Ann Dermatol.
2016 Apr;28(2):192-198. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.2.192.
Immunomodulatory Effects of Deokgu Thermomineral Water Balneotherapy on Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis Murine Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. jwkim52@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Ewha Woman's University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Earth Environmental System, Pusan National University, Pusan, Korea.
- 5Oh&Kim's Aesthetic Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2171376
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.2.192
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Although the therapeutic mechanism of balneotherapy for atopic dermatitis has not been clarified, many atopic patients who visit thermomineral springs have shown clinical improvements.
OBJECTIVE
This study was aimed to evaluate the immunomodulatory effect of thermomineral water balneotherapy on the atopic dermatitis murine model.
METHODS
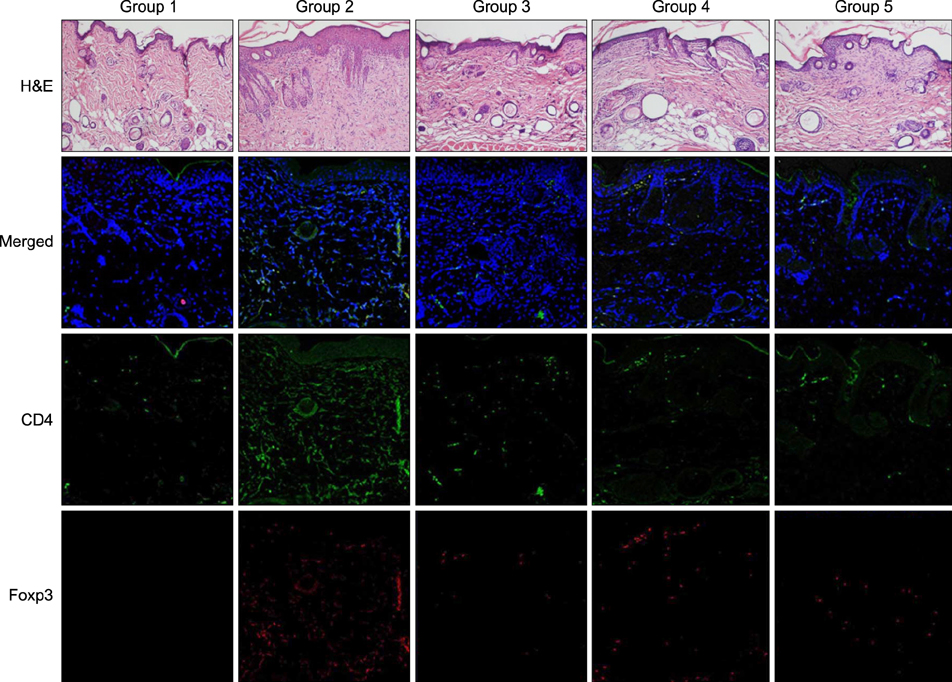
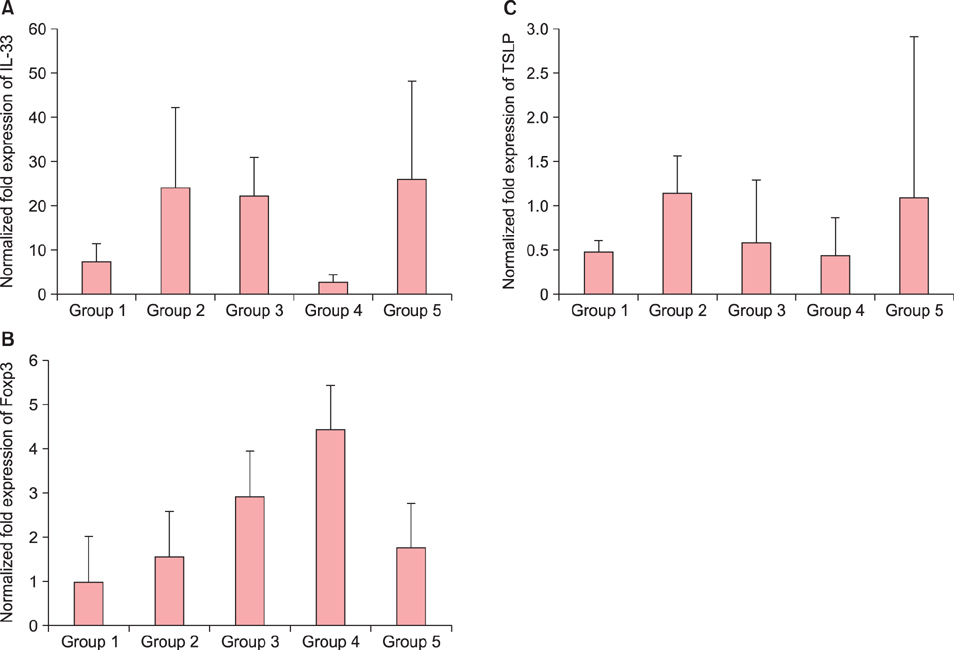
The oxazolone-induced atopic dermatitis murine model was used to evaluate the therapeutic effect of balneotherapy with Deokgu thermomineral water compared with distilled water. Histologic evaluation and confocal microscopic imaging were performed to analyze the lesional expression of cluster-of-differentiation (CD)4 and forkhead box p3 (Foxp3). Lesional mRNA expression of interleukin (IL) 33, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), and Foxp3 was evaluated by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
RESULTS
Compared with the distilled water bath group, confocal microscopic evaluation of CD4 and Foxp3 merged images showed increased expression of regulatory T cells in the thermomineral balneotherapy group. The lesional mRNA level of IL-33 showed a reduced trend in the thermomineral balneotherapy group, whereas the level of mRNA of Foxp3 was increased. TSLP showed a decreased trend in both distilled water and thermomineral water bath groups. There was a trend of reduced expression in lesional IL-33 mRNA but increased cell count of CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in thermomineral balneotherapy compared with distilled water bath.
CONCLUSION
Therefore, thermomineral balneotherapy can be an effective and safe adjuvant therapeutic option for atopic dermatitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Serial Changes of Heat Shock Protein 70 and Interleukin-8 in Burn Blister Fluid
Kicheol Yoo, Kang Yeol Suh, Gi Hun Choi, In-Suk Kwak, Dong Kook Seo, Dohern Kym, Hyeon Yoon, Yong Se Cho, Hye One Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2017;29(2):194-199. doi: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.2.194.
Reference
-
1. Hann SK. Mineral water and spas in Korea. Clin Dermatol. 1996; 14:633–635.
Article2. Kim JW. Therapeutic effectiveness and its underlying immunologic mechanisms of Korean hot spring water on atopic dermatitis. J Korean Acad Hot Spring. 2012; 1:48–54.3. Cozzi F, Lazzarin P, Todesco S, Cima L. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation in healthy subjects undergoing mud-bath applications. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:724–726.
Article4. Kubota K, Machida I, Tamura K, Take H, Kurabayashi H, Akiba T, et al. Treatment of refractory cases of atopic dermatitis with acidic hot-spring bathing. Acta Derm Venereol. 1997; 77:452–454.5. Inoue T, Inoue S, Kubota K. Bactericidal activity of manganese and iodide ions against Staphylococcus aureus: a possible treatment for acute atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1999; 79:360–362.
Article6. Akiyama H, Yamasaki O, Tada J, Kubota K, Arata J. Antimicrobial effects of acidic hot-spring water on Staphy-lococcus aureus strains isolated from atopic dermatitis patients. J Dermatol Sci. 2000; 24:112–118.
Article7. Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR, et al. Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128:79–86.
Article8. Lee YB, Lee JY, Lee HJ, Yun ST, Lee JT, Kim HJ, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of balneotherapy with hae-un-dae thermal water on imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like murine model. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:221–230.
Article9. Chae GT, Yun ST, Mayer B, Kim KH, Kim SY, Kwon JS, et al. Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Sci Total Environ. 2007; 385:272–283.
Article10. Merial-Kieny C, Mengual X, Guerrero D, Sibaud V. Clinical efficacy of Avène hydrotherapy measured in a large cohort of more than 10,000 atopic or psoriatic patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 25:Suppl 1. 30–34.
Article11. Portalès P, Ariès MF, Licu D, Pinton J, Hernandez-Pion C, Gall Y, et al. Immunomodulation induced by Avène spring water on Th1- and Th2-dependent cytokine production in healthy subjects and atopic dermatitis patients. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2001; 14:234–242.
Article12. Merial-Kieny C, Castex-Rizzi N, Selas B, Mery S, Guerrero D. Avène Thermal Spring Water: an active component with specific properties. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 25:Suppl 1. 2–5.
Article13. Castex-Rizzi N, Charveron M, Merial-Kieny C. Inhibition of TNF-alpha induced-adhesion molecules by Avène Thermal Spring Water in human endothelial cells. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011; 25:Suppl 1. 6–11.
Article14. Lee JH, Jin SY, Choi YS, Kwon HB, Lee SH, Lee J, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of hot spring sea water therapy in atopic dermatitis: a pilot study. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:124–130.15. Choi YJ, Lee HJ, Lee DH, Woo SY, Lee KH, Yun ST, et al. Therapeutic effects and immunomodulation of Suanbo mineral water therapy in a murine model of atopic dermatitis. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:462–470.
Article16. Lee HP, Choi YJ, Cho KA, Woo SY, Yun ST, Lee JT, et al. Effect of spa spring water on cytokine expression in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells and on differentiation of CD4(+) T cells. Ann Dermatol. 2012; 24:324–336.
Article17. Cevikbas F, Steinhoff M. IL-33: a novel danger signal system in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2012; 132:1326–1329.
Article18. Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Okuzawa Y, Masuda K, Katoh N. Increased serum levels of interleukin 33 in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014; 70:882–888.
Article19. Nabe T. Interleukin (IL)-33: new therapeutic target for atopic diseases. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 126:85–91.
Article20. Jariwala SP, Abrams E, Benson A, Fodeman J, Zheng T. The role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the immunopathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:1515–1520.
Article21. Wu WH, Park CO, Oh SH, Kim HJ, Kwon YS, Bae BG, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-activated invariant natural killer T cells trigger an innate allergic immune response in atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:290–299. 299.e1–299.e4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Balneotherapy as an Adjuvant Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis at Yuseong Spa, Korea
- Immunomodulatory Effects of Balneotherapy with Hae-Un-Dae Thermal Water on Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-Like Murine Model
- The Efficacy and Safety of Balneotherapy as an Adjuvant Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis at Samsan Spa, Korea: A Randomized Controlled Split-body Trial
- The Effect of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Cultured Media on Oxazolone Treated Atopic Dermatitis-Like Murine Model
- Dioscorea japonica Thunb. Ethanolic Extract Attenuated Oxazolone-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions in BALB/c Mice