Endocrinol Metab.
2014 Sep;29(3):349-355. 10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.349.
Polarized and Stage-Dependent Distribution of Immunoreactivity for Novel PDZ-Binding Protein Preso1 in Adult Neurogenic Regions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, BK21 Program, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. woongsun@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Emergency Medical Technology, Kyungil University College of Nursing and Public Health, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2169472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.349
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Adult neural stem cells have the potential for self-renewal and differentiation into multiple cell lineages via symmetric or asymmetric cell division. Preso1 is a recently identified protein involved in the formation of dendritic spines and the promotion of axonal growth in developing neurons. Preso1 can also bind to cell polarity proteins, suggesting a potential role for Preso1 in asymmetric cell division.
METHODS
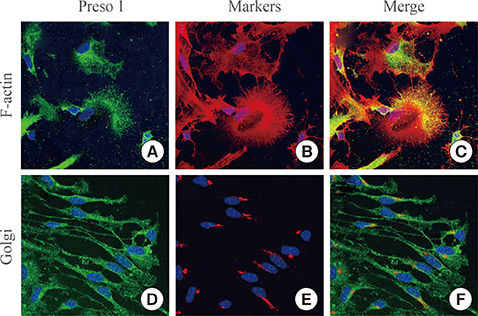
To investigate the distribution of Preso1, we performed immunohistochemistry with adult mouse brain slice. Also, polarized distribution of Preso1 was assessed by immunocytochemistry in cultured neural stem cells.
RESULTS
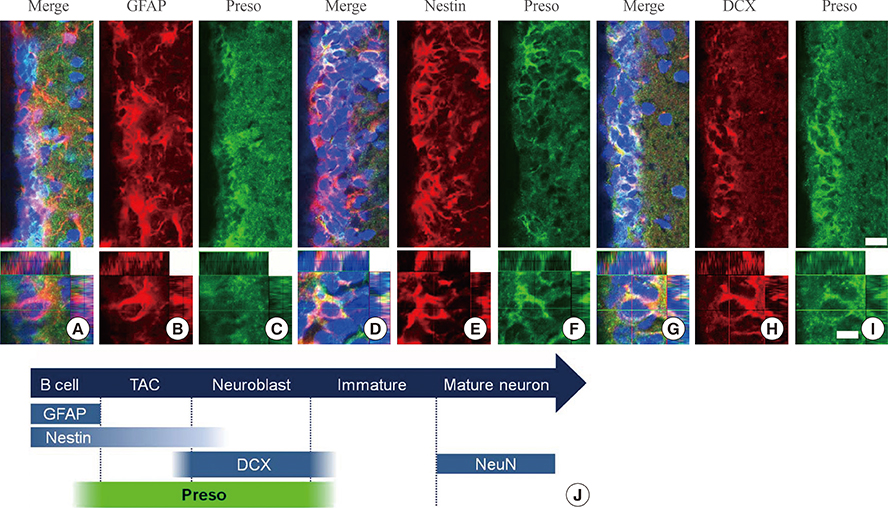
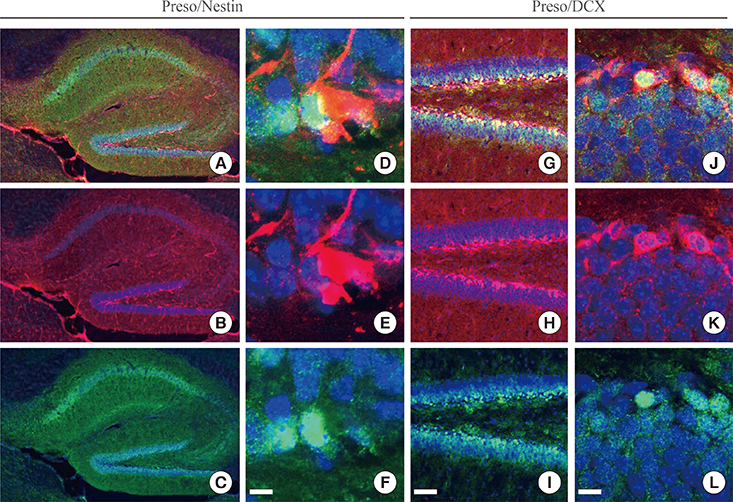
Immunoreactivity for Preso1 (Preso1-IR) was strong in the rostral migratory stream and subventricular zone, where proliferating transit-amplifying cells and neuroblasts are prevalent. In cultured neural stem cells, Preso1-IR was unequally distributed in the cell cytosol. We also observed the distribution of Preso1 in the subgranular zone of the hippocampal dentate gyrus, another neurogenic region in the adult brain. Interestingly, Preso1-IR was transiently observed in the nuclei of doublecortin-expressing neuroblasts immediately after asymmetric cell division.
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that Preso1 is asymmetrically distributed in the cytosol and nuclei of neural stem/progenitor cells in the adult brain, and may play a significant role in cell differentiation via association with cell polarity machinery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee HW, Choi J, Shin H, Kim K, Yang J, Na M, Choi SY, Kang GB, Eom SH, Kim H, Kim E. Preso, a novel PSD-95-interacting FERM and PDZ domain protein that regulates dendritic spine morphogenesis. J Neurosci. 2008; 28:14546–14556.2. Mo J, Lee D, Hong S, Han S, Yeo H, Sun W, Choi S, Kim H, Lee HW. Preso regulation of dendritic outgrowth through PI(4,5)P2-dependent PDZ interaction with betaPix. Eur J Neurosci. 2012; 36:1960–1970.3. Hu JH, Yang L, Kammermeier PJ, Moore CG, Brakeman PR, Tu J, Yu S, Petralia RS, Li Z, Zhang PW, Park JM, Dong X, Xiao B, Worley PF. Preso1 dynamically regulates group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat Neurosci. 2012; 15:836–844.4. Yuzawa S, Kamakura S, Iwakiri Y, Hayase J, Sumimoto H. Structural basis for interaction between the conserved cell polarity proteins Inscuteable and Leu-Gly-Asn repeat-enriched protein (LGN). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:19210–19215.5. Moon Y, Kim JY, Kim WR, Kim HJ, Jang MJ, Nam Y, Kim K, Kim H, Sun W. Function of ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins in migration of subventricular zone-derived neuroblasts following traumatic brain injury. Stem Cells. 2013; 31:1696–1705.6. Kim WR, Chun SK, Kim TW, Kim H, Ono K, Takebayashi H, Ikenaka K, Oppenheim RW, Sun W. Evidence for the spontaneous production but massive programmed cell death of new neurons in the subcallosal zone of the postnatal mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci. 2011; 33:599–611.7. Schwamborn JC, Berezikov E, Knoblich JA. The TRIM-NHL protein TRIM32 activates microRNAs and prevents self-renewal in mouse neural progenitors. Cell. 2009; 136:913–925.8. Kim SK. Polarized signaling: basolateral receptor localization in epithelial cells by PDZ-containing proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997; 9:853–859.9. Stenzel N, Fetzer CP, Heumann R, Erdmann KS. PDZ-domain-directed basolateral targeting of the peripheral membrane protein FRMPD2 in epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 18):3374–3384.10. Pan Z, Shang Y, Jia M, Zhang L, Xia C, Zhang M, Wang W, Wen W. Structural and biochemical characterization of the interaction between LGN and Frmpd1. J Mol Biol. 2013; 425:1039–1049.11. Tsukita S, Yonemura S. ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) family: from cytoskeleton to signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997; 9:70–75.12. Tsukita S, Yonemura S. Cortical actin organization: lessons from ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) proteins. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:34507–34510.13. Batchelor CL, Woodward AM, Crouch DH. Nuclear ERM (ezrin, radixin, moesin) proteins: regulation by cell density and nuclear import. Exp Cell Res. 2004; 296:208–222.14. Lin YY, Hsu YH, Huang HY, Shann YJ, Huang CY, Wei SC, Chen CL, Jou TS. Aberrant nuclear localization of EBP50 promotes colorectal carcinogenesis in xenotransplanted mice by modulating TCF-1 and beta-catenin interactions. J Clin Invest. 2012; 122:1881–1894.15. Legg JW, Isacke CM. Identification and functional analysis of the ezrin-binding site in the hyaluronan receptor, CD44. Curr Biol. 1998; 8:705–708.16. Tsukita S, Oishi K, Sato N, Sagara J, Kawai A, Tsukita S. ERM family members as molecular linkers between the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 and actin-based cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol. 1994; 126:391–401.17. Sudol M, Bork P, Einbond A, Kastury K, Druck T, Negrini M, Huebner K, Lehman D. Characterization of the mammalian YAP (Yes-associated protein) gene and its role in defining a novel protein module, the WW domain. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:14733–14741.18. Gee ST, Milgram SL, Kramer KL, Conlon FL, Moody SA. Yes-associated protein 65 (YAP) expands neural progenitors and regulates Pax3 expression in the neural plate border zone. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20309.19. Kanai F, Marignani PA, Sarbassova D, Yagi R, Hall RA, Donowitz M, Hisaminato A, Fujiwara T, Ito Y, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB. TAZ: a novel transcriptional co-activator regulated by interactions with 14-3-3 and PDZ domain proteins. EMBO J. 2000; 19:6778–6791.20. Liu C, Huang W, Lei Q. Regulation and function of the TAZ transcription co-activator. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2011; 2:247–256.21. Murakami M, Tominaga J, Makita R, Uchijima Y, Kurihara Y, Nakagawa O, Asano T, Kurihara H. Transcriptional activity of Pax3 is co-activated by TAZ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006; 339:533–539.22. Di Palma T, D'Andrea B, Liguori GL, Liguoro A, de Cristofaro T, Del Prete D, Pappalardo A, Mascia A, Zannini M. TAZ is a coactivator for Pax8 and TTF-1, two transcription factors involved in thyroid differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2009; 315:162–175.23. Cui CB, Cooper LF, Yang X, Karsenty G, Aukhil I. Transcriptional coactivation of bone-specific transcription factor Cbfa1 by TAZ. Mol Cell Biol. 2003; 23:1004–1013.24. Varelas X, Sakuma R, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Peerani R, Rao BM, Dembowy J, Yaffe MB, Zandstra PW, Wrana JL. TAZ controls Smad nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and regulates human embryonic stem-cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10:837–848.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distribution of the Immunoreactivity for Glycoprotein M6B in the Neurogenic Niche and Reactive Glia in the Injury Penumbra Following Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice
- Postnatal Development of Calbindin D-28k Immunoreactivities in the Canine Hippocampus
- Differential Expression and Cellular Localization of Na+-K+-ATPase Isoforms in Rat Salivary Gland
- Effects of Kainic Acid-induced Seizures on c-fos Protein Expression in the Rat Hippocampus
- Expression of ErbB4 in the apoptotic neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain