Diabetes Metab J.
2011 Jun;35(3):207-215. 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.207.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance: The Contribution of Dioxin-Like Substances
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkleemd@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2175418
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.207
Abstract
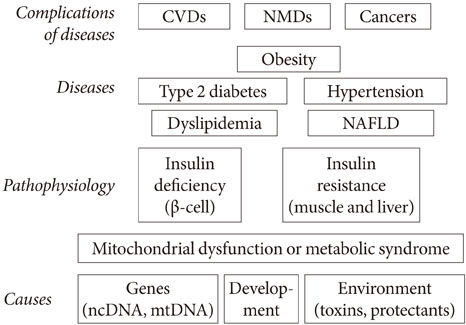
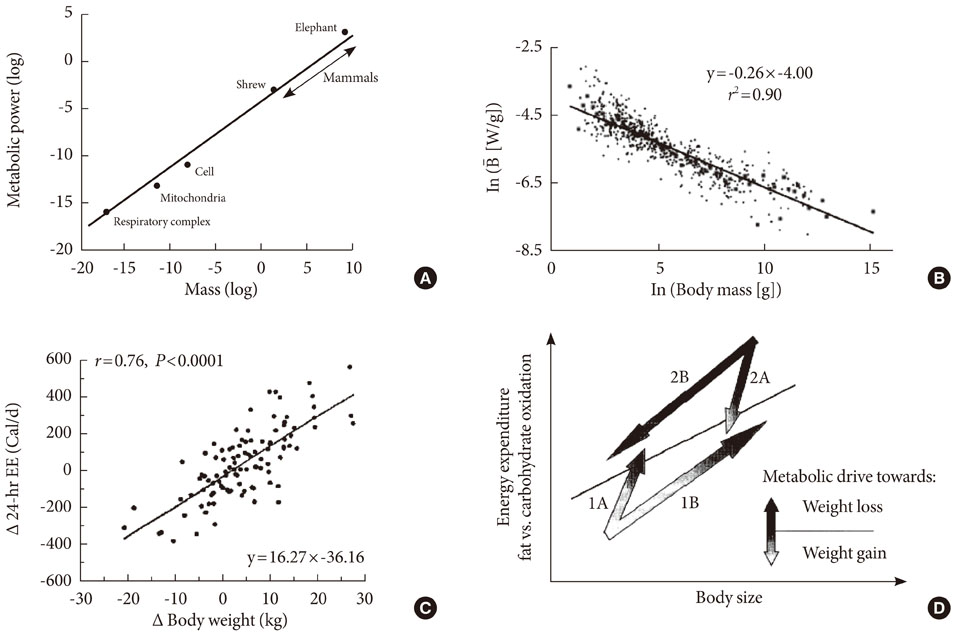
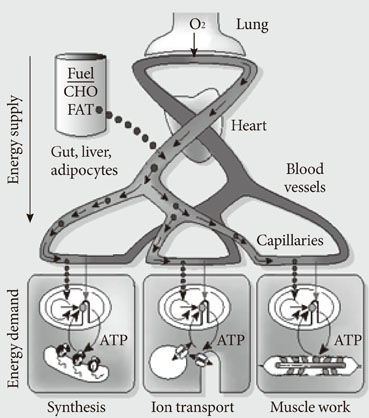
- Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are known to cause mitochondrial dysfunction and this in turn is linked to insulin resistance, a key biochemical abnormality underlying the metabolic syndrome. To establish the cause and effect relationship between exposure to POPs and the development of the metabolic syndrome, Koch's postulates were considered. Problems arising from this approach were discussed and possible solutions were suggested. In particular, the difficulty of establishing a cause and effect relationship due to the vagueness of the metabolic syndrome as a disease entity was discussed. Recently a bioassay, aryl-hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) trans-activation activity using a cell line expressing AhR-luciferase, showed that its activity is linearly related with the parameters of the metabolic syndrome in a population. This finding suggests the possible role of bioassays in the analysis of multiple pollutants of similar kinds in the pathogenesis of several closely related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Understanding the effects of POPs on mitochondrial function will be very useful in understanding the integration of various factors involved in this process, such as genes, fetal malnutrition and environmental toxins and their protectors, as mitochondria act as a unit according to the metabolic scaling law.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Value of Serum Mitochondria-Inhibiting Substances in Assessing Renal Hazards: A Community-Based Prospective Study in Korea
Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Wook Ha Park, Youngmi Kim Pak, Sung Woo Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1298-1306. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2021.1226.
Reference
-
1. Lim S, Cho YM, Park KS, Lee HK. Persistent organic pollutants, mitochondrial dysfunction, and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. 1201:166–176.2. Lee HK, Cho YM, Kwak SH, Lim S, Park KS, Shim EB. Mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic syndrome-looking for environmental factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. 1800:282–289.3. Savage VM, Allen AP, Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Herman AB, Woodruff WH, West GB. Scaling of number, size, and metabolic rate of cells with body size in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. 104:4718–4723.4. Weibel ER. Physiology: the pitfalls of power laws. Nature. 2002. 417:131–132.5. Fuku N, Park KS, Yamada Y, Nishigaki Y, Cho YM, Matsuo H, Segawa T, Watanabe S, Kato K, Yokoi K, Nozawa Y, Lee HK, Tanaka M. Mitochondrial haplogroup N9a confers resistance against type 2 diabetes in Asians. Am J Hum Genet. 2007. 80:407–415.6. Cho YM, Park KS, Lee HK. Genetic factors related to mitochondrial function and risk of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 77:Suppl 1. S172–S177.7. Palmieri VO, De Rasmo D, Signorile A, Sardanelli AM, Grattagliano I, Minerva F, Cardinale G, Portincasa P, Papa S, Palasciano G. T16189C mitochondrial DNA variant is associated with metabolic syndrome in Caucasian subjects. Nutrition. 2011. 27:773–777.8. Wilson FH, Hariri A, Farhi A, Zhao H, Petersen KF, Toka HR, Nelson-Williams C, Raja KM, Kashgarian M, Shulman GI, Scheinman SJ, Lifton RP. A cluster of metabolic defects caused by mutation in a mitochondrial tRNA. Science. 2004. 306:1190–1194.9. Lee YY, Park KS, Pak YK, Lee HK. The role of mitochondrial DNA in the development of type 2 diabetes caused by fetal malnutrition. J Nutr Biochem. 2005. 16:195–204.10. Baillie-Hamilton PF. Chemical toxins: a hypothesis to explain the global obesity epidemic. J Altern Complement Med. 2002. 8:185–192.11. Lee DH, Lee IK, Song K, Steffes M, Toscano W, Baker BA, Jacobs DR Jr. A strong dose-response relation between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and diabetes: results from the National Health and Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:1638–1644.12. Lee DH, Lee IK, Porta M, Steffes M, Jacobs DR Jr. Relationship between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among non-diabetic adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2002. Diabetologia. 2007. 50:1841–1851.13. Lee DH, Steffes MW, Sjodin A, Jones RS, Needham LL, Jacobs DR Jr. Low dose of some persistent organic pollutants predicts type 2 diabetes: a nested case-control study. Environ Health Perspect. 2010. 118:1235–1242.14. Lim S, Ahn SY, Song IC, Chung MH, Jang HC, Park KS, Lee KU, Pak YK, Lee HK. Chronic exposure to the herbicide, atrazine, causes mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e5186.15. Ruzzin J, Petersen R, Meugnier E, Madsen L, Lock EJ, Lillefosse H, Ma T, Pesenti S, Sonne SB, Marstrand TT, Malde MK, Du ZY, Chavey C, Fajas L, Lundebye AK, Brand CL, Vidal H, Kristiansen K, Froyland L. Persistent organic pollutant exposure leads to insulin resistance syndrome. Environ Health Perspect. 2010. 118:465–471.16. Lee DH, Steffes MW, Sjodin A, Jones RS, Needham LL, Jacobs DR Jr. Low dose organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls predict obesity, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance among people free of diabetes. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e15977.17. Haggarty P, Shetty P, Thangam S, Kumar S, Kurpad A, Ashton J, Milne E, Earl C. Free and esterified fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis in adult males and its effect on the doubly-labelled water method. Br J Nutr. 2000. 83:227–234.18. Kamimura N, Nishimaki K, Ohsawa I, Ohta S. Molecular hydrogen improves obesity and diabetes by inducing hepatic FGF21 and stimulating energy metabolism in db/db mice. Obesity (Silver Spring). Epub 2011 Feb 3. DOI:10.1038/oby.2011.6.19. Yamaoka-Tojo M, Tojo T, Izumi T. Beyond cholesterol lowering: pleiotropic effects of bile acid binding resins against cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008. 6:271–281.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insulin Resistance and Intracellular Thyroid Hormone Dysfunction
- The relationship between muscle mitochondrial nutritional overloading and insulin resistance
- Insulin Resistance and Insulin Resistance Syndrome
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance
- Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria and Insulin Resistance: The Role of Exercise