Ann Dermatol.
2011 Feb;23(1):44-52. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.44.
Characterizing Cutaneous Elastic Fibers by Eosin Fluorescence Detected by Fluorescence Microscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. hjsongmd@gmail.com
- KMID: 2171951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.44
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
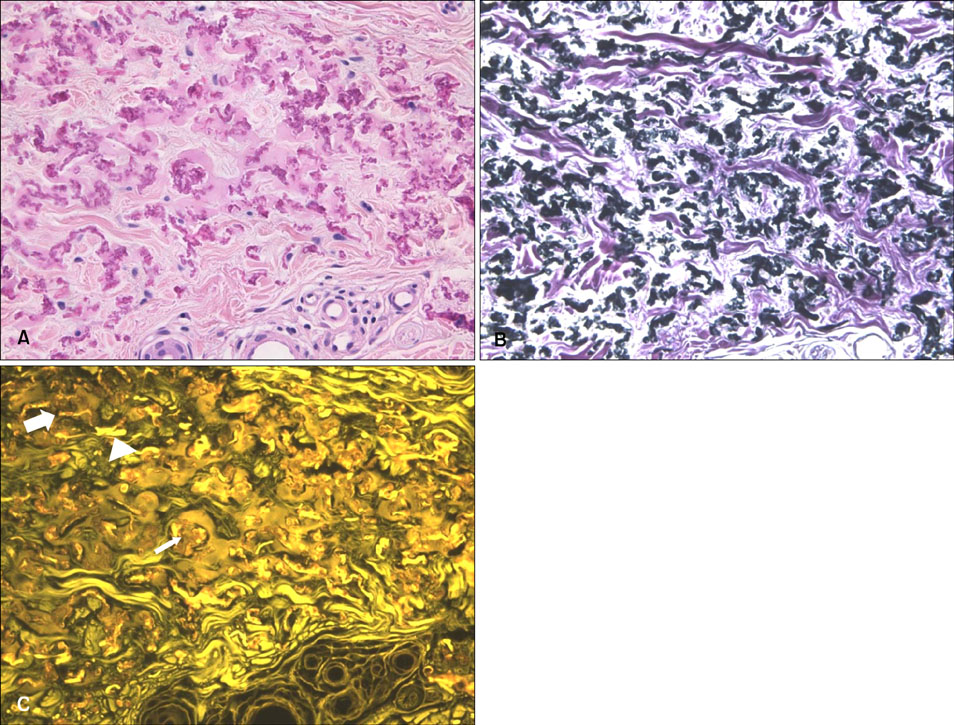
Though elastic fibers are as important as collagen fibers in interpretation of the histopathologic findings, it is impossible to observe them on the hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) stained specimen.
OBJECTIVE
Characterizing eosin fluorescence emitted by elastic fibers in H&E stained specimens.
METHODS
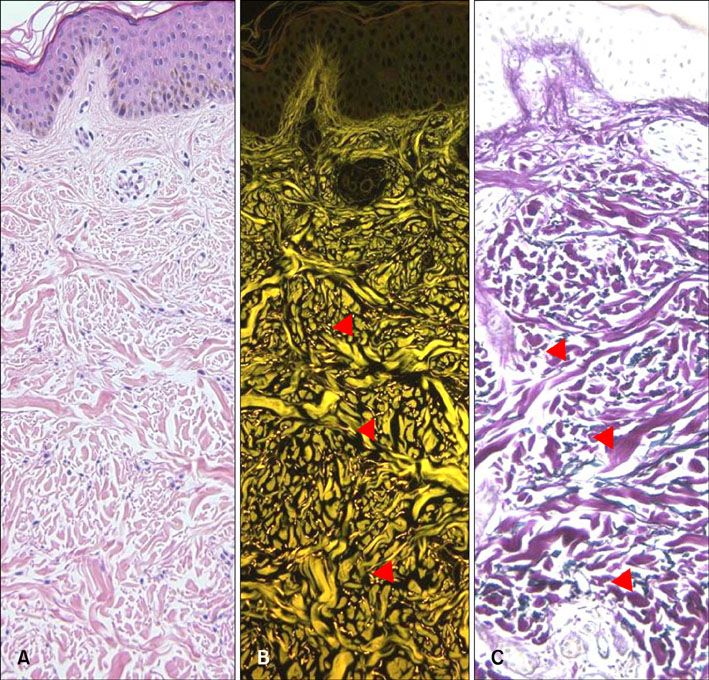
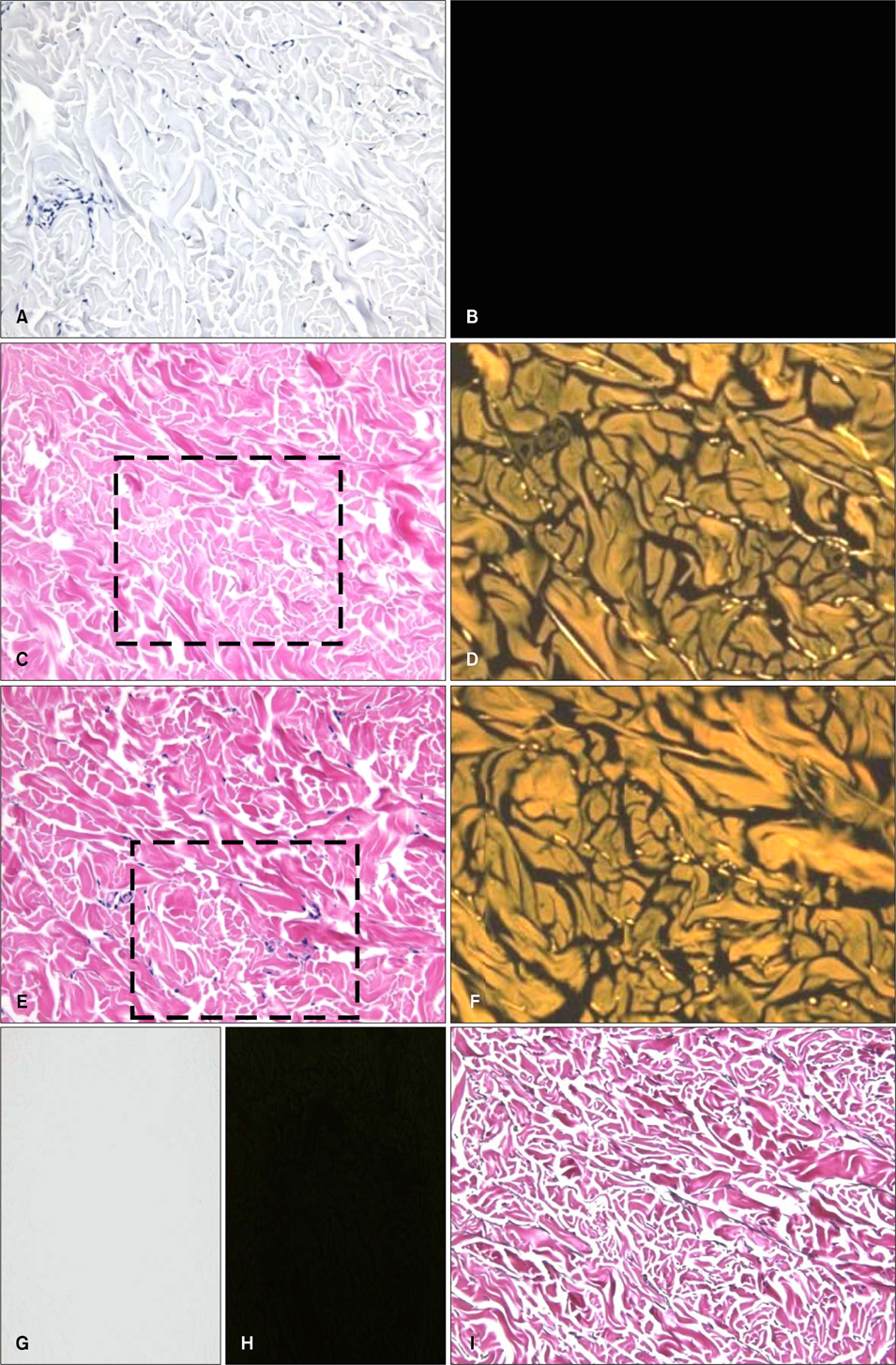
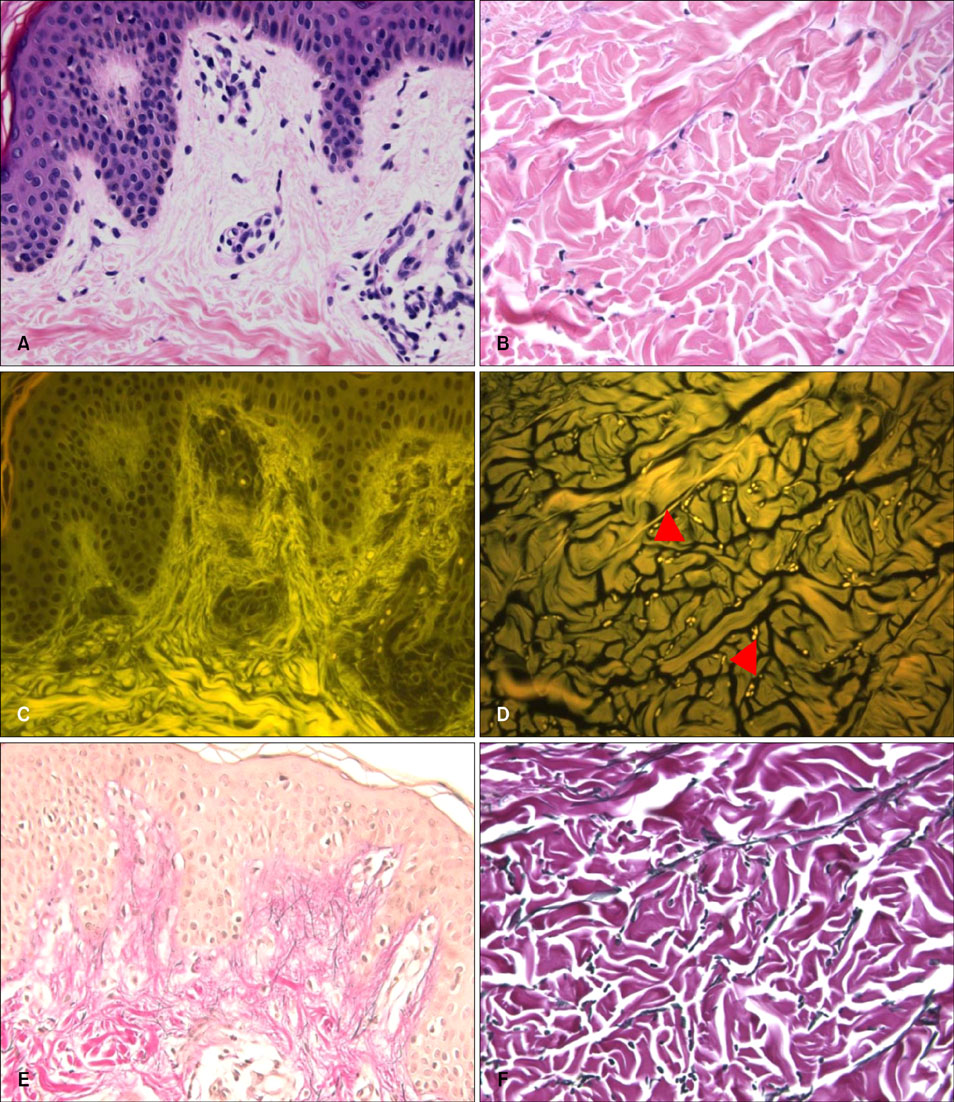
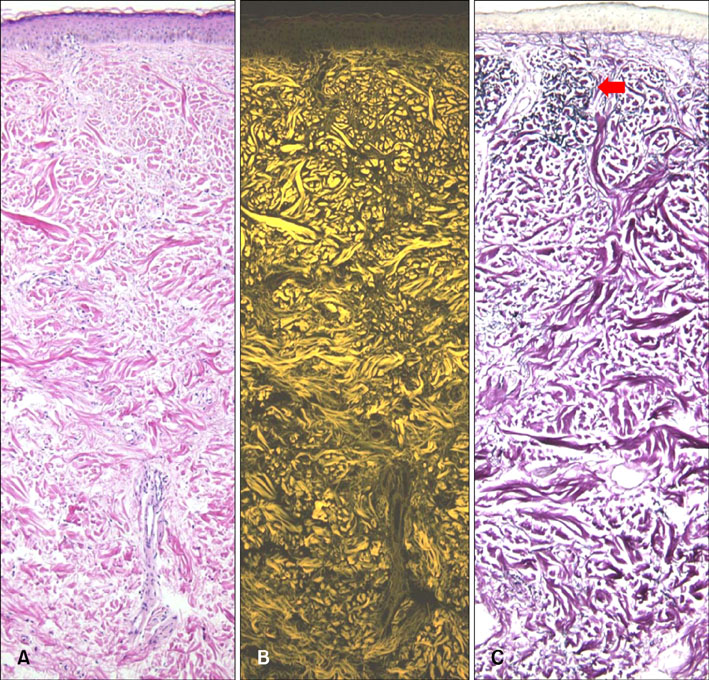
Normal skin tissue sections were stained in 4 different ways (unstained, hematoxylin only, eosin only, H&E) and observed under a fluorescence microscope using a FITC filter set. Fluorescent findings of 30 H&E-stained specimens showing abnormal dermal findings were compared with bright field findings of Miller's elastic stained specimen.
RESULTS
Strong eosin fluorescence was related to the differential binding property of eosin with elastic fibers. Hematoxylin stain quenched excessive eosin fluorescence from other tissue components and contributed to better contrast. Fluorescence microscopy of H&E-stained sections was found to be especially useful in observing mature elastic fibers in the reticular dermis. In 74% of the specimens, eosin fluorescence findings of elastic fibers in reticular dermis matched well with that of specimens with elastic fiber special stain.
CONCLUSION
Analysis of skin elastic fibers by fluorescence microscopy is a useful and complementary method to reveal hidden elastic fibers in H&E-stained specimens.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schwartz E, Fleischmajer R. Association of elastin with oxytalan fibers of the dermis and with extracellular microfibrils of cultured skin fibroblasts. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986. 34:1063–1068.
Article2. Goldstein DJ. The fluorescence of elastic fibres stained with eosin and excited by visible light. Histochem J. 1969. 1:187–198.
Article3. Song H, Kim C. Eosin fluorescence microscopy of hematoxylin-eosin stained histopathologic specimens [abstract]. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 114:821.4. Huntington H. Autofluorescence of eosinophilic substances. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986. 110:93.5. Varadi DP. Studies on the chemistry and fine structure of elastic fibers from normal adult skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1972. 59:238–246.
Article6. Elder DE, Elenitsas R, Murphy GF, Johnson BL, Xu X, editors. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 2009. 10th ed. Philadelphia: LIppincott Williams & Wilkins;49.7. Chadwick CS, Mc EM, Nairn RC. Fluorescent protein tracers; a trial of new fluorochromes and the development of an alternative to fluorescein. Immunology. 1958. 1:315–327.8. de Carvalho HF, Taboga SR. Fluorescence and confocal laser scanning microscopy imaging of elastic fibers in hematoxylin-eosin stained sections. Histochem Cell Biol. 1996. 106:587–592.
Article9. de Carvalho HF, Taboga SR. The applicability of hematoxylin-eosin staining plus fluorescence or confocal laser scanning microscopy to the study of elastic fibers in cartilages. C R Acad Sci III. 1996. 319:991–996.10. Bancroft JD, Gamble M, editors. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 2002. 15th ed. London: Churchill Livinstone;143.11. Suwabe H, Serizawa A, Kajiwara H, Ohkido M, Tsutsumi Y. Degenerative processes of elastic fibers in sun-protected and sun-exposed skin: immunoelectron microscopic observation of elastin, fibrillin-1, amyloid P component, lysozyme and alpha1-antitrypsin. Pathol Int. 1999. 49:391–402.
Article12. Sherer DW, Sapadin AN, Lebwohl MG. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum: an update. Dermatology. 1999. 199:3–7.
Article13. Pope FM. Historical evidence for the genetic heterogeneity of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Br J Dermatol. 1975. 92:493–509.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Erythropoietic Protoporphyria Screened by RBC Fluorescence Microscopy
- Recent trends in two-photon auto-fluorescence lifetime imaging (2P-FLIM) and its biomedical applications
- Whole blood cyclosporine measurement by fluorescence polarization immunoassay
- Electron-microscopic Findings of Elastic Fibers in Zebrafish Skin
- Characterizing Atypical BCL6 Signal Patterns Detected by Digital Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Analysis