collecting Veins: In-Vivo Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Study
- Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging for the Detection of Developmental Venous Anomaly: Comparison with T2 and FLAIR Imaging
- Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging for the Detection of Isolated Cortical Vein Thrombosis in a Patient with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
- Arterial Spin Labelling Perfusion, Proton MR Spectroscopy and Susceptibility-Weighted MR Findings of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: a Case Report
- MR imaging findings of moyamoya disease