Anat Cell Biol.
2010 Dec;43(4):332-339. 10.5115/acb.2010.43.4.332.
Expression of ErbB4 in the apoptotic neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience, College of Medicine, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea. tkbaik@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 1455348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2010.43.4.332
Abstract
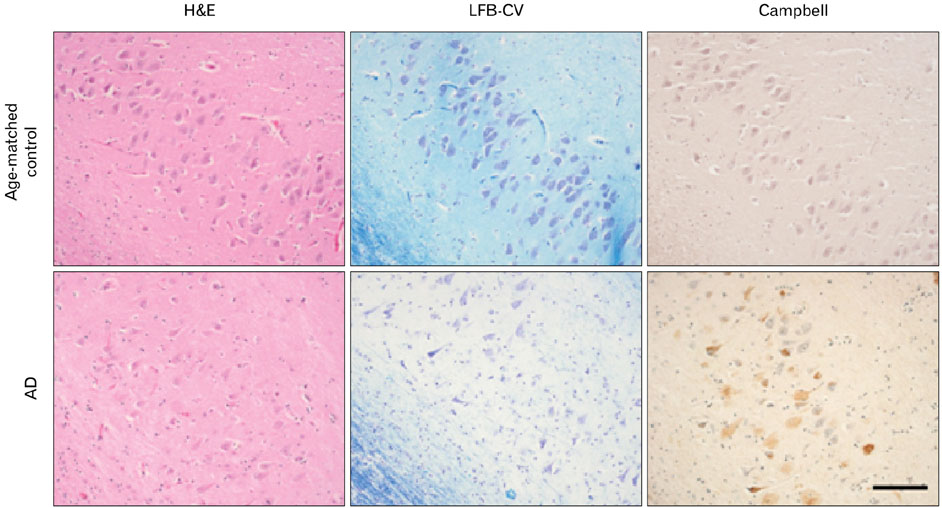
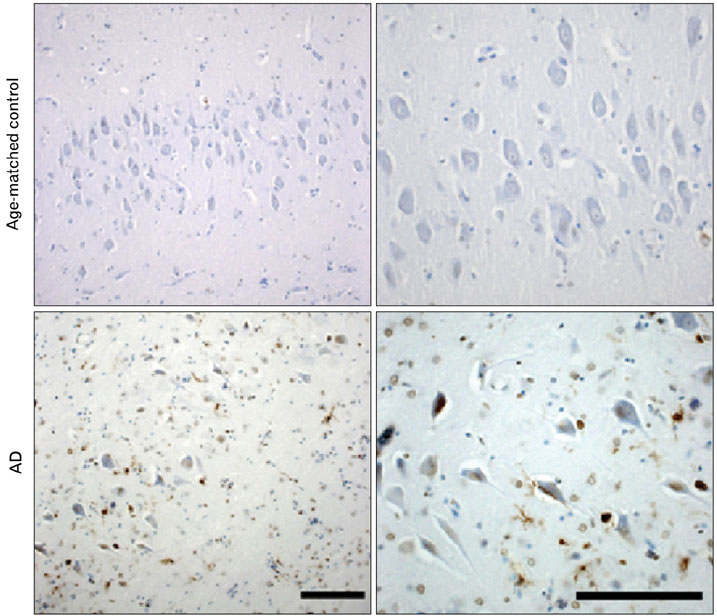
- Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) signaling participates in the synaptic plasticity, maintenance or regulation of adult brain. Although ErbB4, a key NRG1 receptor, is expressed in multiple regions in the adult animal brain, little is known about its localization in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains. We previously reported that ErbB4 immunoreactivity showed regional difference in the hippocampus of age-matched control. In the present paper, immunohistochemical characterization of the distribution of ErbB4 receptor in the hippocampus relative to pathology staging were performed in age-matched control (Braak stage 0, n=6) and AD (Braak stage I/V, n=10). Here, we found that ErbB4 immunoreactivity was significantly increased in apoptotic hippocampal pyramidal neurons in the brains of AD patients, compared to those of age-matched control subjects. In AD brains, ErbB4 immunoreactivity was demonstrated to colocalize with the apoptotic signal Bax in apoptotic hippocampal pyramidal neurons. These results suggest that up-regulation of ErbB4 immunoreactivity in apoptotic neuron may involve in the progression of pathology of AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991. 82:239–259.2. Campbell SK, Switzer RC, Martin TL. Alzheimers plaques and tangles: a controled and enhanced silver staining method. Proceeding Soc Neurosci 678. 1987.3. Chaudhury AR, Gerecke KM, Wyss JM, Morgan DG, Gordon MN, Carroll SL. Neuregulin-1 and erbB4 immunoreactivity is associated with neuritic plaques in Alzheimer disease brain and in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003. 62:42–54.4. Clementi ME, Pezzotti M, Orsini F, et al. Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) induces cell death in human neuroblastoma via bax/bcl-2 ratio increase: an intriguing role for methionine 35. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. 342:206–213.5. Croslan DR, Schoell MC, Ford GD, et al. Neuroprotective effects of neuregulin-1 on B35 neuronal cells following ischemia. Brain Res. 2008. 1210:39–47.6. Cutler RG, Kelly J, Storie K, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced abnormalities in ceramide and cholesterol metabolism in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004. 101:2070–2075.7. Di Segni A, Shaharabani E, Stein R, Pinkas-Kramarski R. Neuregulins rescue PC12-ErbB-4 cells from cell death induced by beta-amyloid peptide: involvement of PI3K and PKC. J Mol Neurosci. 2005. 26:57–69.8. Ezaki T. Antigen retrieval on formaldehyde-fixed paraffin sections: its potential drawbacks and optimization for double immunostaining. Micron. 2000. 31:639–649.9. Garcia RA, Vasudevan K, Buonanno A. The neuregulin receptor ErbB-4 interacts with PDZ-containing proteins at neuronal synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:3596–3601.10. Goldshmit Y, Erlich S, Pinkas-Kramarski R. Neuregulin rescues PC12-ErbB4 cells from cell death induced by H(2)O(2). Regulation of reactive oxygen species levels by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:46379–46385.11. Gonatas NK, Anderson W, Evangelista I. The contribution of altered synapses in the senile plaque: an electron microscopic study in Alzheimer's dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967. 26:25–39.12. Huang YZ, Won S, Ali DW, et al. Regulation of neuregulin signaling by PSD-95 interacting with ErbB4 at CNS synapses. Neuron. 2000. 26:443–455.13. Law AJ, Shannon Weickert C, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Harrison PJ. Neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) mRNA and protein in the adult human brain. Neuroscience. 2004. 127:125–136.14. Lee HJ, Jung KM, Huang YZ, et al. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:6318–6323.15. Li B, Woo RS, Mei L, Malinow R. The neuregulin-1 receptor erbB4 controls glutamatergic synapse maturation and plasticity. Neuron. 2007a. 54:583–597.16. Li BS, Ma W, Jaffe H, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 is involved in neuregulin-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt activity mediating neuronal survival. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:35702–35709.17. Li Y, Xu Z, Ford GD, et al. Neuroprotection by neuregulin-1 in a rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2007b. 1184:277–283.18. Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG. Survival signalling in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. 34:1277–1282.19. Marchionni MA, Goodearl AD, Chen MS, et al. Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced erbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature. 1993. 362:312–318.20. Mattson MP. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2004. 430:631–639.21. Mattson MP, Meffert MK. Roles for NF-kappaB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death Differ. 2006. 13:852–860.22. Meyer D, Birchmeier C. Multiple essential functions of neuregulin in development. Nature. 1995. 378:386–390.23. Murata K, Dalakas MC. Expression of the costimulatory molecule BB-1, the ligands CTLA-4 and CD28, and their mRNA in inflammatory myopathies. Am J Pathol. 1999. 155:453–460.24. Ni CY, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Carpenter G. gamma-Secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science. 2001. 294:2179–2181.25. Ricart K, J Pearson R Jr, Viera L, et al. Interactions between beta-neuregulin and neurotrophins in motor neuron apoptosis. J Neurochem. 2006. 97:222–233.26. Sathasivam S, Ince PG, Shaw PJ. Apoptosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a review of the evidence. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2001. 27:257–274.27. Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Yang HI, Thajeb P, Li H. Neuregulin-1 reduces ischemia-induced brain damage in rats. Neurobiol Aging. 2004. 25:935–944.28. Stankovic K, Rio C, Xia A, et al. Survival of adult spiral ganglion neurons requires erbB receptor signaling in the inner ear. J Neurosci. 2004. 24:8651–8661.29. Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991. 30:572–580.30. Woo RS, Li XM, Tao Y, et al. Neuregulin-1 enhances depolarization-induced GABA release. Neuron. 2007. 54:599–610.31. Zhang L, Fletcher-Turner A, Marchionni MA, et al. Neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects of the neuregulin glial growth factor-2 on dopaminergic neurons in rat primary midbrain cultures. J Neurochem. 2004. 91:1358–1368.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of ErbB4 in the neurons of Alzheimer's disease brain and APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease
- An Immunohistochemical Study of ErbB4 Receptor in Alzheimer's Disease Hippocampus
- Neuregulin 1/ErbB4 signaling attenuates neuronal cell damage under oxygen-glucose deprivation in primary hippocampal neurons
- Expressional Change of Nitric Oxide Synthase and erbB4 in Rat Hippocampus after Seizure
- Evidence of early involvement of apoptosis inducing factor-induced neuronal death in Alzheimer brain